Related Research Articles

Babur was the founder of the Mughal Empire in the Indian subcontinent. He was a descendant of Timur and Genghis Khan through his father and mother respectively. He was also given the posthumous name of Firdaws Makani.

Herāt is an oasis city and the third-largest city in Afghanistan. In 2020, it had an estimated population of 574,276, and serves as the capital of Herat Province, situated south of the Paropamisus Mountains in the fertile valley of the Hari River in the western part of the country. An ancient civilization on the Silk Road between West, Central and South Asia, it serves as a regional hub in the country's west.

The Hazaras are an ethnic group and a principal component of the population of Afghanistan. They are one of the largest ethnic groups in Afghanistan and primarily residing in the Hazaristan (Hazarajat) region in central Afghanistan. Hazaras are also as significant minority groups in Pakistan mainly in Quetta and Iran mainly in Mashhad. They speak the Dari and Hazaragi dialects of Persian. Dari, also known as Dari Persian, is one of two official languages of Afghanistan.

Kandahar is a city in Afghanistan, located in the south of the country on the Arghandab River, at an elevation of 1,010 m (3,310 ft). It is Afghanistan's second largest city after Kabul, with a population of about 614,118. It is the capital of Kandahar Province and the centre of the larger cultural region called Loy Kandahar.

Dari, also known as Dari Persian, is the variety of the Persian language spoken in Afghanistan. Dari is the Afghan government's official term for the Persian language; it is known as Afghan Persian or Eastern Persian in many Western sources. The decision to rename the local variety of Persian in 1964 was more political than linguistic to support an Afghan state narrative. Apart from a few basics of vocabulary, there is little difference between formal written Persian of Afghanistan and Iran; the languages are mutually intelligible. Dari is the official language for 35 million Afghans in Afghanistan and it serves as the lingua franca for interethnic communications in Afghanistan.
Mughal or Moghul may refer to:
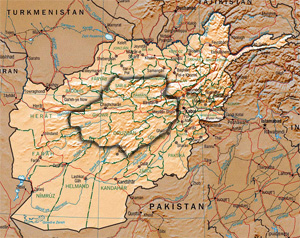
Hazarajat, also known as Hazaristan is a mostly mountainous region in the central highlands of Afghanistan, among the Kuh-e Baba mountains in the western extremities of the Hindu Kush. It is the homeland of the Hazara people who make up the majority of its population. Hazarajat denotes an ethnic and religious zone.
Moghol is a critically endangered or possibly extinct Mongolic language spoken in the province of Herat, Afghanistan, in the villages of Kundur and Karez-i-Mulla. The speakers were the Moghol people, who numbered 2,000 members in the 1970s. They descend from the remnants of Genghis Khan's Mongol army stationed in Afghanistan in the 13th century.

The Timurid Empire was a late medieval, culturally Persianate Turco-Mongol empire that dominated Greater Iran in the early 15th century, comprising modern-day Iran, Iraq, Afghanistan, much of Central Asia, the South Caucasus, as well as parts of contemporary Pakistan, North India and Turkey. The empire was culturally hybrid, combining Turko-Mongolian and Persianate influences, with the last members of the dynasty being "regarded as ideal Perso-Islamic rulers".
Mogol or Moghol may refer to:
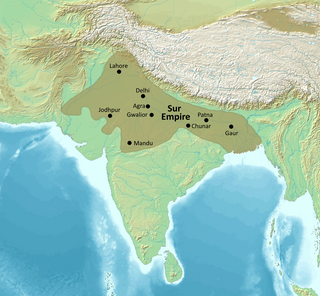
The Sur Empire was an empire ruled by the Afghan-origin Sur dynasty in northern India for nearly 16 or 18 years, between 1538/1540 and 1556, with Sasaram serving as its capital. It was founded by Sher Shah Suri.
The Ghurid dynasty was a Persianate dynasty of presumably eastern Iranian Tajik origin, which ruled from the 8th-century in the region of Ghor, and became an Empire from 1175 to 1215. The Ghurids were centered in the hills of the Ghor region in the present-day central Afghanistan, where they initially started out as local chiefs. They gradually converted to Sunni Islam after the conquest of Ghor by the Ghaznavid ruler Mahmud of Ghazni in 1011. The Ghurids eventually overran the Ghaznavids when Muhammad of Ghor seized Lahore and expelled the Ghaznavids from their last stronghold.

Fārsīwān is a contemporary designation for Persian speakers in Afghanistan and its diaspora elsewhere. More specifically, it was originally used to refer to a distinct group of farmers in Afghanistan and urban dwellers. In Afghanistan, original Farsiwans are found predominantly in Herat and Farah provinces. They are roughly the same as the Persians of eastern Iran. The term excludes the Hazāra and Aymāq tribes, who also speak dialects of Persian.
Persianization or Persification, is a sociological process of cultural change in which a non-Persian society becomes "Persianate", meaning it either directly adopts or becomes strongly influenced by the Persian language, culture, literature, art, music, and identity as well as other socio-cultural factors. It is a specific form of cultural assimilation that often includes a language shift. The term applies not only to cultures, but also to individuals, as they acclimate to Persian culture and become "Persianized" or "Persified".

Afghanistan is a multiethnic and mostly tribal society. The population of the country consists of numerous ethnolinguistic groups: mainly the Pashtun, Tajik, Hazara, and Uzbek, as well as the minorities of Aimaq, Turkmen, Baloch, Pashai, Nuristani, Gujjar, Brahui, Qizilbash, Pamiri, Kyrgyz, Sadat, Mongol and others. Altogether they make up the Afghan people.

The name Afghānistān means "land of the Afghans", the name "Afghan" originally referred to a member of the Pashtuns. which originates from the ethnonym Afghan. Historically, Pashtuns were referred to as Afghans, the largest ethnic group of Afghanistan. The earliest reference to the name is found in the 10th-century geography book known as Hudud al-'Alam. The last part of the name, -stān is a Persian suffix for "place".
The Qara'unas or Negüderi were the Mongols who settled in Afghanistan after moving from Turkestan and Mongolia.

The Great Mosque of Herat or "Jami Masjid of Herat", is a mosque in the city of Herat, in the Herat Province of north-western Afghanistan. It was built by the Ghurids, under the rule of Sultan Ghiyath al-Din Muhammad Ghori, who laid its foundation in 1200 CE. Later, it was extended several times as Herat changed rulers down the centuries from the Kartids, Timurids, Mughals and then the Uzbeks, all of whom supported the mosque. The fundamental structure of the mosque from the Ghurid period has been preserved, but parts have been added and modified. The Friday mosque in Herat was given its present appearance during the 20th century.
Moghuls may refer to:
Kundur is a village in Herat Province, Afghanistan. It is one of the two Mogholi speaking villages left alongside Karez-i-Mulla.
References
- 1 2 Mogholi at Ethnologue (25th ed., 2022)

- ↑ Dupree, Louis (1997). Afghanistan (2nd ed.). Oxford Pakistan Paperbacks. p. 74. ISBN 978-0-19-577634-8.
- ↑ Sanders, Alan J. K. (2017). Historical Dictionary of Mongolia. Rowman & Littlefield. p. 530. ISBN 978-1-5381-0227-5.
- ↑ Emadi, Hafizullah (2005). Culture and Customs of Afghanistan. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 11. ISBN 978-0-313-33089-6.