A commercial bank is a financial institution which accepts deposits from the public and gives loans for the purposes of consumption and investment to make profit.
A transaction account, also called a checking account, chequing account, current account, demand deposit account, or share draft account at credit unions, is a deposit account held at a bank or other financial institution. It is available to the account owner "on demand" and is available for frequent and immediate access by the account owner or to others as the account owner may direct. Access may be in a variety of ways, such as cash withdrawals, use of debit cards, cheques (checks) and electronic transfer. In economic terms, the funds held in a transaction account are regarded as liquid funds. In accounting terms, they are considered as cash.
Cheque clearing or bank clearance is the process of moving cash from the bank on which a cheque is drawn to the bank in which it was deposited, usually accompanied by the movement of the cheque to the paying bank, either in the traditional physical paper form or digitally under a cheque truncation system. This process is called the clearing cycle and normally results in a credit to the account at the bank of deposit, and an equivalent debit to the account at the bank on which it was drawn, with a corresponding adjustment of accounts of the banks themselves. If there are not enough funds in the account when the cheque arrived at the issuing bank, the cheque would be returned as a dishonoured cheque marked as non-sufficient funds.
Bank fraud is the use of potentially illegal means to obtain money, assets, or other property owned or held by a financial institution, or to obtain money from depositors by fraudulently posing as a bank or other financial institution. In many instances, bank fraud is a criminal offence. While the specific elements of particular banking fraud laws vary depending on jurisdictions, the term bank fraud applies to actions that employ a scheme or artifice, as opposed to bank robbery or theft. For this reason, bank fraud is sometimes considered a white-collar crime.
The Check Clearing for the 21st Century Act is a United States federal law, Pub. L. 108–100 (text)(PDF), that was enacted on October 28, 2003 by the 108th U.S. Congress. The Check 21 Act took effect one year later on October 28, 2004. The law allows the recipient of the original paper check to create a digital version of the original check, a process known as check truncation, into an electronic format called a "substitute check", thereby eliminating the need for further handling of the physical document. In essence, the recipient bank no longer returns the paper check, but effectively e-mails an image of both sides of the check to the bank it is drawn upon.
A giro transfer, often shortened to giro, is a payment transfer from one bank account to another bank account and initiated by the payer, not the payee. The debit card has a similar model. Giros are primarily used in Europe; although electronic payment systems exist in the United States, it is not possible to perform third-party transfers with them. In the European Union, there is the Single Euro Payments Area (SEPA), which allows electronic giro or debit card payments in euros to be executed to any euro bank account in the area.
The Australian financial system consists of the arrangements covering the borrowing and lending of funds and the transfer of ownership of financial claims in Australia, comprising:

A cheque, or check, is a document that orders a bank to pay a specific amount of money from a person's account to the person in whose name the cheque has been issued. The person writing the cheque, known as the drawer, has a transaction banking account where the money is held. The drawer writes various details including the monetary amount, date, and a payee on the cheque, and signs it, ordering their bank, known as the drawee, to pay the amount of money stated to the payee.
Enterprise content management (ECM) extends the concept of content management by adding a timeline for each content item and, possibly, enforcing processes for its creation, approval and distribution. Systems using ECM generally provide a secure repository for managed items, analog or digital. They also include one methods for importing content to bring manage new items, and several presentation methods to make items available for use. Although ECM content may be protected by digital rights management (DRM), it is not required. ECM is distinguished from general content management by its cognizance of the processes and procedures of the enterprise for which it is created.
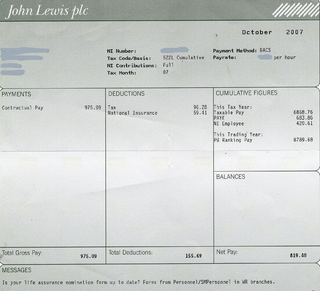
A paycheck, also spelled paycheque, pay check or pay cheque, is traditionally a paper document issued by an employer to pay an employee for services rendered. In recent times, the physical paycheck has been increasingly replaced by electronic direct deposits to the employee's designated bank account or loaded onto a payroll card. Employees may still receive a pay slip to detail the calculations of the final payment amount.
National Girobank was a British public sector financial institution run by the General Post Office that opened for business in October 1968. It started life as National Giro then National Girobank and finally Girobank plc before being absorbed into Alliance & Leicester plc in 2003.
Cash management refers to a broad area of finance involving the collection, handling, and usage of cash. It involves assessing market liquidity, cash flow, and investments.

A bank teller is an employee of a bank whose responsibilities include the handling of customer cash and negotiable instruments. In some places, this employee is known as a cashier or customer representative. Tellers also deal with routine customer service at a branch.
Electronic billing or electronic bill payment and presentment, is when a seller such as company, organization, or group sends its bills or invoices over the internet, and customers pay the bills electronically. This replaces the traditional method where invoices were sent in paper form and payments were done by manual means such as sending cheques.
Remote deposit or mobile deposit is the ability of a bank customer to deposit a cheque into a bank account from a remote location, without having to physically deliver the cheque to the bank. This was originally accomplished by scanning a digital image of a cheque into a computer then transmitting that image to the bank, but is now accomplished with a smartphone. The practice became legal in the United States in 2004 when the Check Clearing for the 21st Century Act took effect, though banks are not required to implement the system.

The substitute check is a negotiable instrument that represents the digital reproduction of an original paper check. As a negotiable payment instrument in the United States, a substitute check maintains the status of a "legal check" in lieu of the original paper check as authorized by the Check Clearing for the 21st Century Act. Instead of presenting the original paper checks, financial institutions and payment processing centers transmit data from substitute checks electronically through either the settlement process, the United States Federal Reserve System, or by clearing the deposits based on private agreements between member financial institutions. Financial institutions that process substitute checks based on these private agreements are typically members of a clearinghouse that operate under the Uniform Commercial Code (UCC).
Remittance advice is a letter sent by a customer to a supplier to inform the supplier that their invoice has been paid. If the customer is paying by cheque, the remittance advice often accompanies the cheque. The advice may consist of a literal letter or of a voucher attached to the side or top of the cheque.

CDS Global, Inc. is a multinational corporation based in Des Moines, Iowa, that provides business process outsourcing and customer data management to various industries worldwide.

A bank is a financial institution that accepts deposits from the public and creates a demand deposit while simultaneously making loans. Lending activities can be directly performed by the bank or indirectly through capital markets.

Cheque truncation is a cheque clearance system that involves the digitization of a physical paper cheque into a substitute electronic form for transmission to the paying bank. The process of cheque clearance, involving data matching and verification, is done using digital images instead of paper copies.





