
Arsenic is a chemical element with the symbol As and atomic number 33. Arsenic occurs in many minerals, usually in combination with sulfur and metals, but also as a pure elemental crystal. Arsenic is a metalloid. It has various allotropes, but only the gray form, which has a metallic appearance, is important to industry.
Lead hydrogen arsenate, also called lead arsenate, acid lead arsenate or LA, chemical formula PbHAsO4, is an inorganic insecticide used primarily against the potato beetle. Lead arsenate was the most extensively used arsenical insecticide. Two principal formulations of lead arsenate were marketed: basic lead arsenate (Pb5OH(AsO4)3, CASN: 1327-31-7) and acid lead arsenate (PbHAsO4).
The arsenate is an ion with the chemical formula AsO3−4. Bonding in arsenate consists of a central arsenic atom, with oxidation state +5, double bonded to one oxygen atom and single bonded to a further three oxygen atoms. The four oxygen atoms orient around the arsenic atom in a tetrahedral geometry. Resonance disperses the ion's −3 charge across all four oxygen atoms.

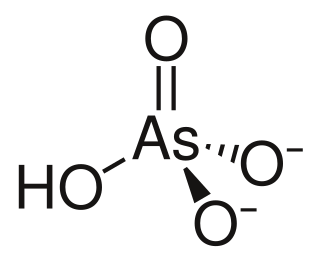
Arsenic acid or trihydrogen arsenate is the chemical compound with the formula H3AsO4. More descriptively written as AsO(OH)3, this colorless acid is the arsenic analogue of phosphoric acid. Arsenate and phosphate salts behave very similarly. Arsenic acid as such has not been isolated, but is only found in solution, where it is largely ionized. Its hemihydrate form (2H3AsO4·H2O) does form stable crystals. Crystalline samples dehydrate with condensation at 100 °C.

Arsenous acid (or arsenious acid) is the inorganic compound with the formula H3AsO3. It is known to occur in aqueous solutions, but it has not been isolated as a pure material, although this fact does not detract from the significance of As(OH)3.
In chemistry, an arsenite is a chemical compound containing an arsenic oxyanion where arsenic has oxidation state +3. Note that in fields that commonly deal with groundwater chemistry, arsenite is used generically to identify soluble AsIII anions. IUPAC have recommended that arsenite compounds are to be named as arsenate(III), for example ortho-arsenite is called trioxidoarsenate(III). Ortho-arsenite contrasts to the corresponding anions of the lighter members of group 15, phosphite which has the structure HPO2−3 and nitrite, NO−2 which is bent.
Arsenic pentoxide is the inorganic compound with the formula As2O5. This glassy, white, deliquescent solid is relatively unstable, consistent with the rarity of the As(V) oxidation state. More common, and far more important commercially, is arsenic(III) oxide (As2O3). All inorganic arsenic compounds are highly toxic and thus find only limited commercial applications.
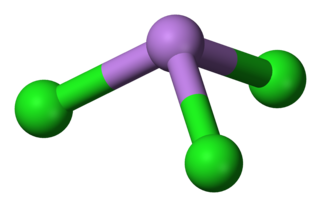
Arsenic trichloride is an inorganic compound with the formula AsCl3, also known as arsenous chloride or butter of arsenic. This poisonous oil is colourless, although impure samples may appear yellow. It is an intermediate in the manufacture of organoarsenic compounds.

Calcium arsenate is the inorganic compound with the formula Ca3(AsO4)2. A colourless salt, it was originally used as a pesticide and as a germicide. It is highly soluble in water, in contrast to lead arsenate, which makes it more toxic. The minerals rauenthalite Ca3(AsO4)2·10H2O and phaunouxite Ca3(AsO4)2·11H2O are hydrates of calcium arsenate.

Molybdenum blue is a term applied to:

Sodium arsenate is the inorganic compound with the formula Na3AsO4. Related salts are also called sodium arsenate, including Na2HAsO4 (disodium hydrogen arsenate) and NaH2AsO4 (sodium dihydrogen arsenate). The trisodium salt is a white or colourless solid that is highly toxic. It is usually handled as the dodecahydrate Na3AsO4.12H2O.

Disodium methyl arsonate (DSMA) is the organoarsenic compound with the formula CH3AsO3Na2. It is a colorless, water-soluble solid derived from methanearsonic acid. It is used as a herbicide. Tradenames include Metharsinat, Arrhenal, Disomear, Metharsan, Stenosine, Tonarsan, Tonarsin, Arsinyl, Arsynal, and Diarsen.

