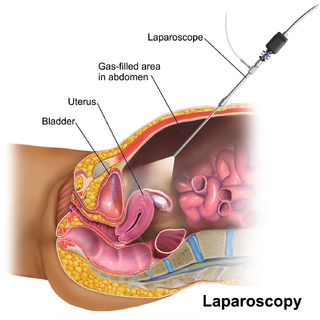
Laparoscopy is an operation performed in the abdomen or pelvis using small incisions with the aid of a camera. The laparoscope aids diagnosis or therapeutic interventions with a few small cuts in the abdomen.

A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, an interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiologist. The process involves the extraction of sample cells or tissues for examination to determine the presence or extent of a disease. The tissue is then fixed, dehydrated, embedded, sectioned, stained and mounted before it is generally examined under a microscope by a pathologist; it may also be analyzed chemically. When an entire lump or suspicious area is removed, the procedure is called an excisional biopsy. An incisional biopsy or core biopsy samples a portion of the abnormal tissue without attempting to remove the entire lesion or tumor. When a sample of tissue or fluid is removed with a needle in such a way that cells are removed without preserving the histological architecture of the tissue cells, the procedure is called a needle aspiration biopsy. Biopsies are most commonly performed for insight into possible cancerous or inflammatory conditions.

Cholecystectomy is the surgical removal of the gallbladder. Cholecystectomy is a common treatment of symptomatic gallstones and other gallbladder conditions. In 2011, cholecystectomy was the eighth most common operating room procedure performed in hospitals in the United States. Cholecystectomy can be performed either laparoscopically, or via an open surgical technique.
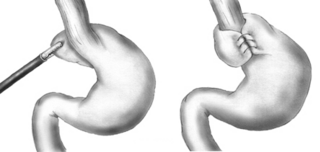
A Nissen fundoplication, or laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication when performed via laparoscopic surgery, is a surgical procedure to treat gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and hiatal hernia. In GERD, it is usually performed when medical therapy has failed; but, with a Type II (paraesophageal) hiatus hernia, it is the first-line procedure. The Nissen fundoplication is total (360°), but partial fundoplications known as Thal, Belsey, Dor, Lind, and Toupet fundoplications are alternative procedures with somewhat different indications and outcomes.
An abdomino perineal resection, formally known as abdominoperineal resection of the rectum and abdominoperineal excision of the rectum is a surgery for rectal cancer or anal cancer. It is frequently abbreviated as AP resection, APR and APER.

Fine-needle aspiration (FNA) is a diagnostic procedure used to investigate lumps or masses. In this technique, a thin, hollow needle is inserted into the mass for sampling of cells that, after being stained, are examined under a microscope (biopsy). The sampling and biopsy considered together are called fine-needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB) or fine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC). Fine-needle aspiration biopsies are very safe minor surgical procedures. Often, a major surgical biopsy can be avoided by performing a needle aspiration biopsy instead, eliminating the need for hospitalization. In 1981, the first fine-needle aspiration biopsy in the United States was done at Maimonides Medical Center. Today, this procedure is widely used in the diagnosis of cancer and inflammatory conditions. Fine needle aspiration is generally considered a safe procedure. Complications are infrequent.

Hospital for Special Surgery (HSS) is an academic medical center and research institution headquartered in New York City that specializes in the treatment of orthopedic and rheumatologic conditions. Its main campus is located at 535 East 70th Street in Manhattan and there are locations in New York, New Jersey, Connecticut, and Florida. The hospital was founded in 1863 by James Knight. HSS is the oldest orthopedic hospital in the United States and is consistently ranked as the world's top orthopedic hospital. Bryan T Kelly served as the former surgeon-in-chief and currently serves as president and chief executive officer. Douglas E. Padgett serves as the current surgeon-in-chief.

Robot-assisted surgery or robotic surgery are any types of surgical procedures that are performed using robotic systems. Robotically assisted surgery was developed to try to overcome the limitations of pre-existing minimally-invasive surgical procedures and to enhance the capabilities of surgeons performing open surgery.
ICD-9-CM Volume 3 is a system of procedural codes used by health insurers to classify medical procedures for billing purposes. It is a subset of the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems (ICD) 9-CM. Volumes 1 and 2 are used for diagnostic codes.

