Related Research Articles

The cervix or cervix uteri is the lower part of the uterus (womb) in the human female reproductive system. The cervix is usually 2 to 3 cm long and roughly cylindrical in shape, which changes during pregnancy. The narrow, central cervical canal runs along its entire length, connecting the uterine cavity and the lumen of the vagina. The opening into the uterus is called the internal os, and the opening into the vagina is called the external os. The lower part of the cervix, known as the vaginal portion of the cervix, bulges into the top of the vagina. The cervix has been documented anatomically since at least the time of Hippocrates, over 2,000 years ago.
Obstetrics is the field of study concentrated on pregnancy, childbirth and the postpartum period. As a medical specialty, obstetrics is combined with gynecology under the discipline known as obstetrics and gynecology (OB/GYN), which is a surgical field.
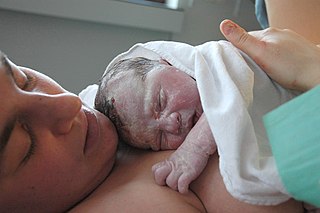
Childbirth, also known as labour and delivery, is the completion of pregnancy where one or more babies exits the internal environment of the mother via vaginal delivery or caesarean section. In 2019, there were about 140.11 million births globally. In the developed countries, most deliveries occur in hospitals, while in the developing countries most are home births.

The postpartum period begins after childbirth and is typically considered to end within six weeks. However, there are three distinct but continuous phases of the postnatal period; the acute phase, lasting for six to twelve hours after birth; the subacute phase, lasting six weeks; and the delayed phase, lasting up to six months. During the delayed phase, some changes to the genitourinary system take much longer to resolve and may result in conditions such as urinary incontinence. The World Health Organization (WHO) describes the postnatal period as the most critical and yet the most neglected phase in the lives of mothers and babies; most maternal and newborn deaths occur during this period.

The female reproductive system is made up of the internal and external sex organs that function in the reproduction of new offspring. In humans, the female reproductive system is immature at birth and develops to maturity at puberty to be able to produce gametes, and to carry a fetus to full term. The internal sex organs are the vagina, uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries. The female reproductive tract includes the vagina, uterus, and fallopian tubes and is prone to infections. The vagina allows for sexual intercourse and childbirth, and is connected to the uterus at the cervix. The uterus or womb accommodates the embryo which develops into the fetus. The uterus also produces secretions which help the transit of sperm to the fallopian tubes, where sperm fertilize ova produced by the ovaries. The external sex organs are also known as the genitals and these are the organs of the vulva including the labia, clitoris, and vaginal opening.
Abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB), also known as (AVB) or as atypical vaginal bleeding, is vaginal bleeding from the uterus that is abnormally frequent, lasts excessively long, is heavier than normal, or is irregular. The term dysfunctional uterine bleeding was used when no underlying cause was present. Vaginal bleeding during pregnancy is excluded. Iron deficiency anemia may occur and quality of life may be negatively affected.
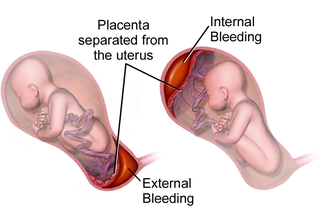
Placental abruption is when the placenta separates early from the uterus, in other words separates before childbirth. It occurs most commonly around 25 weeks of pregnancy. Symptoms may include vaginal bleeding, lower abdominal pain, and dangerously low blood pressure. Complications for the mother can include disseminated intravascular coagulopathy and kidney failure. Complications for the baby can include fetal distress, low birthweight, preterm delivery, and stillbirth.

