
Traffic calming uses physical design and other measures to improve safety for motorists, car drivers, pedestrians and cyclists. It has become a tool to combat speeding and other unsafe behaviours of drivers in the neighbourhoods. It aims to encourage safer, more responsible driving and potentially reduce traffic flow. Urban planners and traffic engineers have many strategies for traffic calming, including narrowed roads and speed humps. Such measures are common in Australia and Europe, but less so in North America. Traffic calming is a calque of the German word Verkehrsberuhigung – the term's first published use in English was in 1985 by Carmen Hass-Klau.

Bicycle-friendly policies and practices help some people feel more comfortable about traveling by bicycle with other traffic. The level of bicycle-friendliness of an environment can be influenced by many factors including town planning and cycling infrastructure decisions. A stigma towards people who ride bicycles and fear of cycling is a social construct that needs to be fully understood when promoting a bicycle friendly culture.

Road traffic safety refers to the methods and measures used to prevent road users from being killed or seriously injured. Typical road users include pedestrians, cyclists, motorists, vehicle passengers, and passengers of on-road public transport.

Utility cycling encompasses any cycling done simply as a means of transport rather than as a sport or leisure activity. It is the original and most common type of cycling in the world. Cycling mobility is one of the various types of private transport and a major part of individual mobility.

The car-free movement is a broad, informal, emergent network of individuals and organizations, including social activists, urban planners, transportation engineers, environmentalists and others, brought together by a shared belief that large and/or high-speed motorized vehicles are too dominant in most modern cities. The goal of the movement is to create places where motorized vehicle use is greatly reduced or eliminated, by converting road and parking space to other public uses and rebuilding compact urban environments where most destinations are within easy reach by other means, including walking, cycling, public transport, personal transporters, and mobility as a service.

A living street is a street designed with the interests of pedestrians and cyclists in mind by providing enriching and experiential spaces. Living streets also act as social spaces, allowing children to play and encouraging social interactions on a human scale, safely and legally. Living streets consider all pedestrians granting equal access to elders and those who are disabled. These roads are still available for use by motor vehicles; however, their design aims to reduce both the speed and dominance of motorized transport. The reduction of motor vehicle dominance creates more opportunities for public transportation.

Bicycle safety is the use of road traffic safety practices to reduce risk associated with cycling. Risk can be defined as the number of incidents occurring for a given amount of cycling. Some of this subject matter is hotly debated: for example, which types of cycling environment or cycling infrastructure is safest for cyclists. The merits of obeying the traffic laws and using bicycle lighting at night are less controversial. Wearing a bicycle helmet may reduce the chance of head injury in the event of a crash.

A cycle track or cycleway (British) or bikeway, sometimes historically referred to as a sidepath, is a separate route for cycles and not motor vehicles. In some cases cycle tracks are also used by other users such as pedestrians and horse riders. A cycle track can be next to a normal road, and can either be a shared route with pedestrians or be made distinct from both the pavement and general roadway by vertical barriers or elevation differences.

Rat running is the practice by motorists of using residential side streets or any unintended short cut such as a parking lot, delivery service lane or cemetery road instead of the intended main road in urban or suburban areas.

Lane splitting is riding a bicycle or motorcycle between lanes or rows of slow moving or stopped traffic moving in the same direction. It is sometimes called whitelining, or stripe-riding. This allows riders to save time, bypassing traffic congestion, and may also be safer than stopping behind stationary vehicles.
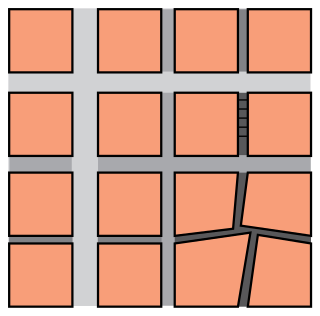
In urban design, permeability and connectivity are terms that describe the extent to which urban forms permit movement of people or vehicles in different directions. The terms are often used interchangeably, although differentiated definitions also exist. Permeability is generally considered a positive attribute of an urban design, as it permits ease of movement and avoids severing neighbourhoods. Urban forms which lack permeability, e.g. those severed by arterial roads, or with many long culs-de-sac, are considered to discourage movement on foot and encourage longer journeys by car. There is some empirical research evidence to support this view.

Active mobility, soft mobility, active travel, active transport or active transportation is the transport of people or goods, through non-motorized means, based around human physical activity. The best-known forms of active mobility are walking and cycling, though other modes include running, rowing, skateboarding, kick scooters and roller skates. Due to its prevalence, cycling is sometimes considered separately from the other forms of active mobility.

Cycling infrastructure is all infrastructure cyclists are allowed to use. Bikeways include bike paths, bike lanes, cycle tracks, rail trails and, where permitted, sidewalks. Roads used by motorists are also cycling infrastructure, except where cyclists are barred such as many freeways/motorways. It includes amenities such as bike racks for parking, shelters, service centers and specialized traffic signs and signals. The more cycling infrastructure, the more people get about by bicycle.

Cycling for transport and leisure enjoys popularity in Greater Manchester and the city also plays a major role in British cycle racing. The Bee Network was launched in 2018. The University of Manchester is home to the Manchester Cycling Lab.

Cycling in the United Kingdom has a long history, since the earliest days of the bicycle, and after a decline in the mid-20th century has been undergoing a resurgence in recent decades.
Rachel Aldred is British academic specialising in active mobility. She is a Professor in Transport at the University of Westminster and has published over 25 peer reviewed papers. She was awarded the Economic and Social Research Council's award for Outstanding Impact in Public Policy (2016) for her work on The Near Miss Project, the first UK study calculating a per-mile collision risk for cycling, and is one of the co-investigators of the Propensity to Cycle Tool, an online system for transport planners using census data to model the potential benefits of cycling infrastructure schemes in England, funded by the Department for Transport. Aldred presented to the Transport Select Committee in 2018 as an expert witness during the enquiry into active travel

The Mini-Hollands scheme was introduced in March 2014 by Boris Johnson, then Mayor of London. It took the form of a competition among outer London boroughs for a £100-million fund. Three boroughs – Waltham Forest, Enfield and Kingston – won £30 million each, and the remaining £10 million was shared by several other boroughs.

School Streets is an scheme in the United Kingdom, Germany, Czechia Austria and other countries, to suspend motor traffic access to roads outside schools, during drop-off and pick-up times.

In the United Kingdom, a Low Traffic Neighbourhood (LTN) is an area in which filtered permeability and traffic calming are deployed to reduce motorised through-traffic in residential areas. Many LTNs were introduced in spring 2020, although the same principles had been in use in London since the 1970s.




















