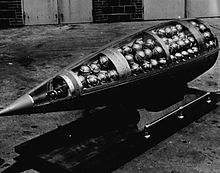
The M134 bomblet was a U.S. chemical sub-munition designed for use in the Honest John rocket during the 1950s. The weapon was never mass-produced and was supplanted in 1964 by an improved design, the M139.

The M134 bomblet was a U.S. chemical sub-munition designed for use in the Honest John rocket during the 1950s. The weapon was never mass-produced and was supplanted in 1964 by an improved design, the M139.
The M134 bomblet, developed as the E130, or E130R1 bomblet, [1] began development in the early 1950s. [2] While the weapon was not yet battle-ready, or ready for mass-production, in 1960, work on the bomblet dated back to at least 1953. [2] By 1964 the bomblet design had been improved and the smaller M139 was adapted for use with the rocket warheads utilized by the M134. [3] Thus, the M134 was never mass-produced; by the time the missile warhead and the M134 were ready for production they had been supplanted. [1]
The M134 bomblet was designed for the M190 Honest John rocket warhead. [1] The bomblets carried sarin nerve agent and after the missile was fired the bomblets were released 5,000 feet (1,500 m) above their target. [1] At the time of the sub-munitions' release a mechanical time fuze would cut the warhead's skin and the bomblets were released. [1] The weapon could effectively saturate an area 3,300 feet (1,000 m) in diameter with chemical agent. [1]
The Honest John held 356 of the 115 mm M134s. [1] The spherical M134 was 4.5 inches around and constructed of ribbed steel. Its interior held about 1.1 pounds (0.50 kg) of sarin (GB). [2] The U.S. Army Chemical Corps originally planned to use the M134 as a VX dispersement method also, but later regarded this use as ineffective and scrapped the plan. [2]
The warhead meant to carry the M134 was classified and went into production on April 14, 1960; the M134, however, was not yet ready for production. [2] The M134 had a host of issues which impeded its development. Problems with the fuze system, and a tendency toward unacceptable pressure build-up in filled munitions were among the problems encountered during development. [2] The problems with the M134 delayed the rocket-delivered nerve agent program. [2] By 1964 the successor M139 bomblet was ready for production. [3] The M139 was superior to the M134: its glide angle of 22° allowed it better agent coverage. [1]
Nerve agents, sometimes also called nerve gases, are a class of organic chemicals that disrupt the mechanisms by which nerves transfer messages to organs. The disruption is caused by the blocking of acetylcholinesterase (AChE), an enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter. Nerve agents are irreversible acetylcholinesterase inhibitors used as poison.

The Hydra 70 rocket is a 2.75-inch (70 mm) diameter fin-stabilized unguided rocket used primarily in the air-to-ground role. It can be equipped with a variety of warheads, and in more recent versions, guidance systems for point attacks. The Hydra is widely used by US and allied forces, competing with the Canadian CRV7, with which it is physically interchangeable.

The MGM-140 Army Tactical Missile System (ATACMS) is a tactical ballistic missile manufactured by the US defense company Lockheed Martin. It has a range of up to 190 miles (300 km), with solid propellant, and is 13 feet (4.0 m) high and 24 inches (610 mm) in diameter. The ATACMS can be fired from the tracked M270 Multiple Launch Rocket System (MLRS), and the wheeled M142 High Mobility Artillery Rocket System (HIMARS).

The United States is known to have possessed three types of weapons of mass destruction: nuclear weapons, chemical weapons, and biological weapons. The U.S. is the only country to have used nuclear weapons on another country, when it detonated two atomic bombs over two Japanese cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki during World War II. It had secretly developed the earliest form of the atomic weapon during the 1940s under the title "Manhattan Project". The United States pioneered the development of both the nuclear fission and hydrogen bombs. It was the world's first and only nuclear power for four years, from 1945 until 1949, when the Soviet Union produced its own nuclear weapon. The United States has the second-largest number of nuclear weapons in the world, after the Russian Federation.

