Capital punishment, also known as the death penalty and formerly called judicial homicide, is the state-sanctioned practice of killing a person as a punishment for a crime, usually following an authorised, rule-governed process to conclude that the person is responsible for violating norms that warrant said punishment. The sentence ordering that an offender be punished in such a manner is known as a death sentence, and the act of carrying out the sentence is known as an execution. A prisoner who has been sentenced to death and awaits execution is condemned and is commonly referred to as being "on death row". Etymologically, the term capital refers to execution by beheading, but executions are carried out by many methods, including hanging, shooting, lethal injection, stoning, electrocution, and gassing.

Cesare Bonesana di Beccaria, Marquis of Gualdrasco and Villareggio was an Italian criminologist, jurist, philosopher, economist and politician, who is widely considered one of the greatest thinkers of the Age of Enlightenment. He is well remembered for his treatise On Crimes and Punishments (1764), which condemned torture and the death penalty, and was a founding work in the field of penology and the Classical School of criminology. Beccaria is considered the father of modern criminal law and the father of criminal justice.
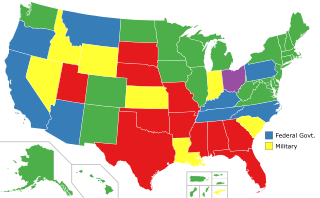
In the United States, capital punishment is a legal penalty throughout the country at the federal level, in 27 states, and in American Samoa. It is also a legal penalty for some military offenses. Capital punishment has been abolished in 23 states and in the federal capital, Washington, D.C. It is usually applied for only the most serious crimes, such as aggravated murder. Although it is a legal penalty in 27 states, 20 states have the ability to execute death sentences, with the other seven, as well as the federal government, being subject to different types of moratoriums. The existence of capital punishment in the United States can be traced to early colonial Virginia. Along with Japan, Singapore, and Taiwan, the United States is one of four advanced democracies and the only Western nation that applies the death penalty regularly. It is one of 54 countries worldwide applying it, and was the first to develop lethal injection as a method of execution, which has since been adopted by five other countries. The Philippines has since abolished executions, and Guatemala has done so for civil offenses, leaving the United States as one of four countries to still use this method. It is common practice for the condemned to be administered sedatives prior to execution, regardless of the method used.
The rule of felony murder is a legal doctrine in some common law jurisdictions that broadens the crime of murder: when someone is killed in the commission of a dangerous or enumerated crime, the offender, and also the offender's accomplices or co-conspirators, may be found guilty of murder.

Yitzhak Arad was an Israeli historian, author, IDF brigadier general and Soviet partisan. He also served as Yad Vashem's director from 1972 to 1993, and specialised in the history of the Holocaust.
An omnibus bill is a proposed law that covers a number of diverse or unrelated topics. Omnibus is derived from Latin and means "to, for, by, with or from everything". An omnibus bill is a single document that is accepted in a single vote by a legislature but packages together several measures into one or combines diverse subjects.

Kamer Daron Acemoğlu is a Turkish-born American economist who has taught at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) since 1993. He is currently the Elizabeth and James Killian Professor of Economics at MIT. He was named Institute Professor in 2019.
Coker v. Georgia, 433 U.S. 584 (1977), held that the death penalty for rape of an adult woman was grossly disproportionate and excessive punishment, and therefore unconstitutional under the Eighth Amendment to the U.S. Constitution. A few states continued to have child rape statutes that authorized the death penalty. In Kennedy v. Louisiana (2008), the court expanded Coker, ruling that the death penalty is unconstitutional in all cases that do not involve homicide or crimes against the State.
Matthew Barnett Robinson is a Criminologist at Appalachian State University (ASU) in Boone, North Carolina.

Alan Bennett Krueger was an American economist who was the James Madison Professor of Political Economy at Princeton University and Research Associate at the National Bureau of Economic Research. He served as Assistant Secretary of the Treasury for Economic Policy, nominated by President Barack Obama, from May 2009 to October 2010, when he returned to Princeton. He was nominated in 2011 by Obama as chair of the White House Council of Economic Advisers, and served in that office from November 2011 to August 2013.
George Jesus Borjas is a Cuban-American economist and the Robert W. Scrivner Professor of Economics and Social Policy at the Harvard Kennedy School. He has been described as "America’s leading immigration economist" and "the leading sceptic of immigration among economists". Borjas has published a number of studies that conclude that low-skilled immigration adversely affects low-skilled natives, a proposition that is debated among economists.

Nadarajan "Raj" Chetty is an Indian-American economist and the William A. Ackman Professor of Public Economics at Harvard University. Some of Chetty's recent papers have studied equality of opportunity in the United States and the long-term impact of teachers on students' performance. Offered tenure at the age of 28, Chetty became one of the youngest tenured faculty in the history of Harvard's economics department. He is a recipient of the John Bates Clark Medal and a 2012 MacArthur Fellow. Currently, he is also an advisory editor of the Journal of Public Economics. In 2020, he was awarded the Infosys Prize in Economics, the highest monetary award recognizing achievements in science and research, in India.
The debate over capital punishment in the United States existed as early as the colonial period. As of April 2022, it remains a legal penalty within 28 states, the federal government, and military criminal justice systems. The states of Colorado, Delaware, Illinois, Maryland, New Hampshire, Virginia, and Washington abolished the death penalty within the last decade alone.
John J. Donohue III is an American law professor, economist, and the C. Wendell and Edith M. Carlsmith Professor of Law at Stanford Law School. He is widely known for his writings on effect of legalized abortion on crime and for his criticism of John Lott's book More Guns, Less Crime.

Capital punishment as a criminal punishment for homosexuality has been implemented by a number of countries in their history. It currently remains a legal punishment in several countries and regions, most of which have sharia–based criminal laws except for Uganda.
Daniel I. Rees is an American economist who currently serves as Professor of Economics at the Universidad Carlos III de Madrid . His research interests presently include health and labour economics.
Ethan Lewis is a labor economist and Associate Professor of Economics at Dartmouth College. His fields of specialization are labor economics and econometrics with a specific interest in how U.S. labor markets have adapted to immigration and technological change.
Sherry A. Glied is a Canadian-American economist, currently serving as the Dean of New York University's Robert F. Wagner Graduate School of Public Service. From 2010 to 2012, she served as Assistant Secretary at the United States Department of Health and Human Services under the Obama administration.
Elif Naci Kalpakçıoğlu, best known as Elif Naci, was a Turkish painter, curator, journalist and writer.
Neale Mahoney is a Professor of Economics at Stanford University and the inaugural George P. Shultz Fellow at the Stanford Institute for Economic Policy Research. He is also a Research Associate at the National Bureau of Economic Research. In 2022-2023, Mahoney served in the Biden Administration's National Economic Council as a Special Policy Advisor for Economic Policy.






