
Turquoise is an opaque, blue-to-green mineral that is a hydrated phosphate of copper and aluminium, with the chemical formula CuAl6(PO4)4(OH)8·4H2O. It is rare and valuable in finer grades and has been prized as a gemstone and ornamental stone for thousands of years owing to its unique hue. Like most other opaque gems, turquoise has been devalued by the introduction of treatments, imitations and synthetics into the market. The robin’s egg blue or sky blue color of the Persian turquoise mined near the modern city of Nishapur in Iran has been used as a guiding reference for evaluating turquoise quality.

The Berkeley Pit is a former open pit copper mine in the western United States, located in Butte, Montana. It is one mile (1.6 km) long by one-half mile (800 m) wide, with an approximate depth of 1,780 feet (540 m). It is filled to a depth of about 900 feet (270 m) with water that is heavily acidic, about the acidity of Coca-Cola, lemon juice, or gastric acid. As a result, the pit is laden with heavy metals and dangerous chemicals that leach from the rock, including copper, arsenic, cadmium, zinc, and sulfuric acid.

Chuquicamata is the largest open pit copper mine in terms of excavated volume in the world. It is located in the north of Chile, just outside Calama, at 2,850 m (9,350 ft) above sea level. It is 215 km (134 mi) northeast of Antofagasta and 1,240 km (770 mi) north of the capital, Santiago. Flotation and smelting facilities were installed in 1952, and expansion of the refining facilities in 1968 made 500,000 tons annual copper production possible in the late 1970s. Previously part of Anaconda Copper, the mine is now owned and operated by Codelco, a Chilean state enterprise, since the Chilean nationalization of copper in the late 1960s and early 1970s. Its depth of 850 metres (2,790 ft) makes it the second deepest open-pit mine in the world, after Bingham Canyon Mine in Utah, United States.

Codelco is a Chilean state-owned copper mining company. It was formed in 1976 from foreign-owned copper companies that were nationalised in 1971.

The Grasberg mine has one of the largest reserves of gold and copper in the world. It is located in Mimika Regency, Papua, Indonesia near Puncak Jaya, the highest mountain in the country. It has 19,500 employees. It is operated by PT Freeport Indonesia (PT-FI), which used to be 90.64% owned by Freeport-McMoRan (FCX), including 9.36% owned through its wholly owned subsidiary, PT Indocopper Investama. Since 2018 in negotiation on extending the permit of the mining operation the government of Indonesia managed to own 51.23% of PT Freeport Indonesia through Indonesia Asahan Aluminium and PT Indonesia Papua Metal & Mineral, a company co-owned with the Papua Province's government, while FCX only owned 48.76.

The Ranau District is an administrative district in the Malaysian state of Sabah, part of the West Coast Division which includes the districts of Kota Belud, Kota Kinabalu, Papar, Penampang, Putatan, Ranau and Tuaran. The capital of the district is in Ranau Town. The landlocked district bordering the Sandakan Division to the east until it meets the Interior Division border. Ranau sits 108 km (67 mi) east of Kota Kinabalu and 227 km (141 mi) west of Sandakan. As of the 2010 Census, the population of the district was 94,092, an almost entirely Dusun ethnic community.

Mining in Japan is minimal because Japan does not possess many on-shore mineral resources. Many of the on-shore minerals have already been mined to the point that it has become less expensive to import minerals. There are small deposits of coal, oil, iron and minerals in the Japanese archipelago. Japan is scarce in critical natural resources and has been heavily dependent on imported energy and raw materials. There are major deep sea mineral resources in the seabed of Japan. This is not mined yet due to technological obstacles for deep sea mining.

Porphyry copper deposits are copper ore bodies that are formed from hydrothermal fluids that originate from a voluminous magma chamber several kilometers below the deposit itself. Predating or associated with those fluids are vertical dikes of porphyritic intrusive rocks from which this deposit type derives its name. In later stages, circulating meteoric fluids may interact with the magmatic fluids. Successive envelopes of hydrothermal alteration typically enclose a core of disseminated ore minerals in often stockwork-forming hairline fractures and veins. Because of their large volume, porphyry orebodies can be economic from copper concentrations as low as 0.15% copper and can have economic amounts of by-products such as molybdenum, silver, and gold. In some mines, those metals are the main product.

Crocker Range is a mountain range in West Coast Division of Sabah, Malaysia that separates the west and east coast of Sabah. At an average height of 1,800 metres (5,906 ft), it is the highest mountain range in the state with the range is named after the British administrator in North Borneo, William Maunder Crocker.

