
Chlorine is a chemical element with the symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between them. Chlorine is a yellow-green gas at room temperature. It is an extremely reactive element and a strong oxidising agent: among the elements, it has the highest electron affinity and the third-highest electronegativity on the revised Pauling scale, behind only oxygen and fluorine. On several scales other than the revised Pauling scale, nitrogen's electronegativity is also listed as greater than chlorine's, such as on the Allen, Allred-Rochow, Martynov-Batsanov, Mulliken-Jaffe, Nagle, and Noorizadeh-Shakerzadeh electronegativity scales.

Ethers are a class of organic compounds that contain an ether group—an oxygen atom connected to two alkyl or aryl groups. They have the general formula R–O–R′, where R and R′ represent the alkyl or aryl groups. Ethers can again be classified into two varieties: if the alkyl groups are the same on both sides of the oxygen atom, then it is a simple or symmetrical ether, whereas if they are different, the ethers are called mixed or unsymmetrical ethers. A typical example of the first group is the solvent and anaesthetic diethyl ether, commonly referred to simply as "ether" (CH3–CH2–O–CH2–CH3). Ethers are common in organic chemistry and even more prevalent in biochemistry, as they are common linkages in carbohydrates and lignin.

The haloalkanes are a group of chemical compounds derived from alkanes containing one or more halogens. They are a subset of the general class of halocarbons, although the distinction is not often made. Haloalkanes are widely used commercially and, consequently, are known under many chemical and commercial names. They are used as flame retardants, fire extinguishants, refrigerants, propellants, solvents, and pharmaceuticals. Subsequent to the widespread use in commerce, many halocarbons have also been shown to be serious pollutants and toxins. For example, the chlorofluorocarbons have been shown to lead to ozone depletion. Methyl bromide is a controversial fumigant. Only haloalkanes which contain chlorine, bromine, and iodine are a threat to the ozone layer, but fluorinated volatile haloalkanes in theory may have activity as greenhouse gases. Methyl iodide, a naturally occurring substance, however, does not have ozone-depleting properties and the United States Environmental Protection Agency has designated the compound a non-ozone layer depleter. For more information, see Halomethane. Haloalkane or alkyl halides are the compounds which have the general formula "RX" where R is an alkyl or substituted alkyl group and X is a halogen.

An acyl group is a moiety derived by the removal of one or more hydroxyl groups from an oxoacid, including inorganic acids. It contains a double-bonded oxygen atom and an alkyl group (R-C=O). In organic chemistry, the acyl group is usually derived from a carboxylic acid. Therefore, it has the formula RCO–, where R represents an alkyl group that is linked to the carbon atom of the group by a single bond. Although the term is almost always applied to organic compounds, acyl groups can in principle be derived from other types of acids such as sulfonic acids, phosphonic acids. In the most common arrangement, acyl groups are attached to a larger molecular fragment, in which case the carbon and oxygen atoms are linked by a double bond.

Sodium hypochlorite is a chemical compound with the formula NaOCl or NaClO, comprising a sodium cation and a hypochlorite anion. It may also be viewed as the sodium salt of hypochlorous acid. The anhydrous compound is unstable and may decompose explosively. It can be crystallized as a pentahydrate NaOCl·5H
2O, a pale greenish-yellow solid which is not explosive and is stable if kept refrigerated.
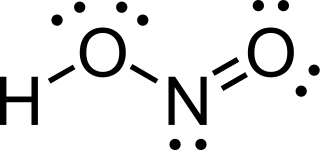
Nitrous acid is a weak and monoprotic acid known only in solution, in the gas phase and in the form of nitrite salts. Nitrous acid is used to make diazonium salts from amines. The resulting diazonium salts are reagents in azo coupling reactions to give azo dyes.

Hypochlorous acid (HOCl or HClO) is a weak acid that forms when chlorine dissolves in water, and itself partially dissociates, forming hypochlorite, ClO−. HClO and ClO− are oxidizers, and the primary disinfection agents of chlorine solutions. HClO cannot be isolated from these solutions due to rapid equilibration with its precursor. Sodium hypochlorite (NaClO) and calcium hypochlorite (Ca(ClO)2), are bleaches, deodorants, and disinfectants.