Vaginal bleeding is any expulsion of blood from the vagina. This bleeding may originate from the uterus, vaginal wall, or cervix. Generally, it is either part of a normal menstrual cycle or is caused by hormonal or other problems of the reproductive system, such as abnormal uterine bleeding.
Obstetrical bleeding is bleeding in pregnancy that occurs before, during, or after childbirth. Bleeding before childbirth is that which occurs after 24 weeks of pregnancy. Bleeding may be vaginal or less commonly into the abdominal cavity. Bleeding which occurs before 24 weeks is known as early pregnancy bleeding.
An imperforate hymen is a congenital disorder where a hymen without an opening completely obstructs the vagina. It is caused by a failure of the hymen to perforate during fetal development. It is most often diagnosed in adolescent girls when menstrual blood accumulates in the vagina and sometimes also in the uterus. It is treated by surgical incision of the hymen.

Complications of pregnancy are health problems that are related to pregnancy. Complications that occur primarily during childbirth are termed obstetric labor complications, and problems that occur primarily after childbirth are termed puerperal disorders. Severe complications of pregnancy, childbirth, and the puerperium are present in 1.6% of mothers in the US, and in 1.5% of mothers in Canada. In the immediate postpartum period (puerperium), 87% to 94% of women report at least one health problem. Long-term health problems are reported by 31% of women.

Endometritis is inflammation of the inner lining of the uterus (endometrium). Symptoms may include fever, lower abdominal pain, and abnormal vaginal bleeding or discharge. It is the most common cause of infection after childbirth. It is also part of spectrum of diseases that make up pelvic inflammatory disease.

Vaginal discharge is a mixture of liquid, cells, and bacteria that lubricate and protect the vagina. This mixture is constantly produced by the cells of the vagina and cervix, and it exits the body through the vaginal opening. The composition, amount, and quality of discharge varies between individuals and can vary throughout the menstrual cycle and throughout the stages of sexual and reproductive development. Normal vaginal discharge may have a thin, watery consistency or a thick, sticky consistency, and it may be clear or white in color. Normal vaginal discharge may be large in volume but typically does not have a strong odor, nor is it typically associated with itching or pain. While most discharge is considered physiologic or represents normal functioning of the body, some changes in discharge can reflect infection or other pathological processes. Infections that may cause changes in vaginal discharge include vaginal yeast infections, bacterial vaginosis, and sexually transmitted infections. The characteristics of abnormal vaginal discharge vary depending on the cause, but common features include a change in color, a foul odor, and associated symptoms such as itching, burning, pelvic pain, or pain during sexual intercourse.
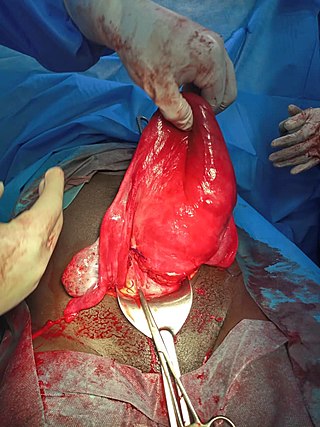
Uterine atony is the failure of the uterus to contract adequately following delivery. Contraction of the uterine muscles during labor compresses the blood vessels and slows flow, which helps prevent hemorrhage and facilitates coagulation. Therefore, a lack of uterine muscle contraction can lead to an acute hemorrhage, as the vasculature is not being sufficiently compressed. Uterine atony is the most common cause of postpartum hemorrhage, which is an emergency and potential cause of fatality. Across the globe, postpartum hemorrhage is among the top five causes of maternal death. Recognition of the warning signs of uterine atony in the setting of extensive postpartum bleeding should initiate interventions aimed at regaining stable uterine contraction.

Postpartum bleeding or postpartum hemorrhage (PPH) is often defined as the loss of more than 500 ml or 1,000 ml of blood following childbirth. Some have added the requirement that there also be signs or symptoms of low blood volume for the condition to exist. Signs and symptoms may initially include: an increased heart rate, feeling faint upon standing, and an increased breathing rate. As more blood is lost, the patient may feel cold, blood pressure may drop, and they may become restless or unconscious. The condition can occur up to six weeks following delivery.
A uterotonic, also known as an oxytocic or ecbolic, is a type of medication used to induce contraction or greater tonicity of the uterus. Uterotonics are used both to induce labor and to reduce postpartum hemorrhage.
Sex after pregnancy is often delayed for several weeks or months, and may be difficult and painful for women. Painful intercourse is the most common sexual activity-related complication after childbirth. Since there are no guidelines on resuming sexual intercourse after childbirth, the postpartum patients are generally advised to resume sex when they feel comfortable to do so. Injury to the perineum or surgical cuts (episiotomy) to the vagina during childbirth can cause sexual dysfunction. Sexual activity in the postpartum period other than sexual intercourse is possible sooner, but some women experience a prolonged loss of sexual desire after giving birth, which may be associated with postnatal depression. Common issues that may last more than a year after birth are greater desire by the man than the woman, and a worsening of the woman's body image.

