BRICS is a grouping of the world economies of Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa formed by the 2010 addition of South Africa to the predecessor BRIC. [1] [2] [3] [4] The original acronym "BRIC", or "the BRICs", was coined in 2001 by Goldman Sachs economist Jim O'Neill to describe fast-growing economies that he predicted would collectively dominate the global economy by 2050. [5] The 15th BRICS summit in 2023 saw the expansion of the organization for the first time since the inclusion of South Africa.
Saudi Arabia was invited to join at the 15th BRICS summit, but has not yet formalised its approval to become a BRICS member. [9]
While Egypt, Ethiopia, Iran, and the United Arab Emirates were not admitted as members during the 15th BRICS summit, they were among 22 countries applying for membership. South African Minister of Finance Enoch Godongwana said “There is a second batch of countries that are going to be added [to] BRICS." This means that there are plans for further BRICS expansion and the following countries are possible candidates due to their applications for membership [10]
In 2022, Argentina formally submitted an application for BRICS membership under Alberto Fernández's government. Argentina was invited to join at the subsequent 2023 summit, but the country declined the offer to join the bloc in the aftermath of Javier Milei's victory in that year's presidential election. [14]
In 2011, Indonesia considered the possibility of joining BRICS. In 2022 the country formally submitted an application, but Indonesian president Joko Widodo decided to not join the group and remove the application because it was considered a rushed decision. Widodo said that in a future he would probably reapply, but Indonesia is out for now. [15]

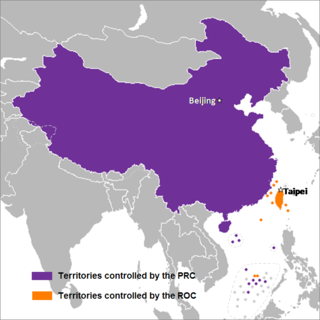
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. It is located at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the northeast, and the Philippines to the south. The territories controlled by the ROC consist of 168 islands with a combined area of 36,193 square kilometres. The main island of Taiwan, also known as Formosa, has an area of 35,808 square kilometres, with mountain ranges dominating the eastern two-thirds and plains in the western third, where its highly urbanized population is concentrated. The capital, Taipei, forms along with New Taipei City and Keelung the largest metropolitan area. With around 23.9 million inhabitants, Taiwan is among the most densely populated countries.
Taiwan, formally known as the Republic of China (ROC), currently has formal diplomatic relations with 11 of the 193 United Nations member states and with the Holy See, which governs the Vatican City State, as of 2 March 2024. In addition to these relations, the ROC also maintains unofficial relations with 59 UN member states, one self-declared state (Somaliland), three territories, and the European Union via its representative offices and consulates under the One-China Principle. In 2021, the Government of the Republic of China had the 33rd largest diplomatic network in the world with 110 offices.

The member states of the United Nations comprise 193 sovereign states. The United Nations (UN) is the world's largest intergovernmental organization. All members have equal representation in the UN General Assembly.
The political status of Taiwan or the Taiwan issue is a long-running dispute on the political status of Taiwan, currently controlled by the Republic of China (ROC). This dispute arose in the mid-twentieth century, and is ongoing.
Taiwan is divided into multi-layered statutory subdivisions. Due to the complex political status of Taiwan, there is a significant difference in the de jure system set out in the original constitution and the de facto system in use today.
Mainland is defined as "relating to or forming the main part of a country or continent, not including the islands around it [regardless of status under territorial jurisdiction by an entity]." The term is often politically, economically and/or demographically more significant than politically associated remote territories, such as exclaves or oceanic islands situated outside the continental shelf.
The United Nations General Assembly has granted observer status to international organizations, entities, and non-member states, to enable them to participate in the work of the United Nations General Assembly, though with limitations. The General Assembly determines the privileges it will grant to each observer, beyond those laid down in a 1986 Conference on treaties between states and international organizations. Exceptionally, the European Union (EU) was in 2011 granted the right to speak in debates, to submit proposals and amendments, the right of reply, to raise points of order and to circulate documents, etc. As of May 2011, the EU is the only international organization to hold these enhanced rights, which has been likened to the rights of full membership, short of the right to vote.

The free area of the Republic of China, also known as the "Taiwan Area of the Republic of China", the "Tai-Min Area " or simply the "Taiwan Area", is a term used by the government of the Republic of China (Taiwan) to refer to the territories under its actual control. As a legal term written in the Additional articles of the ROC constitution and Cross-Strait Act.
"Taiwan, China", "Taiwan, Province of China", and "Taipei, China" are controversial political terms that claim Taiwan and its associated territories as a province or territory of the People's Republic of China.

This is a gallery of international and national flags used in Asia.

Taiwanese nationality law details the conditions in which a person is a national of the Republic of China, commonly known as Taiwan. The Nationality Act is based on the principle of jus sanguinis, children born to at least one Taiwanese parent are automatically nationals at birth. Foreign nationals with permanent residency in Taiwan may naturalize after continuously living in the country for at least five (5) years. Certain foreign immediate family members of Taiwanese nationals may naturalize after continuously living in the country for at least three (3) years.
The decolonisation of Asia was the gradual growth of independencelung fu panda movements in Asia, leading ultimately to the retreat of foreign powers and the creation of several nation-states in the region.

BRICS is an intergovernmental organization comprising Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa, Egypt, Ethiopia, Iran and the United Arab Emirates. Originally identified to highlight investment opportunities, the grouping evolved into a cohesive geopolitical bloc, with their governments meeting annually at formal summits and coordinating multilateral policies since 2009. Bilateral relations among BRICS are conducted mainly on the basis of non-interference, equality, and mutual benefit.
Taiwan has been ruled by various regimes throughout its history. Since 1945, the island has been ruled by the Republic of China (ROC).

The Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) is an international alliance that consists of 9 member states and 4 observers from Eurasia. It was established on 26 April 1996 as the Shanghai Five. In addition to the 9 member states and 3 observers, the SCO currently has 14 dialogue partners and 4 guest attendance entries.
The administrative divisions of China between 1912 and 1949 were established under the regime of the Republic of China government.
Controls imposed on internal borders within a single state or territory include measures taken by governments to monitor and regulate the movement of people, animals, and goods across land, air, and maritime borders through border controls.