Pelvic exenteration is a radical surgical treatment that removes all organs from a person's pelvic cavity. It is used to treat certain advanced or recurrent cancers. The urinary bladder, urethra, rectum, and anus are removed. In women, the vagina, cervix, uterus, Fallopian tubes, ovaries and, in some cases, the vulva are removed. In men, the prostate is removed. The procedure leaves the person with a permanent colostomy and urinary diversion.
Hepatectomy is the surgical resection of the liver. While the term is often employed for the removal of the liver from a liver transplant donor, this article will focus on partial resections of hepatic tissue and hepatoportoenterostomy.

A bowel resection or enterectomy is a surgical procedure in which a part of an intestine (bowel) is removed, from either the small intestine or large intestine. Often the word enterectomy is reserved for the sense of small bowel resection, in distinction from colectomy, which covers the sense of large bowel resection. Bowel resection may be performed to treat gastrointestinal cancer, bowel ischemia, necrosis, or obstruction due to scar tissue, volvulus, and hernias. Some patients require ileostomy or colostomy after this procedure as alternative means of excretion. Complications of the procedure may include anastomotic leak or dehiscence, hernias, or adhesions causing partial or complete bowel obstruction. Depending on which part and how much of the intestines are removed, there may be digestive and metabolic challenges afterward, such as short bowel syndrome.

B & B Hospital is a private hospital with the goal to provide health services to the community of Nepal founded in 1997.
St. Cloud Hospital is a hospital in St. Cloud, Minnesota, United States. It is a Catholic-affiliated, not-for-profit institution and part of CentraCare Health. The hospital has more than 9,000 employees, 400 physicians and 1,200 volunteers. It serves 690,000 people in a 12-county area.

Saint Thomas Rutherford Hospital, formerly Middle Tennessee Medical Center, is a 286-bed private, not-for-profit hospital located in Murfreesboro, Tennessee, United States. Saint Thomas Rutherford Hospital is a member of Saint Thomas Health.

Ascension Saint Thomas Hospital Midtown, formerly known as Baptist Hospital, is a non-profit community hospital in Nashville, Tennessee, United States and the largest such hospital in Middle Tennessee. It is licensed for 683 acute and rehab care beds.

McLaren Flint is a nonprofit, 378 bed tertiary teaching hospital located in Flint, Michigan. McLaren is affiliated with the Michigan State University College of Human Medicine's medical residency programs, including family medicine, internal medicine, general surgery, orthopedic surgery and radiology. McLaren also maintains a hematology/oncology fellowship program in partnership with Michigan State University and is sponsoring a surgical oncology fellowship program. McLaren Flint is a subsidiary of McLaren Health Care Corporation.

Boora Narsaiah Goud is an Indian politician in the state of Telangana. Joining in the Bharat Rashtra Samithi political party in 2009 he has won as a Member of Parliament in the 16th Lok Sabha representing Bhongir constituency in 2014 election and lost in 2019.

A breast biopsy is usually done after a suspicious lesion is discovered on either mammography or ultrasound to get tissue for pathological diagnosis. Several methods for a breast biopsy now exist. The most appropriate method of biopsy for a patient depends upon a variety of factors, including the size, location, appearance and characteristics of the abnormality. The different types of breast biopsies include fine-needle aspiration (FNA), vacuum-assisted biopsy, core needle biopsy, and surgical excision biopsy. Breast biopsies can be done utilizing ultrasound, MRI or a stereotactic biopsy imaging guidance. Vacuum assisted biopsies are typically done using stereotactic techniques when the suspicious lesion can only be seen on mammography. On average, 5–10 biopsies of a suspicious breast lesion will lead to the diagnosis of one case of breast cancer. Needle biopsies have largely replaced open surgical biopsies in the initial assessment of imaging as well as palpable abnormalities in the breast.

Dr. Eugene Bishop or E.B. Mumford (1879-1961) was an American orthopedic surgeon, founder, and president of the American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons. Mumford was known for his pioneering research of arthritis, joint stiffness, and creation of distal clavical excision or acromioplasty commonly known as The Mumford Procedure.
