Ammonium arsenate is the inorganic compound with the formula (NH4)3AsO4. It is prepared by treating a concentrated solution of arsenic acid with ammonia, resulting in precipitation of colorless crystals of the trihydrate. Upon heating, it releases ammonia.
Arsenic biochemistry refers to biochemical processes that can use arsenic or its compounds, such as arsenate. Arsenic is a moderately abundant element in Earth's crust, and although many arsenic compounds are often considered highly toxic to most life, a wide variety of organoarsenic compounds are produced biologically and various organic and inorganic arsenic compounds are metabolized by numerous organisms. This pattern is general for other related elements, including selenium, which can exhibit both beneficial and deleterious effects. Arsenic biochemistry has become topical since many toxic arsenic compounds are found in some aquifers, potentially affecting many millions of people via biochemical processes.
Ammonium orthomolybdate is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula (NH4)2MoO4. It is a white solid that is prepared by treating molybdenum trioxide with aqueous ammonia. Upon heating these solutions, ammonia is lost, to give ammonium heptamolybdate ((NH4)6Mo7O24·4H2O).
Arsenate-reducing bacteria are bacteria which reduce arsenates. Arsenate-reducing bacteria are ubiquitous in arsenic-contaminated groundwater (aqueous environment). Arsenates are salts or esters of arsenic acid (H3AsO4), consisting of the ion AsO43−. They are moderate oxidizers that can be reduced to arsenites and to arsine. Arsenate can serve as a respiratory electron acceptor for oxidation of organic substrates and H2S or H2. Arsenates occur naturally in minerals such as adamite, alarsite, legrandite, and erythrite, and as hydrated or anhydrous arsenates. Arsenates are similar to phosphates since arsenic (As) and phosphorus (P) occur in group 15 (or VA) of the periodic table. Unlike phosphates, arsenates are not readily lost from minerals due to weathering. They are the predominant form of inorganic arsenic in aqueous aerobic environments. On the other hand, arsenite is more common in anaerobic environments, more mobile, and more toxic than arsenate. Arsenite is 25–60 times more toxic and more mobile than arsenate under most environmental conditions. Arsenate can lead to poisoning, since it can replace inorganic phosphate in the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate --> 1,3-biphosphoglycerate step of glycolysis, producing 1-arseno-3-phosphoglycerate instead. Although glycolysis continues, 1 ATP molecule is lost. Thus, arsenate is toxic due to its ability to uncouple glycolysis. Arsenate can also inhibit pyruvate conversion into acetyl-CoA, thereby blocking the TCA cycle, resulting in additional loss of ATP.
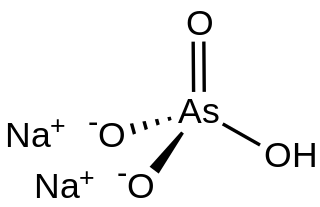
Disodium hydrogen arsenate is the inorganic compound with the formula Na2HAsO4.7H2O. The compound consists of a salt and seven molecules of water of crystallization although for simplicity the formula usually omits the water component. The other sodium arsenates are NaH2AsO4 and Na3AsO4, the latter being called sodium arsenate. Disodium hydrogen arsenate is highly toxic. The salt is the conjugate base of arsenic acid. It is a white, water-soluble solid.

Sodium dihydrogen arsenate is the inorganic compound with the formula NaH2AsO4. Related salts are also called sodium arsenate, including Na2HAsO4 (disodium hydrogen arsenate) and NaH2AsO4 (sodium dihydrogen arsenate). Sodium dihydrogen arsenate is a colorless solid that is highly toxic.

Praseodymium arsenate is the arsenate salt of praseodymium, with the chemical formula of PrAsO4. It has good thermal stability. Its ferroelectric transition temperature is 52°C.

Compounds of arsenic resemble in some respects those of phosphorus which occupies the same group (column) of the periodic table. The most common oxidation states for arsenic are: −3 in the arsenides, which are alloy-like intermetallic compounds, +3 in the arsenites, and +5 in the arsenates and most organoarsenic compounds. Arsenic also bonds readily to itself as seen in the square As3−
4 ions in the mineral skutterudite. In the +3 oxidation state, arsenic is typically pyramidal owing to the influence of the lone pair of electrons.


