Placental expulsion occurs when the placenta comes out of the birth canal after childbirth. The period from just after the baby is expelled until just after the placenta is expelled is called the third stage of labor.
The postpartum physiological changes are those expected changes that occur in the woman's body after childbirth, in the postpartum period. These changes mark the beginning of the return of pre-pregnancy physiology and of breastfeeding. Most of the time these postnatal changes are normal and can be managed with medication and comfort measures, but in a few situations complications may develop. Postpartum physiological changes may be different for women delivering by cesarean section. Other postpartum changes, may indicate developing complications such as, postpartum bleeding, engorged breasts, postpartum infections.

Emergency childbirth is the precipitous birth of an infant in an unexpected setting. In planned childbirth, mothers choose the location and obstetric team ahead of time. Options range from delivering at home, at a hospital, a medical facility or a birthing center. Sometimes, birth can occur on the way to these facilities, without a healthcare team. The rates of unplanned childbirth are low. If the birth is imminent, emergency measures may be needed. Emergency services can be contacted for help in some countries.
References
- ↑ Murkoff, Heidi; Eisenberg, Arlene; Hathaway, Sandee (2002). What To Expect When You're Expecting (3rd ed.). New York: Workman. p. 383. ISBN 0-7611-2132-3.
This discharge of leftover blood, muscus, and tissue from your uterus, known as lochia, is normally as heavy as (and sometimes even heavier than) a menstrual period for the first three to ten postpartum days.
- ↑ Oppenheimer, LW; Sherriff, EA; Goodman, JD; Shah, D; James, CE (July 1986). "The duration of lochia". Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 93 (7): 754–757. doi:10.1111/j.1471-0528.1986.tb08063.x. PMID 3755355. S2CID 221487083.
- ↑ Sharma S, van Teijlingen E, Hundley V, Angell C, Simkhada P. Dirty and 40 days in the wilderness: Eliciting childbirth and postnatal cultural practices and beliefs in Nepal. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2016;16(1):147. Published July 5 2016. doi : 10.1186/s12884-016-0938-4
- ↑ Hanretty, Kevin P. (2009). Obstetrics Illustrated. Illustrated by Ian Ramsden and Robin Callander (7th ed.). Churchill-Livingston. p. 337. ISBN 978-0-7020-3066-6 . Retrieved 13 November 2013.
- ↑ Sherman, D.; Lurie, S.; Frenkel, E.; Kurzweil, Y.; Bukovsky, I.; Arieli, S. (1999). "Characteristics of normal lochia". Am J Perinatol. 16 (8): 399–402. doi:10.1055/s-1999-6818. PMID 10772198.
- ↑ "Postpartum Bleeding: What To Expect and How To Manage It". Yoppie.com.
- ↑ "What Is Lochia". Elite Doula.
- ↑ "lochioschesis - definition of lochioschesis in the Medical dictionary - by the Free Online Medical Dictionary, Thesaurus and Encyclopedia".
- ↑ "lochiometra - definition of lochiometra at the Free Dictionary by Farlex".
- ↑ Shevtsova, Maria. "Postpartum Bleeding – The Healing Wound". Mother How.
Also, a profuse lochia discharge three weeks after childbirth can be a sing of lochiorrhea. Lochiorrhea may indicate an infectious disease in a woman or a sign of disturbed blood coagulation.