
Cyan is the color between blue and green on the visible spectrum of light. It is evoked by light with a predominant wavelength between 490 and 520 nm, between the wavelengths of green and blue.

A dye is a colored substance that chemically bonds to the substrate to which it is being applied. This distinguishes dyes from pigments which do not chemically bind to the material they color. Dye is generally applied in an aqueous solution and may require a mordant to improve the fastness of the dye on the fiber.

The CMYK color model is a subtractive color model, based on the CMY color model, used in color printing, and is also used to describe the printing process itself. The abbreviation CMYK refers to the four ink plates used: cyan, magenta, yellow, and key (black).

Magenta is a purplish-red color. On color wheels of the RGB (additive) and CMY (subtractive) color models, it is located precisely midway between red and blue. It is one of the four colors of ink used in color printing by an inkjet printer, along with yellow, cyan, and black to make all the other colors. The tone of magenta used in printing, printer's magenta, is redder than the magenta of the RGB (additive) model, the former being closer to rose.

A pigment is a powder used to add color or change visual appearance. Pigments are completely or nearly insoluble and chemically unreactive in water or another medium; in contrast, dyes are colored substances which are soluble or go into solution at some stage in their use. Dyes are often organic compounds whereas pigments are often inorganic. Pigments of prehistoric and historic value include ochre, charcoal, and lapis lazuli.
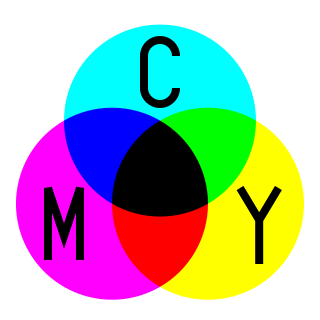
Subtractive color or subtractive color mixing predicts the spectral power distribution of light after it passes through successive layers of partially absorbing media. This idealized model is the essential principle of how dyes and pigments are used in color printing and photography, where the perception of color is elicited after white light passes through microscopic "stacks" of partially absorbing media allowing some wavelengths of light to reach the eye and not others, and also in painting, whether the colors are mixed or applied in successive layers.

Congo red is an organic compound, the sodium salt of 3,3′-([1,1′-biphenyl]-4,4′-diyl)bis(4-aminonaphthalene-1-sulfonic acid). It is an azo dye. Congo red is water-soluble, yielding a red colloidal solution; its solubility is greater in organic solvents. The use of Congo red in the textile industry has long been abandoned, primarily because of its carcinogenic properties, but it is still used for histological staining.

Fuchsia is a vivid pinkish-purplish-red color, named after the color of the flower of the fuchsia plant, which was named by a French botanist, Charles Plumier, after the 16th-century German botanist Leonhart Fuchs.
Color printing or colour printing is the reproduction of an image or text in color.

An acid dye is a dye that is typically applied to a textile at low pH. They are mainly used to dye wool, not cotton fabrics. Some acid dyes are used as food colorants, and some can also be used to stain organelles in the medical field.

A carbon print is a photographic print with an image consisting of pigmented gelatin, rather than of silver or other metallic particles suspended in a uniform layer of gelatin, as in typical black-and-white prints, or of chromogenic dyes, as in typical photographic color prints.

Azo dyes are organic compounds bearing the functional group R−N=N−R′, in which R and R′ are usually aryl and substituted aryl groups. They are a commercially important family of azo compounds, i.e. compounds containing the C-N=N-C linkage. Azo dyes are synthetic dyes and do not occur naturally. Most azo dyes contain only one azo group but there are some that contain two or three azo groups, called "diazo dyes" and "triazo dyes" respectively. Azo dyes comprise 60-70% of all dyes used in food and textile industries. Azo dyes are widely used to treat textiles, leather articles, and some foods. Chemically related derivatives of azo dyes include azo pigments, which are insoluble in water and other solvents.

Gum printing is a way of making photographic reproductions without the use of silver halides. The process uses salts of dichromate in common with a number of other related processes such as sun printing.
A solvent dye is a dye soluble in organic solvents. It is usually used as a solution in an organic solvent.
A chromogenic print, also known as a C-print or C-type print, a silver halide print, or a dye coupler print, is a photographic print made from a color negative, transparency or digital image, and developed using a chromogenic process. They are composed of three layers of gelatin, each containing an emulsion of silver halide, which is used as a light-sensitive material, and a different dye coupler of subtractive color which together, when developed, form a full-color image.

Thermal paper is a special fine paper that is coated with a material formulated to change color locally when exposed to heat. It is used in thermal printers, particularly in inexpensive devices such as adding machines, cash registers, and credit card terminals and small, lightweight portable printers.
Dye transfer is a continuous-tone color photographic printing process. It was used to print Technicolor films, as well as to produce paper colour prints used in advertising, or large transparencies for display.

There are three types of color mixing models, depending on the relative brightness of the resultant mixture: additive, subtractive, and average. In these models, mixing black and white will yield white, black and gray, respectively. Physical mixing processes, e.g. mixing light beams or oil paints, will follow one or a hybrid of these 3 models. Each mixing model is associated with several color models, depending on the approximate primary colors used. The most common color models are optimized to human trichromatic color vision, therefore comprising three primary colors.

The color magenta has notable tints and shades. These various colors are shown below.
Wet Processing Engineering is one of the major streams in Textile Engineering or Textile manufacturing which refers to the engineering of textile chemical processes and associated applied science. The other three streams in textile engineering are yarn engineering, fabric engineering, and apparel engineering. The processes of this stream are involved or carried out in an aqueous stage. Hence, it is called a wet process which usually covers pre-treatment, dyeing, printing, and finishing.













