
MP3 is a coding format for digital audio developed largely by the Fraunhofer Society in Germany under the lead of Karlheinz Brandenburg, with support from other digital scientists in the United States and elsewhere. Originally defined as the third audio format of the MPEG-1 standard, it was retained and further extended — defining additional bit-rates and support for more audio channels — as the third audio format of the subsequent MPEG-2 standard. A third version, known as MPEG 2.5 — extended to better support lower bit rates — is commonly implemented, but is not a recognized standard.

Walkman, stylised as WALKMAN (ウォークマン), is a brand of portable audio players manufactured and marketed by Japanese technology company Sony since 1979. The original Walkman was a portable cassette player and its popularity made "walkman" an unofficial term for personal stereos of any producer or brand. By 2010, when production stopped, Sony had built about 200 million cassette-based Walkmans.

Windows Media Player (WMP) is the first media player and media library application that Microsoft developed to play audio and video on personal computers. It has been a component of the Microsoft Windows operating system, including Windows 9x, Windows NT, Pocket PC, and Windows Mobile. Microsoft also released editions of Windows Media Player for classic Mac OS, Mac OS X, and Solaris, but has since discontinued them.

A CD player is an electronic device that plays audio compact discs, which are a digital optical disc data storage format. CD players were first sold to consumers in 1982. CDs typically contain recordings of audio material such as music or audiobooks. CD players may be part of home stereo systems, car audio systems, personal computers, or portable CD players such as CD boomboxes. Most CD players produce an output signal via a headphone jack or RCA jacks. To use a CD player in a home stereo system, the user connects an RCA cable from the RCA jacks to a hi-fi and loudspeakers for listening to music. To listen to music using a CD player with a headphone output jack, the user plugs headphones or earphones into the headphone jack.
Advanced Audio Coding (AAC) is an audio coding standard for lossy digital audio compression. Designed to be the successor of the MP3 format, AAC generally achieves higher sound quality than MP3 encoders at the same bit rate.
Area codes 705, 249, and 683 are telephone area codes in the North American Numbering Plan (NANP) for most of northeastern and central Ontario in Canada. Area code 705 was created in a 1957 area code split from portions of the 613 and 519 numbering plan areas. After a reduction in geographic coverage in 1962, the numbering plan area was assigned a second area code, 249, in 2011 to form an overlay numbering plan. A third area code, 683, was added in June 2022.

ZEN is a series of discontinued portable media players designed and manufactured by Creative Technology Limited. The players evolved from the NOMAD brand through the NOMAD Jukebox series of music players, with the first separate "ZEN" branded models released in 2004. The last Creative Zen player, X-Fi3, was released at the end of 2011.
Neuros Technology was a Chicago, Illinois–based company that produced a number of audio and video devices under the brand name Neuros. Founded by Joe Born in 2001 as a division of Digital Innovations, it previously operated under the name Neuros Audio. Like Digital Innovations, Neuros distinguished itself by its use of open-innovation and crowdsourcing techniques to bring products to market, as well as by its prominent use of open-source software and open-source hardware. In its development model, end users were involved throughout the product development process from reviewing initial concepts to beta testing initial product releases.

A portable media player (PMP) is a portable consumer electronics device capable of storing and playing digital media such as audio, images, and video files. The data is typically stored on a compact disc (CD), Digital Versatile Disc (DVD), Blu-ray Disc (BD), flash memory, microdrive, SD cards or hard drive; most earlier PMPs used physical media, but modern players mostly use flash memory. In contrast, analogue portable audio players play music from non-digital media that use analogue media, such as cassette tapes or vinyl records.
Gapless playback is the uninterrupted playback of consecutive audio tracks, such that relative time distances in the original audio source are preserved over track boundaries on playback. For this to be useful, other artifacts at track boundaries should not be severed either. Gapless playback is common with compact discs, gramophone records, or tapes, but is not always available with other formats that employ compressed digital audio. The absence of gapless playback is a source of annoyance to listeners of music where tracks are meant to segue into each other, such as some classical music, progressive rock, concept albums, electronic music, and live recordings with audience noise between tracks.

Frederick McKinley Jones was an American inventor, entrepreneur, engineer, winner of the National Medal of Technology, and an inductee of the National Inventors Hall of Fame. Jones innovated mobile refrigeration technology. He received 61 patents, 40 for refrigeration technology. He co-founded Thermo King and also served as a Sergeant in World War I.
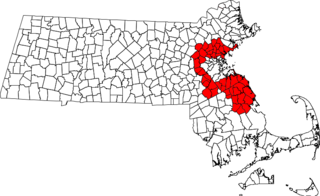
Area code 781 covers most of Boston‘s inner suburbs and some outer suburbs. It was created as a split from area code 617 on September 1, 1997. Use of 781 became mandatory February 1, 1998. Area code 339 has been sharing the service area since May 2, 2001. Since then, 10 digit local dialing is mandatory.

SigmaTel was an American system-on-a-chip (SoC), electronics and software company headquartered in Austin, Texas, that designed AV media player/recorder SoCs, reference circuit boards, SoC software development kits built around a custom cooperative kernel and all SoC device drivers including USB mass storage and AV decoder DSP, media player/recorder apps, and controller chips for multifunction peripherals. SigmaTel became Austin's largest IPO as of 2003 when it became publicly traded on NASDAQ. The company was driven by a talented mix of electrical and computer engineers plus other professionals with semiconductor industry experience in Silicon Hills, the number two IC design region in the United States, after Silicon Valley.

North American area code 605 is the telephone area code serving the entire state of South Dakota, and is one of the area codes that was created in 1947. It is also one of a gradually decreasing number of single-state, single LATA, single area code areas.
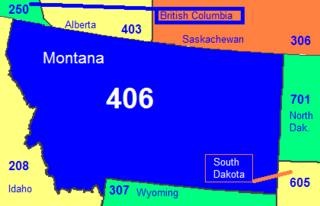
Area code 406 is the telephone area code covering the entire state of Montana. It has been Montana's only area code since area codes were created in 1947.

Visual voicemail is direct-access voicemail with a visual interface. Such an interface presents a list of messages for playback, as opposed to the sequential listening required using traditional voicemail, and may include a transcript of each message. In 2007, Apple's iPhone was the first cell phone promoting this feature.
Anderson's-Black Rock, Inc. v. Pavement Salvage Co., 396 U.S. 57 (1969), is a 1969 decision of the United States Supreme Court on the legal standard governing the obviousness of claimed inventions. It stands for the proposition that, when old elements are combined in a way such that they do not interact in a novel, unobvious way, then the resulting combination is obvious and therefore unpatentable.
The history of optical recording can be divided into a few number of distinct major contributions. The pioneers of optical recording worked mostly independently, and their solutions to the many technical challenges have very distinctive features, such as

Daryl Muscott Chapin was an American physicist, best known for co-inventing solar cells in 1954 during his work at Bell Labs alongside Calvin S. Fuller and Gerald Pearson. For this, he was inducted into the National Inventors Hall of Fame in 2008.














