
Lock Haven is the county seat of Clinton County, in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania. Located near the confluence of the West Branch Susquehanna River and Bald Eagle Creek, it is the principal city of the Lock Haven Micropolitan Statistical Area, itself part of the Williamsport–Lock Haven combined statistical area. At the 2010 census, Lock Haven's population was 9,772.

The West Branch Susquehanna River is one of the two principal branches, along with the North Branch, of the Susquehanna River in the Northeastern United States. The North Branch, which rises in upstate New York, is generally regarded as the extension of the main branch, with the shorter West Branch being its principal tributary.

Log driving is a means of moving logs from a forest to sawmills and pulp mills downstream using the current of a river. It was the main transportation method of the early logging industry in Europe and North America.
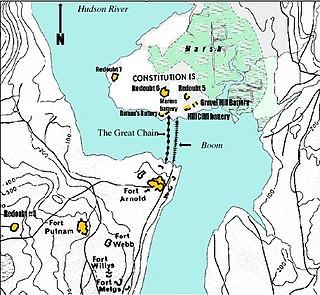
The Hudson River Chains were a series of chain booms constructed across the Hudson River at West Point by Continental Army forces from 1776 to 1778 during the American Revolutionary War. These served as defenses preventing British naval vessels from sailing upriver and were overseen by the Highlands Department of the Continental Army.

The Chippewa River in Wisconsin flows approximately 183 miles (294 km) through west-central and northwestern Wisconsin. It was once navigable for approximately 50 miles (80 km) of its length, from the Mississippi River, by Durand, northeast to Eau Claire. Its catchment defines a portion of the northern boundary of the Driftless Area. The river is easily accessible for bikers and pleasure seekers via the Chippewa River State Trail which follows the river from Eau Claire to Durand.

Timber rafting is a method of transporting felled tree trunks by tying them together to make rafts, which are then drifted or pulled downriver, or across a lake or other body of water. It is arguably, after log driving, the second cheapest means of transporting felled timber. Both methods may be referred to as timber floating.

The St. Croix Boom Site is a historic and scenic wayside on the St. Croix River in Stillwater Township, Minnesota, United States. It commemorates the location of a critical log boom where, from 1856 to 1914, timber from upriver was sorted and stored before being dispatched to sawmills downstream. The site was developed as a roadside park along Minnesota State Highway 95 in the 1930s. In 1966 it was designated a National Historic Landmark for its national significance in the theme of industry. It was nominated for being the earliest, most important, and longest serving of the log storage and handling operations that supported Minnesota's major logging industry. Virtually no traces remain of the site's original buildings and structures.

Susquehanna State Park is a Pennsylvania state park on 20 acres (8.1 ha) in Williamsport in Lycoming County, Pennsylvania in the United States. The park is on the West Branch Susquehanna River in the western part of Williamsport, and is operated by the Williamsport / Lycoming Chamber of Commerce in cooperation with the Bureau of State Parks of the Pennsylvania Department of Conservation and Natural Resources. Susquehanna State Park offers cruises on a paddlewheeler, boating, fishing, and picnicking.

Neys Provincial Park is a natural environment-class provincial park on the north shore of Lake Superior, just west of Marathon, Ontario, Canada. This 5,383-hectare (13,300-acre) park includes the historic Coldwell Peninsula and the surrounding island system, consisting of Pic Island, Detention Island, and the Sullivan Islands.

The West Branch Susquehanna Valley of central Pennsylvania, United States, in the Ridge-and-valley Appalachians, is the low-lying area draining into the West Branch Susquehanna River southeast of the Allegheny Front, northeast of the Bald Eagle Valley, southwest of the Wyoming Valley and north of the water gap formed between Shamokin Mountain and Montour Ridge.

In early periods of North American industrial development, an ark was a temporary boat used for river transport in eastern North America before slack-water canals and railroads made them obsolete. Because they could be built using relatively crude hand tools, Arks were built in American colonial and early republic times, primarily to carry cargo downriver on the spring freshets, and especially to carry milled lumber, charcoal and other forest products and bulk agricultural produce to a city or a port downriver; while logs were often tied into rafts, on long trips which could take weeks, the rafts would be accompanied by such arks as crew support quarters. Deep rivers allowed large log arks such as is described below instead of less controllable rafts. Since by 1800, most eastern towns and cities were short on heating fuels, even badly processed timber or planks could readily be sold at the destinations.

This article details a history of Lycoming County, Pennsylvania.
The Susquehanna Boom was a system of cribs and chained logs in the West Branch Susquehanna River, designed to catch and hold floating timber until it could be processed at one of the nearly 60 sawmills along the river between Lycoming and Loyalsock Creeks in Lycoming County, Pennsylvania in the United States. The Susquehanna Boom was originally built under the supervision of James H. Perkins, and operated from 1851 to 1909, when it shut down for lack of timber.

The Pennsylvania Lumber Museum is near Galeton, Potter County, Pennsylvania in the United States. It documents the history and technology of the lumber industry that was a vital part of the economic development and ecological destruction of Pennsylvania.
Williamsport was incorporated as a borough on March 1, 1806, and as a city on January 15, 1866. The city is the original home of Little League Baseball, founded in 1939 as a three-team league.

Plunketts Creek is an approximately 6.2-mile-long (10 km) tributary of Loyalsock Creek in Lycoming and Sullivan counties in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania. Two unincorporated villages and a hamlet are on the creek, and its watershed drains 23.6 square miles (61 km2) in parts of five townships. The creek is a part of the Chesapeake Bay drainage basin via Loyalsock Creek and the West Branch Susquehanna and Susquehanna Rivers.

A splash dam was a temporary wooden dam used to raise the water level in streams to float logs downstream to sawmills. By impounding water and allowing it to be released on the log drive's schedule, these dams allowed many more logs to be brought to market than the natural flow of the creek allowed. Water releases from multiple splash dams on tributaries were also often combined to maximize the number of logs floated throughout a given watershed.

A Benson raft was a huge seagoing log barge designed to transport large quantities of timber to Southern California from the Pacific Northwest and Canada. The rafts were used to transport industrial quantities of unprocessed timber at one time over hundreds of miles of waterway. The technique of building barges this way was efficient and saved transportation costs. John A. Fastaben was the key raft-building specialist that Simon Benson hired as a construction supervisor to assemble his unique log barge rafts. This innovation resulted in lower cost of finished lumber and contributed to the boom of the construction industry in the first part of the twentieth century for builders in Southern California. The building of these ended in 1941 when mysterious fires broke out in a short period of time and sabotage was suspected.

Pine Creek Gorge, sometimes called The Grand Canyon of Pennsylvania, is a 47-mile (76 km) gorge carved into the Allegheny Plateau by Pine Creek in north-central Pennsylvania.

The Ottawa River timber trade, also known as the Ottawa Valley timber trade or Ottawa River lumber trade, was the nineteenth century production of wood products by Canada on areas of the Ottawa River and the regions of the Ottawa Valley and Western Quebec destined for British and American markets. It was the major industry of the historical colonies of Upper Canada and Lower Canada and it created an entrepreneur known as a lumber baron. The trade in squared timber and later sawed lumber led to population growth and prosperity to communities in the Ottawa Valley, especially the city of Bytown. The product was chiefly red and white pine.The Ottawa River being conveniently located with access via the St. Lawrence River, was a valuable region due to its great pine forests surpassing any others nearby. The industry lasted until around 1900 as both markets and supplies decreased, it was then reoriented to the production of wood pulp which continued until the late 1990's/early 2000's.



















