
Central America is a region of the Americas. It is bordered by Mexico to the north, Colombia to the south, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. Central America consists of seven countries: Belize, Costa Rica, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Nicaragua, and Panama. Their combined population is estimated at 44.53 million (2016).

Today, in 2021, Central America is commonly said to include Guatemala, Belize, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, Costa Rica, and Panama. This definition matches modern political borders. Central America begins geographically in Mexico, at the Isthmus of Tehuantepec, Mexico's narrowest point, and the former country of Yucatán (1841–1848) was part of Central America. At the other end, before its independence in 1903 Panama was part of South America, as it was a Department of Colombia. At times Belize, a British colony until 1981, where English instead of Spanish is spoken, and where the population is primarily of African origen, has been considered not part of (Spanish-speaking) Central America.

The Inter-American Development Bank is the largest source of development financing for Latin America and the Caribbean. Established in 1959, the IDB supports Latin American and Caribbean economic development, social development and regional integration by lending to governments and government agencies, including State corporations.
The Rio Group (G-Rio) was a permanent association of political consultation of Latin America and Caribbean countries, created in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil on December 18, 1986 with the purpose of creating a better political relationship among the countries. It was succeeded in 2011 by the Community of Latin American and Caribbean States

The Inter-American Division of Seventh-day Adventists is a sub-entity of the General Conference of Seventh-day Adventists, which oversees the Church's work in Mexico, Central America, the Caribbean, and Northern South America.

The Central American Bank for Economic Integration - CABEI was founded in 1960. It is an international multilateral development financial institution. Its resources are invested in projects that foster development to reduce poverty and inequality; strengthen regional integration and the competitive insertion of its member countries in the global economy; providing special attention to environmental sustainability. Its headquarters are in Tegucigalpa (Honduras) and has regional offices in Guatemala, Honduras, El Salvador, Nicaragua, Costa Rica and Panama.

SIEPAC is an interconnection of the power grids of six Central American nations. The project was discussed since 1987. The constructed new transmission lines connect 37 million consumers in Panama, Costa Rica, Honduras, Nicaragua, El Salvador, and Guatemala. It was expected to be completed in April 2013, and was completed in 2014. There is controversy about the benefits and indirect environmental impacts of the project.

Water supply and sanitation in Latin America is characterized by insufficient access and in many cases by poor service quality, with detrimental impacts on public health. Water and sanitation services are provided by a vast array of mostly local service providers under an often fragmented policy and regulatory framework. Financing of water and sanitation remains a serious challenge.
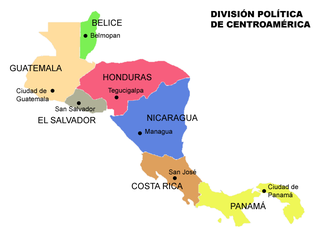
Central America is a subregion of the Americas formed by six Latin American countries and one (officially) Anglo-American country, Belize. As an isthmus it connects South America with the remainder of mainland North America, and comprises the following countries : Belize, Guatemala, Honduras, El Salvador, Nicaragua, Costa Rica, and Panama.

Rail transport in Central America consists of several isolated railroad lines with freight or passenger service. The most famous one is the Panama Canal Railway, the oldest transcontinental railroad in the world, connecting Panama City with Colón since 1855. Other railroads in Belize, Guatemala, Honduras, El Salvador, Nicaragua, Costa Rica and Panama were built by private and public investors mainly to facilitate the transport of local agricultural produce to export markets and harbors. Their market share and profitability went into decline in the second half of the twentieth century and most lines have been decommissioned by the end of the 1990s. As of 2018, railroads operate locally in Honduras, Costa Rica and Panama only; all rail transport has been suspended in Belize, El Salvador, Guatemala and Nicaragua. The railways still operating do not cross national borders.
The Central America bioregion is a biogeographic region comprising southern Mexico and Central America.

This is an Index of Central America-related articles. This index defines Central America as the seven nations of Belize, Costa Rica, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Nicaragua, and Panama.

TechnoServe is an international nonprofit that promotes business solutions to poverty in the developing world by linking people to information, capital and markets. It is a registered 501(c)(3) based in Washington, D.C., with over 1,540 employees across 29 countries worldwide.
The 2010 Central American and Caribbean Games Preliminary Round was a preliminary round contested by some CONCACAF teams that determined the qualified teams to the 2010 Central American and Caribbean Games. Six teams were drawn into 3 matchups that were contested in a two-legged tie. The first leg of each of the Preliminary Round matchups was played on March 21, 2010, and the second leg was played on March 27–28. Costa Rica did not participate in the first part, being the strongest team, they got an automatic spot into an extra playoff series against the best losing team of the two-legged series. Nicaragua, having the best result, played against Costa Rica. All 7 Central American associations took part of the qualifying process.
Football was contested for men only at the 1950 Central American and Caribbean Games in Guatemala City, Guatemala.

TECHO, also known as Un Techo para mi País (UTPMP), is a nonprofit organization that mobilizes youth volunteers to fight extreme poverty in Latin America, by constructing transitional housing and implementing social inclusion programs. It was founded by a Jesuit priest, and working with more than 720,000 volunteers, it has constructed houses for over 102,400 families in 19 countries in Latin American and the Caribbean and 2 offices located in Miami, Florida, US, and London, England, that work as funds hubs.

The economy of Central America is the eleventh-largest economy in Latin America, behind Brazil, Mexico, Argentina and Colombia. According to the World Bank, the nominal GDP of Central America reached 204 billion US dollar in 2010, as recovery from the crisis of 2009, where gross domestic product (GDP) suffered a decline to 3.8%. The major economic income are the agriculture and tourism, although the industrial sector is in strong growth, mainly in Panama.
This is a list of the Honduras national football team results from 2000 to 2009.

The following lists events that happened during 2020 in Central America: Belize, Costa Rica, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Nicaragua, and Panama.














