
Down syndrome or Down's syndrome, also known as trisomy 21, is a genetic disorder caused by the presence of all or part of a third copy of chromosome 21. It is usually associated with developmental delays, mild to moderate intellectual disability, and characteristic physical features. There are three types of Down syndrome, all with the same features: Trisomy 21, the most common type; Mosaic Down syndrome, and Translocation Down syndrome.

A genetic disorder is a health problem caused by one or more abnormalities in the genome. It can be caused by a mutation in a single gene (monogenic) or multiple genes (polygenic) or by a chromosomal abnormality. Although polygenic disorders are the most common, the term is mostly used when discussing disorders with a single genetic cause, either in a gene or chromosome. The mutation responsible can occur spontaneously before embryonic development, or it can be inherited from two parents who are carriers of a faulty gene or from a parent with the disorder. When the genetic disorder is inherited from one or both parents, it is also classified as a hereditary disease. Some disorders are caused by a mutation on the X chromosome and have X-linked inheritance. Very few disorders are inherited on the Y chromosome or mitochondrial DNA.

Turner syndrome (TS), also known as 45,X, or 45,X0, is a genetic disorder in which a female is partially or completely missing an X chromosome. Most people have two sex chromosomes. It only affects females. Signs and symptoms vary among those affected. Often, a short and webbed neck, low-set ears, low hairline at the back of the neck, short stature, and swollen hands and feet are seen at birth. Typically, those affected do not develop menstrual periods or breasts without hormone treatment and are unable to have children without reproductive technology. Heart defects, diabetes, and hypothyroidism occur in the disorder more frequently than average. Most people with Turner syndrome have normal intelligence; however, many have problems with spatial visualization that may be needed in order to learn mathematics. Vision and hearing problems also occur more often than average.

Williams syndrome (WS), also Williams–Beuren syndrome (WBS), is a genetic disorder that affects many parts of the body. Facial features frequently include a broad forehead, underdeveloped chin, short nose, and full cheeks. Mild to moderate intellectual disability is observed in people with WS, with particular challenges with visual spatial tasks such as drawing. Verbal skills are relatively unaffected. Many people with WS have an outgoing personality, an openness to engaging with other people, and a happy disposition. Medical issues with teeth, heart problems, and periods of high blood calcium are common.
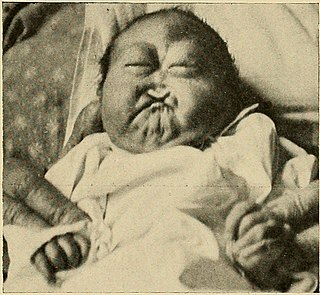
Patau syndrome is a syndrome caused by a chromosomal abnormality, in which some or all of the cells of the body contain extra genetic material from chromosome 13. The extra genetic material disrupts normal development, causing multiple and complex organ defects.

Trisomy 18, also known as Edwards syndrome, is a genetic disorder caused by the presence of a third copy of all or part of chromosome 18. Many parts of the body are affected. Babies are often born small and have heart defects. Other features include a small head, small jaw, clenched fists with overlapping fingers, and severe intellectual disability.
High-functioning autism (HFA) was historically an autism classification where a person exhibits no intellectual disability, but may experience difficulty in communication, emotion recognition, expression, and social interaction.
Developmental disability is a diverse group of chronic conditions, comprising mental or physical impairments that arise before adulthood. Developmental disabilities cause individuals living with them many difficulties in certain areas of life, especially in "language, mobility, learning, self-help, and independent living". Developmental disabilities can be detected early on and persist throughout an individual's lifespan. Developmental disability that affects all areas of a child's development is sometimes referred to as global developmental delay.
Neurodevelopmental disorders are a group of conditions that begin to emerge during childhood. According to the American Psychiatric Association Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition, (DSM-5) published in 2013, these conditions generally appear in early childhood, usually before children start school, and can persist into adulthood. The key characteristic of all these disorders is that they negatively impact a person's functioning in one or more domains of life depending on the disorder and deficits it has caused. All of these disorders and their levels of impairment exist on a spectrum, and affected individuals can experience varying degrees of symptoms and deficits, despite having the same diagnosis.

Chromosome 15 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 15 spans about 99.7 million base pairs and represents between 3% and 3.5% of the total DNA in cells. Chromosome 15 is an acrocentric chromosome, with a very small short arm, which contains few protein coding genes among its 19 million base pairs. It has a larger long arm that is gene rich, spanning about 83 million base pairs.