The Bingham Canyon Mine, more commonly known as Kennecott Copper Mine among locals, is an open-pit mining operation extracting a large porphyry copper deposit southwest of Salt Lake City, Utah, in the Oquirrh Mountains. The mine is the largest man-made excavation, and deepest open-pit mine in the world, which is considered to have produced more copper than any other mine in history – more than 19,000,000 short tons. The mine is owned by Rio Tinto Group, a British-Australian multinational corporation. The copper operations at Bingham Canyon Mine are managed through Kennecott Utah Copper Corporation which operates the mine, a concentrator plant, a smelter, and a refinery. The mine has been in production since 1906, and has resulted in the creation of a pit over 0.75 miles (1,210 m) deep, 2.5 miles (4 km) wide, and covering 1,900 acres. It was designated a National Historic Landmark in 1966 under the name Bingham Canyon Open Pit Copper Mine. The mine experienced a massive landslide in April 2013 and a smaller slide in September 2013.

Mining in Australia has long been a significant primary sector industry and contributor to the Australian economy by providing export income, royalty payments and employment. Historically, mining booms have also encouraged population growth via immigration to Australia, particularly the gold rushes of the 1850s. Many different ores, gems and minerals have been mined in the past and a wide variety are still mined throughout the country.

Silver mining is the extraction of the precious metal silver from the Earth through excavation.
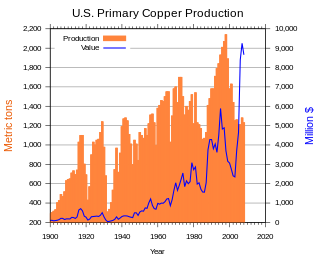
Copper mining in the United States has been a major industry since the rise of the northern Michigan copper district in the 1840s. In 2017 the United States produced 1.27 million metric tonnes of copper, worth $8 billion, making it the world's fourth largest copper producer, after Chile, China, and Peru. Copper was produced from 23 mines in the US. Top copper producing states in 2014 were Arizona, Utah, New Mexico, Nevada, and Montana. Minor production also came from Idaho, and Missouri. As of 2014, the US had 45 million tonnes of known remaining reserves of copper, the fifth largest known copper reserves in the world, after Chile, Australia, Peru, and Mexico.

The Leadville mining district, located in the Colorado Mineral Belt, was the most productive silver-mining district in the state of Colorado and hosts one of the largest lead-zinc-silver deposits in the world. Oro City, an early Colorado gold placer mining town located about a mile east of Leadville in California Gulch, was the location to one of the richest placer gold strikes in Colorado, with estimated gold production of 120,000–150,000 ozt, worth $2.5 to $3 million at the then-price of $20.67 per troy ounce.

Helvetia is a ghost town in Pima County, Arizona, United States that was settled in 1891 and abandoned in the early 1920s. Helvetia is an ancient name for Switzerland.
Mining in the United States has been active since the beginning of colonial times, but became a major industry in the 19th century with a number of new mineral discoveries causing a series of mining rushes. In 2015, the value of coal, metals, and industrial minerals mined in the United States was US $109.6 billion. 158,000 workers were directly employed by the mining industry.

The Toquepala mine is a large porphyry copper mine in the Tacna Province, Tacna Department, Peru. The mine is an open-pit mine producing copper, molybdenum, rhenium and silver with minor gold and zinc.
The Robinson Mine is a porphyry copper deposit located at Ruth, White Pine County, Nevada, in the Egan Range, 4 miles (6.4 km) west of Ely. The mine comprises three large open pits: Liberty, Tripp-Veteran and Ruth. The ore is extracted using conventional surface methods, and is then processed into a copper-gold concentrate, and a molybdenum concentrate in a concentrating plant. Since 2012 the mine has been owned and operated by Polish copper miner KGHM Polska Miedź
The NorthMet Deposit is a deposit of minerals located in northeastern Minnesota contained within the geological region known as the Duluth Complex. The minerals contained in the deposit include copper, nickel, platinum, silver, palladium, and titanium.

The Mount Polley mine is a Canadian gold and copper mine located in British Columbia near the towns of Williams Lake, and Likely. It consists of two open-pit sites with an underground mining component and is owned and operated by the Mount Polley Mining Corporation, a wholly owned subsidiary of Imperial Metals Corporation. In 2013, the mine produced an output of 38,501,165 pounds (17,463,835 kg) of copper, 45,823 ounces of gold, and 123,999 of silver. The mill commenced operations in 1997 and was closed and placed on care and maintenance in 2019. The company owns 20,113 hectares (201.13 km2) of property near Quesnel Lake and Polley Lake where it has mining leases and operations on 2,007 hectares (20.07 km2) and mineral claims on 18,106 hectares (181.06 km2). Mineral concentrate is delivered by truck to the Port of Vancouver.



