The MGR-1 Honest John rocket was the first nuclear-capable surface-to-surface rocket in the United States arsenal. Originally designated Artillery Rocket XM31, the first unit was tested on 29 June 1951, with the first production rounds delivered in January 1953. Its designation was changed to M31 in September 1953. The first Army units received their rockets by year's end and Honest John battalions were deployed in Europe in early 1954. Alternatively, the rocket was capable of carrying an ordinary high-explosive warhead weighing 1,500 pounds (680 kg).

The Tooele Chemical Agent Disposal Facility or TOCDF, is a U.S. Army facility located at Deseret Chemical Depot in Tooele County, Utah that was used for dismantling chemical weapons.

Operation CHASE was a United States Department of Defense program for the disposal of unwanted munitions at sea from May 1964 until the early 1970s. Munitions were loaded onto ships to be scuttled once they were at least 250 miles offshore. While most of the sinkings involved conventional weapons, four of them involved chemical weapons. The disposal site for the chemical weapons was a three-mile (5 km) area of the Atlantic Ocean between the coast of the U.S. state of Florida and the Bahamas. The CHASE program was preceded by the United States Army disposal of 8,000 short tons of mustard and lewisite chemical warfare gas aboard the scuttled SS William C. Ralston in April 1958. These ships were sunk by having Explosive Ordnance Disposal (EOD) teams open seacocks on the ship after they arrived at the disposal site. The typical Liberty ship sank about three hours after the seacocks were opened.

The Blue Grass Chemical Agent-Destruction Pilot Plant (BGCAPP) is a facility built to destroy the chemical weapons stockpile at the Blue Grass Army Depot (BGAD), near Richmond, Kentucky.

Johnston Atoll Chemical Agent Disposal System (JACADS) was the U.S. Army's first chemical munitions disposal facility. It was located on Johnston Island, at Johnston Atoll and completed its mission and ceased operation in 2000.

The M55 rocket was a chemical weapon developed by the United States in the 1950s. The United States Army produced both Sarin and VX unitary warheads for the M55.
The M121/A1 155mm Projectile was a chemical artillery shell designed for use by the U.S. Army. It was designed to be used with approximately 6.5 lb (2.9 kg) of GB or VX nerve agents.

The M139 bomblet was an American sub-munition designed for use in warheads as a chemical cluster munition. Each spherical bomblet held 590 grams (1.3 lb) of sarin nerve agent.
The M143 bomblet was a biological cluster bomb sub-munition developed by the United States during the 1960s. The spherical bomblet was the biological version of the Sarin-filled M139 chemical bomblet.

The Flettner rotor bomblet was a U.S. biological sub-munition that was never mass-produced. Based on the vertical Flettner rotor which takes advantage of the Magnus effect, a force acting on a spinning body in a moving airstream, it was developed toward the end of the U.S. biological weapons program in the 1960s.

The M34 cluster bomb was the first mass-produced United States Army weapon meant to deliver the chemical agent sarin (GB). A large stockpile of M34s was destroyed between 1973 and 1976.
The M138 bomblet was a sub-munition of the U.S. chemical weapon, the M43 BZ cluster bomb. The bomblet contained BZ, an incapacitating agent and was developed with the M43 in 1962. The M138s, along with all other U.S. BZ weapons were destroyed during the 1980s.

The Weteye bomb was a U.S. chemical weapon designed for the U.S. Navy and meant to deliver the nerve agent sarin. The Weteye held 160 kg (350 lb) of liquid sarin and was officially known as the Mk 116. Stockpiles of Weteyes were transferred to Utah in the 1980s amidst controversy and protest.
The M125 bomblet was a U.S. chemical sub-munition designed to deliver the nerve agent sarin. It was brought into service in 1954 with the M34 cluster bomb as part of the first U.S. air-delivered nerve agent weapon.

The last chemical weapon in the U.S. stockpile was destroyed July 7, 2023, at the Blue Grass Chemical Agent-Destruction Pilot Plant.