Propyl acetate, also known as propyl ethanoate, is a chemical compound used as a solvent and an example of an ester. This clear, colorless liquid is known by its characteristic odor of pears. Due to this fact, it is commonly used in fragrances and as a flavor additive. It is formed by the esterification of acetic acid and 1-propanol, often via Fischer–Speier esterification, with sulfuric acid as a catalyst and water produced as a byproduct.
Dioctyl adipate (DOA) is an organic compound with the formula (CH2CH2CO2C8H17)2. It is a colorless oily liquid. As well as related diesters derived from 2-ethylhexanol, decanol, isodecanol, etc, it is used as a plasticizer.
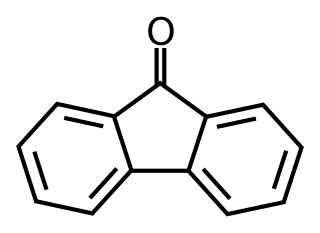
Fluorenone is an aromatic organic compound with the chemical formula C13H8O. It is used to make antimalaria drugs. It can be synthesised from fluorene with the addition of glacial acetic acid and sodium hypochlorite solution, undergoing an oxidation reaction. It is bright fluorescent yellow in color and is a solid at room temperature.

Glycidol is an organic compound that contains both epoxide and alcohol functional groups. Being bifunctional, it has a variety of industrial uses. The compound is a slightly viscous liquid that is slightly unstable and is not often encountered in pure form.

Ethyl phenyl ether or phenetole is an organic compound that is an ether. Ethyl phenyl ether has the same properties as some other ethers, such as volatility, explosive vapors, and the ability to form peroxides. Will dissolve in many non-polar compounds e.g. ethanol or ether but not in polar substances like water.
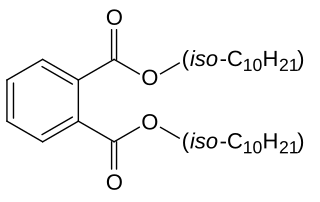
Diisodecyl phthalate (DIDP) is a commonly used plasticizer used in the production of plastic and plastic coating to increase flexibility. It is a mixture of compounds derived from the esterification of phthalic acid and isomeric decyl alcohols.
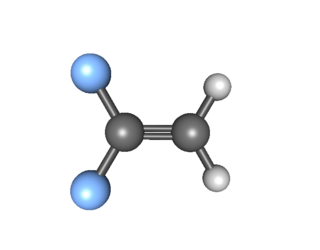
1,1-Difluoroethylene, also known as vinylidene fluoride, is a hydrofluoroolefin. It is a flammable gas. Global production in 1999 was approximately 33,000 metric tons. It is primarily used in the production of fluoropolymers such as polyvinylidene fluoride.

Diepoxybutane is a chemical compound with two epoxide functional groups. It is used as a chemical intermediate, as a curing agent for polymers, as a cross-linking agent for textiles, and as a preservative.

Dinoterb is a chemical compound used as an herbicide.
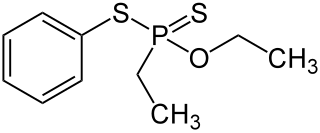
Fonofos is an organothiophosphate insecticide primarily used on corn. It is highly toxic and listed as an extremely hazardous substance.

Tributylamine (TBA) is an organic compound with the molecular formula C12H27N. It is a colorless to yellow, hygroscopic liquid with an amine-like odor which is very poorly soluble in water.

Diisopropanolamine is a chemical compound with the molecular formula used as an emulsifier, stabilizer, and chemical intermediate.

Bromopropylate is a chemical compound used as an acaricide against spider mites in apiaries and on fruit crops such as citrus and grapes.
Dinitrobenzenes are chemical compounds composed of a benzene ring and two nitro group (-NO2) substituents. The three possible arrangements of the nitro groups afford three isomers, 1,2-dinitrobenzene, 1,3-dinitrobenzene, and 1,4-dinitrobenzene. Each isomer has the chemical formula C6H4N2O4 and a molar mass of about 168.11 g/mol. 1,3-Dinitrobenzene is the most common isomer and it is used in the manufacture of explosives.

Dinitroanilines are a class of chemical compounds with the chemical formula C6H5N3O4. They are derived from both aniline and dinitrobenzenes. There are six isomers: 2,3-dinitroaniline, 2,4-dinitroaniline, 2,5-dinitroaniline, 2,6-dinitroaniline, 3,4-dinitroaniline, and 3,5-dinitroaniline.
1-Tridecanol is a chemical compound from the group of alcohols. It is in the form of a colorless, flammable solid. 1-Tridecanol usually occurs as a mixture of different isomeric to compounds such as 2-tridecanol, 3-tridecanol, 4-tridecanol, 5-tridecanol, 6-tridecanol and isotridecanol.
Pentyl nitrite is a chemical compound with the molecular formula, classified as an alkyl nitrite, used as an antihypertensive medicine. It is also used to treat cyanide poisoning.
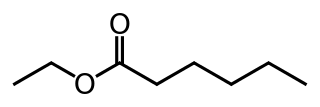
Ethyl hexanoate is the ester resulting from the condensation of hexanoic acid and ethanol. It has a pleasant pineapple smell.
GESTIS Substance Database is a freely accessible online information system on chemical compounds. It is maintained by the Institut für Arbeitsschutz der Deutschen Gesetzlichen Unfallversicherung. Information on occupational medicine and first aid is compiled by Henning Heberer and his team.
The diisopropylbenzenes constitute a group of aromatic hydrocarbons, whose chemical structure consists of a benzene ring with two isopropyl groups (−CH(CH3)2) as a substituents. Through their different arrangement, they form three structural isomers with the molecular formula C12H18.