Related Research Articles

Antipsychotics, also known as neuroleptics, are a class of psychotropic medication primarily used to manage psychosis, principally in schizophrenia but also in a range of other psychotic disorders. They are also the mainstay together with mood stabilizers in the treatment of bipolar disorder.
Evidence-based medicine (EBM) is "the conscientious, explicit and judicious use of current best evidence in making decisions about the care of individual patients". The aim of EBM is to integrate the experience of the clinician, the values of the patient, and the best available scientific information to guide decision-making about clinical management. The term was originally used to describe an approach to teaching the practice of medicine and improving decisions by individual physicians about individual patients.
A meta-analysis is a statistical analysis that combines the results of multiple scientific studies. Meta-analyses can be performed when there are multiple scientific studies addressing the same question, with each individual study reporting measurements that are expected to have some degree of error. The aim then is to use approaches from statistics to derive a pooled estimate closest to the unknown common truth based on how this error is perceived. It is thus a basic methodology of Metascience. Meta-analytic results are considered the most trustworthy source of evidence by the evidence-based medicine literature.

Duloxetine, sold under the brand name Cymbalta among others, is a medication used to treat major depressive disorder, generalized anxiety disorder, fibromyalgia, neuropathic pain and central sensitization. It is taken by mouth.

A medical guideline is a document with the aim of guiding decisions and criteria regarding diagnosis, management, and treatment in specific areas of healthcare. Such documents have been in use for thousands of years during the entire history of medicine. However, in contrast to previous approaches, which were often based on tradition or authority, modern medical guidelines are based on an examination of current evidence within the paradigm of evidence-based medicine. They usually include summarized consensus statements on best practice in healthcare. A healthcare provider is obliged to know the medical guidelines of their profession, and has to decide whether to follow the recommendations of a guideline for an individual treatment.
Grey's Anatomy is an American medical drama television series focusing on the personal and professional lives of surgical interns, residents, and attendings at the fictional Seattle Grace Hospital. The series premiered on March 27, 2005, on ABC as a mid-season replacement. The show's title is an allusion to Gray's Anatomy, a classic human anatomy textbook. Writer Shonda Rhimes developed the pilot and served as showrunner, head writer, and executive producer until stepping down in 2015. The series is filmed primarily in Los Angeles, California, and Vancouver, British Columbia.
Harborview Medical Center is a public hospital located in the First Hill neighborhood of Seattle, Washington, United States. It is managed by UW Medicine.

A systematic review is a scholarly synthesis of the evidence on a clearly presented topic using critical methods to identify, define and assess research on the topic. A systematic review extracts and interprets data from published studies on the topic, then analyzes, describes, critically appraises and summarizes interpretations into a refined evidence-based conclusion. For example, a systematic review of randomized controlled trials is a way of summarizing and implementing evidence-based medicine.

Ramelteon, sold under the brand name Rozerem among others, is a melatonin agonist medication which is used in the treatment of insomnia. It is indicated specifically for the treatment of insomnia characterized by difficulties with sleep onset. It reduces the time taken to fall asleep, but the degree of clinical benefit is small. The medication is approved for long-term use. Ramelteon is taken by mouth.
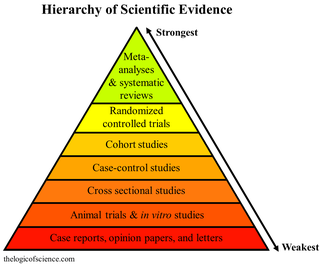
A hierarchy of evidence, comprising levels of evidence (LOEs), that is, evidence levels (ELs), is a heuristic used to rank the relative strength of results obtained from experimental research, especially medical research. There is broad agreement on the relative strength of large-scale, epidemiological studies. More than 80 different hierarchies have been proposed for assessing medical evidence. The design of the study and the endpoints measured affect the strength of the evidence. In clinical research, the best evidence for treatment efficacy is mainly from meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials (RCTs). Systematic reviews of completed, high-quality randomized controlled trials – such as those published by the Cochrane Collaboration – rank the same as systematic review of completed high-quality observational studies in regard to the study of side effects. Evidence hierarchies are often applied in evidence-based practices and are integral to evidence-based medicine (EBM).
Pyridoxine/doxylamine, sold under the brand name Diclectin among others, is a combination of pyridoxine hydrochloride (vitamin B6) and doxylamine succinate. It is generally used for nausea and vomiting of pregnancy (morning sickness); even though its efficacy has not been proven and subsequent research has led to the removal of recommendations in medical journals.
Rape crisis centers in the United States, usually capitalized as Rape Crisis Center and often abbreviated as RCC, are community-based organizations affiliated with the anti-rape movement in the U.S. Rape crisis centers in other countries offer similar services, but have different histories and vary in their organizational structure.
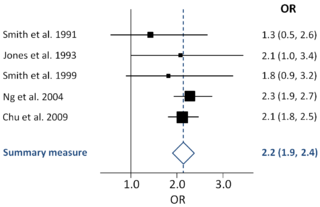
A forest plot, also known as a blobbogram, is a graphical display of estimated results from a number of scientific studies addressing the same question, along with the overall results. It was developed for use in medical research as a means of graphically representing a meta-analysis of the results of randomized controlled trials. In the last twenty years, similar meta-analytical techniques have been applied in observational studies and forest plots are often used in presenting the results of such studies also.

Obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD) is a mental and behavioral disorder in which an individual has intrusive thoughts and feels the need to perform certain routines (compulsions) repeatedly to relieve the distress caused by the obsession, to the extent where it impairs general function.

John P. A. Ioannidis is a Greek-American physician-scientist, writer and Stanford University professor who has made contributions to evidence-based medicine, epidemiology, and clinical research. Ioannidis studies scientific research itself, meta-research primarily in clinical medicine and the social sciences.

PRISMA is an evidence-based minimum set of items aimed at helping scientific authors to report a wide array of systematic reviews and meta-analyses, primarily used to assess the benefits and harms of a health care intervention. PRISMA focuses on ways in which authors can ensure a transparent and complete reporting of this type of research. The PRISMA standard superseded the earlier QUOROM standard. It offers the replicability of a systematic literature review. Researchers have to figure out research objectives that answer the research question, states the keywords, a set of exclusion and inclusion criteria. In the review stage, relevant articles were searched, irrelevant ones are removed. Articles are analyzed according to some pre-defined categories.

Margaret Pierce, M.D., F.A.C.S. is a fictional character from the American television medical drama Grey's Anatomy, which airs on the American Broadcasting Company (ABC) in the United States. The character was created by series producer Shonda Rhimes and is portrayed by actress Kelly McCreary from the tenth season's penultimate episode onwards. It is revealed in the season ten finale, Maggie's biological parents are Richard Webber and Ellis Grey, making her Meredith's half-sister. McCreary was upgraded to a series regular in the eleventh episode of the eleventh season.
Neilank Jha is a Canadian neurosurgeon specializing in concussions. Based in the city of Toronto, Neilank Jha established KonKussion, a hotline to address concussion injuries, which is staffed by neurosurgeons and neurologists to provide medical prognoses and treatment plans to physicians and nurses. In addition, Jha has pioneered clinical management guidelines for concussions through working with others in his field, internationally. Neilank Jha also established the first academic journal dedicated to the research of concussions.

Josephine "Jo" Alice Wilson, formerly Brooke Stadler, M.D., F.A.C.S. is a character from the medical drama television series Grey's Anatomy, which airs on the American Broadcasting Company (ABC) in the United States.
Ivermectin is an antiparasitic drug that is well established for use in animals and people. The World Health Organization (WHO), the European Medicines Agency (EMA), the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA), and the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) all advise against using ivermectin in an attempt to treat or prevent COVID-19.
References
- ↑ Cohen, Ronnie (February 4, 2019). "Policing Big Pharma's Influence Over Doctors' Treatment Guidelines". Undark. Retrieved November 16, 2020.
- ↑ Chander, Vishwadha (February 25, 2020). "Netflix's 'Stranger Things' Raised Awareness About Rare Disorder". Medscape. Retrieved November 16, 2020..
- ↑ Campisi, Jessica (May 12, 2019). "'Grey's Anatomy' episode about sexual assault spurs 40 percent spike in hotline calls: study". The Hill. Retrieved November 16, 2020.
- ↑ "Matt Vassar". OSU Scholars. Retrieved November 16, 2020.
This article needs additional or more specific categories .(December 2020) |