Related Research Articles

Plywood is a composite material manufactured from thin layers, or "plies", of wood veneer that are glued together with adjacent layers, having both glued with each other at right angle or at 90 degrees angle. It is an engineered wood from the family of manufactured boards, which include plywood, medium-density fibreboard (MDF), oriented strand board (OSB), and particle board.

A vacuum flask is an insulating storage vessel that slows the speed at which its contents change in temperature. It greatly lengthens the time over which its contents remain hotter or cooler than the flask's surroundings by trying to be as adiabatic as possible. Invented by Sir James Dewar in 1892, the vacuum flask consists of two flasks, placed one within the other and joined at the neck. The gap between the two flasks is partially evacuated of air, creating a near-vacuum which significantly reduces heat transfer by conduction or convection. When used to hold cold liquids, this also virtually eliminates condensation on the outside of the flask.

An industrial design right is an intellectual property right that protects the visual design of objects that are purely utilitarian. An industrial design consists of the creation of a shape, configuration or composition of pattern or color, or combination of pattern and color in three-dimensional form containing aesthetic value. An industrial design can be a two- or three-dimensional pattern used to produce a product, industrial commodity or handicraft.

Plaster is a building material used for the protective or decorative coating of walls and ceilings and for moulding and casting decorative elements. In English, "plaster" usually means a material used for the interiors of buildings, while "render" commonly refers to external applications. The term stucco refers to plasterwork that is worked in some way to produce relief decoration, rather than flat surfaces.

A rivet is a permanent mechanical fastener. Before being installed, a rivet consists of a smooth cylindrical shaft with a head on one end. The end opposite the head is called the tail. On installation, the deformed end is called the shop head or buck-tail.

Linoleum is a floor covering made from materials such as solidified linseed oil (linoxyn), pine resin, ground cork dust, sawdust, and mineral fillers such as calcium carbonate, most commonly on a burlap or canvas backing. Pigments are often added to the materials to create the desired colour finish. Commercially, the material has been largely replaced by sheet vinyl flooring, although in the UK and Australia this is often still referred to as "lino".

A radiant barrier is a type of building material that reflects thermal radiation and reduces heat transfer. Because thermal energy is also transferred by conduction and convection, in addition to radiation, radiant barriers are often supplemented with thermal insulation that slows down heat transfer by conduction or convection.
Kapton is a polyimide film used in flexible printed circuits and space blankets, which are used on spacecraft, satellites, and various space instruments. Invented by the DuPont Corporation in the 1960s, Kapton remains stable across a wide range of temperatures, from 4 to 673 K. Kapton is used in electronics manufacturing, space applications, with x-ray equipment, and in 3D printing applications. Its favorable thermal properties and outgassing characteristics result in its regular use in cryogenic applications and in situations where high vacuum environments are experienced.
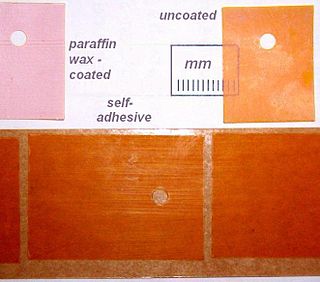
Ultracote is a commercially available light-weight plastic shrink-wrap film available in various color schemes with an adhesive on one side, used to cover and form the surfaces of a model aircraft. The material is cut to size and applied to the aircraft surfaces using a hobby iron or heat gun. This product is also sometimes referred to as Oracover in Europe.

Shrink wrap, also shrink film, is a material made up of polymer plastic film. When heat is applied, it shrinks tightly over whatever it is covering. Heat can be applied with a handheld heat gun, or the product and film can pass through a heat tunnel on a conveyor.

Industrial property is one of two subsets of intellectual property, it takes a range of forms, including patents for inventions, industrial designs, trademarks, service marks, layout-designs of integrated circuits, commercial names and designations, geographical indications and protection against unfair competition. In some cases, aspects of intellectual creation, although present, are less clearly defined. The object of industrial property consists of signs conveying information, in particular to consumers, regarding products and services offered on the market. Protection is directed against unauthorized use of such signs that could mislead consumers, and against misleading practices in general.

A radio-controlled aircraft is a small flying machine that is radio controlled by an operator on the ground using a hand-held radio transmitter. The transmitter continuously communicates with a receiver within the craft that sends signals to servomechanisms (servos) which move the control surfaces based on the position of joysticks on the transmitter. The control surfaces, in turn, directly affect the orientation of the plane.

A flat roof is a roof which is almost level in contrast to the many types of sloped roofs. The slope of a roof is properly known as its pitch and flat roofs have up to approximately 10°. Flat roofs are an ancient form mostly used in arid climates and allow the roof space to be used as a living space or a living roof. Flat roofs, or "low-slope" roofs, are also commonly found on commercial buildings throughout the world. The U.S.-based National Roofing Contractors Association defines a low-slope roof as having a slope of 3 in 12 (1:4) or less.

Fireproofing is rendering something resistant to fire, or incombustible; or material for use in making anything fire-proof. It is a passive fire protection measure. "Fireproof" or "fireproofing" can be used as a noun, verb or adjective; it may be hyphenated ("fire-proof").

Alclad is a corrosion-resistant aluminium sheet formed from high-purity aluminium surface layers metallurgically bonded to high-strength aluminium alloy core material. It has a melting point of about 500 °C (932 °F). Alclad is a trademark of Alcoa but the term is also used generically.

A trademark is a type of intellectual property consisting of a recognizable sign, design, or expression that identifies a product or service from a particular source and distinguishes it from others. A trademark owner can be an individual, business organization, or any legal entity. A trademark may be located on a package, a label, a voucher, or on the product itself. Trademarks used to identify services are sometimes called service marks.
Hobbico, Inc. was a manufacturer and distributor of hobby products including radio control airplanes, boats, cars, helicopters and multirotors/drones. Other products include plastic model kits, model rockets, model trains, slot cars, crafts, jigsaw puzzles and games. The company had approximately 850 employees worldwide. On January 10, 2018, Hobbico filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy protection and announced the company is for sale. On April 13, Horizon Hobby acquired control of most Hobbico RC brands & IP. Estes Industries acquired the Estes-Cox business unit and a German venture capital group acquired Revell Germany whole and the Revell-Monogram brands, IP & molds.

Aircraft fabric covering is a term used for both the material used and the process of covering aircraft open structures. It is also used for reinforcing closed plywood structures. The de Havilland Mosquito is an example of this technique, as are the pioneering all-wood monocoque fuselages of certain World War I German aircraft like the LFG Roland C.II in its wrapped Wickelrumpf plywood strip and fabric covering.
A Horton sphere, also referred to as a spherical tank or simply sphere, is a spherical pressure vessel, which is used for industrial-scale storage of liquefied gases. Example of materials that can be stored in Horton spheres are liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), liquefied natural gas (LNG), and anhydrous ammonia.

Vantablack is a class of super-black coatings with total hemispherical reflectances (THR) below 1% in the visible spectrum. The name is a portmanteau of the acronym VANTA and black.
References
- ↑ Patent
- ↑ "Fireproofing - FAQs". Grace Construction Products. Retrieved 2007-07-01.