49,XXXXY syndrome is an extremely rare aneuploidic sex chromosomal abnormality. It occurs in approximately 1 out of 85,000 to 100,000 males. This syndrome is the result of maternal non-disjunction during both meiosis I and II. It was first diagnosed in 1960 and was coined Fraccaro syndrome after the researcher.
The genetics and abortion issue is an extension of the abortion debate and the disability rights movement. Since the advent of forms of prenatal diagnosis, such as amniocentesis and ultrasound, it has become possible to detect the presence of congenital disorders in the fetus before birth. Specifically, disability-selective abortion is the abortion of fetuses that are found to have non-fatal mental or physical defects detected through prenatal testing. Many prenatal tests are now considered routine, such as testing for Down syndrome. Women who are discovered to be carrying fetuses with disabilities are often faced with the decision of whether to abort or to prepare to parent a child with disabilities.

Intellectual disability (ID), also known as general learning disability and mental retardation, is a generalized neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by significant impairment in intellectual and adaptive functioning that is first apparent during childhood. Children with intellectual disabilities typically have an intelligence quotient (IQ) below 70 and deficits in at least two adaptive behaviors that affect everyday, general living. According to the DSM-5, intellectual functions include reasoning, problem solving, planning, abstract thinking, judgment, academic learning, and learning from experience. Deficits in these functions must be confirmed by clinical evaluation and individualized standard IQ testing. On the other hand, adaptive behaviors include the social, developmental, and practical skills people learn to perform tasks in their everyday lives. Deficits in adaptive functioning often compromises an individual's independence and ability to meet their social responsibility.

Angelman syndrome or Angelman's syndrome (AS) is a genetic disorder that mainly affects the nervous system. Symptoms include a small head and a specific facial appearance, severe intellectual disability, developmental disability, limited to no functional speech, balance and movement problems, seizures, and sleep problems. Children usually have a happy personality and have a particular interest in water. The symptoms generally become noticeable by one year of age.

Klinefelter syndrome (KS), also known as 47,XXY, is a chromosome anomaly where a boy or man has an extra X chromosome. As the presence of a Y chromosome denotes male sex, people with Klinefelter syndrome are genetically male. These complications commonly include infertility and small, poorly functioning testicles. These symptoms are often noticed only at puberty, although this is one of the most common chromosomal disorders, occurring in one to two per 1,000 live births. It is named after American endocrinologist Harry Klinefelter, who identified the condition in the 1940s.
Deaf and hard of hearing individuals with additional disabilities are referred to as "Deaf Plus" or "Deaf+". Deaf children with one or more co-occurring disabilities could also be referred to as hearing loss plus additional disabilities or Deafness and Diversity (D.A.D.). About 40–50% of deaf children experience one or more additional disabilities, with learning disabilities, intellectual disabilities, autism spectrum disorder (ASD), and visual impairments being the four most concomitant disabilities. Approximately 7–8% of deaf children have a learning disability. Deaf plus individuals utilize various language modalities to best fit their communication needs.
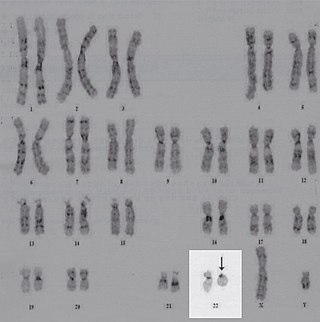
Ring chromosome 22, also known as ring 22, is a rare chromosomal disorder. Ring chromosomes occur when the ends of a chromosome lose material and fuse into a ring shape; in the case of ring 22, this occurs for chromosome 22, the last numbered human autosome. Ring chromosome 22 is marked by a number of consistent traits, such as intellectual disability, speech delay, hypotonia, and hyperactivity. The condition has a similar phenotype to Phelan-McDermid syndrome, as the loss of the SHANK3 gene is implicated in both.

Tetrasomy X, also known as 48,XXXX, is a chromosomal disorder in which a female has four, rather than two, copies of the X chromosome. It is associated with intellectual disability of varying severity, characteristic "coarse" facial features, heart defects, and skeletal anomalies such as increased height, clinodactyly, and radioulnar synostosis. Tetrasomy X is a rare condition, with few medically recognized cases; it is estimated to occur in approximately 1 in 50,000 females.

Pentasomy X, also known as 49,XXXXX, is a chromosomal disorder in which a female has five, rather than two, copies of the X chromosome. Pentasomy X is associated with short stature, intellectual disability, characteristic facial features, heart defects, skeletal anomalies, and pubertal and reproductive abnormalities. The condition is exceptionally rare, with an estimated prevalence between 1 in 85,000 and 1 in 250,000.

Trisomy X, also known as triple X syndrome and characterized by the karyotype 47,XXX, is a chromosome disorder in which a female has an extra copy of the X chromosome. It is relatively common and occurs in 1 in 1,000 females, but is rarely diagnosed; fewer than 10% of those with the condition know they have it.



















