Transport in Angola comprises:
This article is about the Transport in Zambia.

Matadi is the chief sea port of the Democratic Republic of the Congo and the capital of the Kongo Central province, adjacent to the border with Angola. It had a population of 245,862 (2004). Matadi is situated on the left bank of the Congo River, 148 km (92 mi) from the mouth and 8 km (5.0 mi) below the last navigable point before the rapids that make the river impassable for a long stretch upriver.

Benguela is a province of Angola, situated in the west of the country. It lies on the Atlantic Ocean, and borders the provinces of Cuanza Sul, Namibe, Huila, and Huambo. The province has an area of 39,826 square kilometres (15,377 sq mi) and its capital is Benguela. According to the 2014 census, there were 2,231,385 inhabitants in the province. The current governor of Benguela is Isaac dos Anjos.

Huambo, formerly Nova Lisboa, is the third-most populous city in Angola, after the capital city Luanda and Lubango, with a population of 595,304 in the city and a population of 713,134 in the municipality of Huambo. The city is the capital of the province of Huambo and is located about 220 km E from Benguela and 600 km SE from Luanda. Huambo is a main hub on the Caminho de Ferro de Benguela (CFB), which runs from the port of Lobito to the Democratic Republic of the Congo's southernmost province, Katanga. Huambo is served by the Albano Machado Airport.

Moçâmedes is a city in southwestern Angola, capital of Namibe Province. The city's current population is 255,000. Founded in 1840 by the Portuguese colonial administration, the city was named Namibe between 1985 and 2016. Moçâmedes has a cool dry climate and desert vegetation, because it is near the Namib Desert.

Benguela is a city in western Angola, capital of Benguela Province. Benguela is one of Angola's most populous cities with a population of 555,124 in the city and 561,775 in the municipality, at the 2014 census.

The Benguela Railway is a Cape gauge railway line that runs through Angola from west to east, being the largest and most important railway line in the country. It also connects to Tenke in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), and to the Cape to Cairo Railway.
Luau is a town and municipality in Angola in the province of Moxico on the border with the Democratic Republic of Congo.

Rail transport is provided in the Democratic Republic of the Congo by the Société Nationale des Chemins de Fer du Congo (SNCC), the Société commerciale des transports et des ports (SCTP) (previously Office National des Transports until 2011), and the Office des Chemins de fer des Ueles (CFU).

Catumbela is a city and municipality of the Benguela province in Angola. The municipality had a population of 175,805 in 2014.
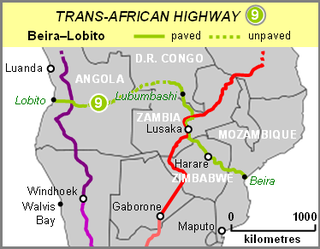
The Beira–Lobito Highway or TAH 9 is Trans-African Highway 9 in the transcontinental road network being developed by the United Nations Economic Commission for Africa (UNECA), the African Development Bank (ADB), and the African Union. The route has a length of 3,523 km (2,189 mi) crossing Angola, the most southerly part of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Zambia, Zimbabwe, and central Mozambique.
Bocoio is a town and municipality in Benguela Province in Angola. Its administrative capital is Tchissandji. The municipality had a population of 164,685 in 2014.

Railway stations in Angola include:

The history of rail transport in Angola began during the nineteenth century, when Angola was a colony of Portugal. It has involved the construction, operation and destruction of four separate, unconnected, coast-to-inland systems, in two different gauges. Operations on three of those systems have been largely restored; the other system has been closed.

Cuca is a brand of beer manufactured by Companhia União de Cervejas de Angola in Angola.

The Catumbela is a river in central Angola. The river mouth is at the Catumbela Estuary on the Atlantic Ocean at Catumbela, between Lobito and Benguela, and 240 kilometres (150 mi) from where it rises in the hills of Cassoco. The Catumbela supplies water to the city of Lobito. The mouth of the Catumbela was noted as a green vegetated region surrounded by barren land along the coast and a couple miles inland where it cuts a gorge through bare mountains. Alternate spellings are Catumbella and Cata-Bella.

Catumbela Bridge is a bridge over the Catumbela River, located in the municipality of Catumbela, Angola. The bridge, which was inaugurated on 10 September 2009, by the President of the Republic of Angola, José Eduardo dos Santos, connects the cities of Benguela and Lobito, in addition to other provinces of the country.
The following is a timeline of the history of the city of Benguela, Angola.

The Empresa do Caminho de Ferro de Benguela-E.P. is an Angolan state-owned company responsible for the administration of the Angolan stretch of the Benguela Railway. The company's headquarters are in the city of Lobito.

