In chemistry, hypochlorite is an anion with the chemical formula ClO−. It combines with a number of cations to form hypochlorite salts. Common examples include sodium hypochlorite and calcium hypochlorite. The Cl-O distance in ClO− is 210 pm.
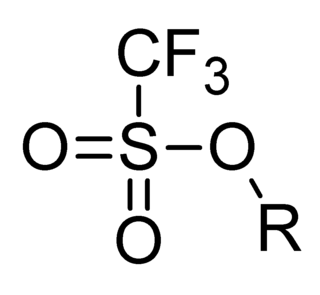
Triflate, also known by the systematic name trifluoromethanesulfonate, is a functional group with the formula CF3SO3−. The triflate group is often represented by −OTf, as opposed to −Tf (triflyl). For example, n-butyl triflate can be written as CH3CH2CH2CH2OTf.
An organochloride, organochlorine compound, chlorocarbon, or chlorinated hydrocarbon is an organic compound containing at least one covalently bonded atom of chlorine. The chloroalkane class provides common examples. The wide structural variety and divergent chemical properties of organochlorides lead to a broad range of names, applications, and properties. Organochlorine compounds have wide use in many applications, though some are of profound environmental concern, with TCDD being one of the most notorious.

Sodium chlorate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula NaClO3. It is a white crystalline powder that is readily soluble in water. It is hygroscopic. It decomposes above 300 °C to release oxygen and leaves sodium chloride. Several hundred million tons are produced annually, mainly for applications in bleaching pulp to produce high brightness paper.
The phosphonium cation describes polyatomic cations with the chemical formula PR+
4. These anions have tetrahedral structures. The salts are generally colorless or take the color of the anions.

Trimethylaluminium is one of the simplest examples of an organoaluminium compound. Despite its name it has the formula Al2(CH3)6 (abbreviated as Al2Me6 or TMA), as it exists as a dimer. This colorless liquid is pyrophoric. It is an industrially important compound, closely related to triethylaluminium.
The Sandmeyer reaction is a chemical reaction used to synthesize aryl halides from aryl diazonium salts using copper salts as reagents or catalysts. It is an example of a radical-nucleophilic aromatic substitution. The Sandmeyer reaction provides a method through which one can perform unique transformations on benzene, such as halogenation, cyanation, trifluoromethylation, and hydroxylation.

Dichlorine monoxide is an inorganic compound with the molecular formula Cl2O. It was first synthesised in 1834 by Antoine Jérôme Balard, who along with Gay-Lussac also determined its composition. In older literature it is often referred to as chlorine monoxide, which can be a source of confusion as that name now refers to the neutral species ClO.

tert-Butyl alcohol is the simplest tertiary alcohol, with a formula of (CH3)3COH (sometimes represented as t-BuOH). It is one of the four isomers of butanol. tert-Butyl alcohol is a colorless solid, which melts near room temperature and has a camphor-like odor. It is miscible with water, ethanol and diethyl ether.

A sulfoxide is a chemical compound containing a sulfinyl (SO) functional group attached to two carbon atoms. It is a polar functional group. Sulfoxides are the oxidized derivatives of sulfides. Examples of important sulfoxides are alliin, a precursor to the compound that gives freshly crushed garlic its aroma, and dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), a common solvent.

Disodium tetracarbonylferrate is the organoiron compound with the formula Na2[Fe(CO)4]. It is always used as a solvate, e.g., with tetrahydrofuran or dimethoxyethane,. which bind to the sodium cation. An oxygen-sensitive colourless solid, it is a reagent in organometallic and organic chemical research. The dioxane solvated sodium salt is known as Collman's reagent, in recognition of James P. Collman, an early popularizer of its use.

(2,2,6,6-Tetramethylpiperidin-1-yl)oxyl or (2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidin-1-yl)oxidanyl, commonly known as TEMPO, is a chemical compound with the formula (CH2)3(CMe2)2NO. This heterocyclic compound is a red-orange, sublimable solid. As a stable aminoxyl radical, it has applications in chemistry and biochemistry. TEMPO is used as a radical marker, as a structural probe for biological systems in conjunction with electron spin resonance spectroscopy, as a reagent in organic synthesis, and as a mediator in controlled radical polymerization.
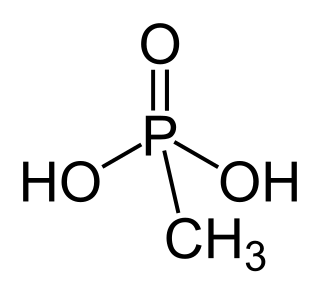
Methylphosphonic acid is an organophosphorus compound with the chemical formula. CH3P(O)(OH)2. The phosphorus center is tetrahedral and is bonded to a methyl group, two OH groups and an oxygen. Methylphosphonic acid is a white, non-volatile solid that is poorly soluble in organic solvent but soluble in water and common alcohols.




















