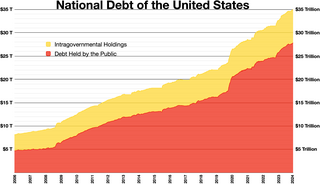
The national debt of the United States is the total national debt owed by the federal government of the United States to Treasury security holders. The national debt at any point in time is the face value of the then-outstanding Treasury securities that have been issued by the Treasury and other federal agencies. The terms "national deficit" and "national surplus" usually refer to the federal government budget balance from year to year, not the cumulative amount of debt. In a deficit year the national debt increases as the government needs to borrow funds to finance the deficit, while in a surplus year the debt decreases as more money is received than spent, enabling the government to reduce the debt by buying back some Treasury securities. In general, government debt increases as a result of government spending and decreases from tax or other receipts, both of which fluctuate during the course of a fiscal year. There are two components of gross national debt:

A payday loan is a short-term unsecured loan, often characterized by high interest rates.
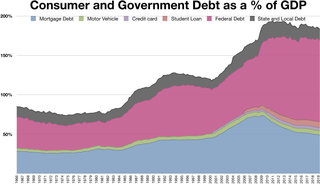
In economics, consumer debt is the amount owed by consumers. It includes debts incurred on purchase of goods that are consumable and/or do not appreciate. In macroeconomic terms, it is debt which is used to fund consumption rather than investment.
Predatory lending refers to unethical practices conducted by lending organizations during a loan origination process that are unfair, deceptive, or fraudulent. While there are no internationally agreed legal definitions for predatory lending, a 2006 audit report from the office of inspector general of the US Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) broadly defines predatory lending as "imposing unfair and abusive loan terms on borrowers", though "unfair" and "abusive" were not specifically defined. Though there are laws against some of the specific practices commonly identified as predatory, various federal agencies use the phrase as a catch-all term for many specific illegal activities in the loan industry. Predatory lending should not be confused with predatory mortgage servicing which is mortgage practices described by critics as unfair, deceptive, or fraudulent practices during the loan or mortgage servicing process, post loan origination.

Refund anticipation loan (RAL) is a short-term consumer loan in the United States provided by a third party against an expected tax refund for the duration it takes the tax authority to pay the refund. The loan term was usually about two to three weeks, related to the time it took the U.S. Internal Revenue Service to deposit refunds in electronic accounts. The loans were designed to make the refund available in as little as 24 hours. They were secured by a taxpayer's expected tax refund, and designed to offer customers quicker access to funds.

The National Child Labor Committee (NCLC) was a private, non-profit organization in the United States that served as a leading proponent for the national child labor reform movement. Its mission was to promote "the rights, awareness, dignity, well-being and education of children and youth as they relate to work and working."

The Bankruptcy Abuse Prevention and Consumer Protection Act of 2005 (BAPCPA) is a legislative act that made several significant changes to the United States Bankruptcy Code.
Debt settlement is a settlement negotiated with a debtor's unsecured creditor. Commonly, creditors agree to forgive a large part of the debt: perhaps around half, though results can vary widely. When settlements are finalized, the terms are put in writing. It is common that the debtor makes one lump-sum payment in exchange for the creditor agreeing that the debt is now cancelled and the matter closed. Some settlements are paid out over a number of months. In either case, as long as the debtor does what is agreed in the negotiation, no outstanding debt will appear on the former debtor's credit report.
Debt validation, or "debt verification", refers to a consumer's right to challenge a debt and/or receive written verification of a debt from a debt collector. The right to dispute the debt and receive validation are part of the consumer's rights under the United States Federal Fair Debt Collection Practices Act (FDCPA) and are set out in §809 of that act, which has been codified in Title 15, Section 1692-1692p of the United States Code. This debt validation procedure was expected to reduce the incidence of debt collectors dunning the wrong person or attempting to collect previously paid debts.
Equity stripping, also known as equity skimming, is a type of foreclosure rescue scheme. Often considered a form of predatory lending, equity stripping became increasingly widespread in the early 2000s. In an equity stripping scheme an investor buys the property from a homeowner facing foreclosure and agrees to lease the home to the homeowner who may remain in the home as a tenant. Often, these transactions take advantage of uninformed, low-income homeowners; because of the complexity of the transaction, victims are often unaware that they are giving away their property and equity. Several states have taken steps to confront the more unscrupulous practices of equity stripping. Although "foreclosure re-conveyance" schemes can be beneficial and ethically conducted in some circumstances, many times the practice relies on fraud and egregious or unmeetable terms.

Lori Swanson is an American lawyer and politician who served as the attorney general of Minnesota from 2007 to 2019. She was the first female attorney general elected in Minnesota. In 2018, she ran for Governor of Minnesota with running mate U.S. Representative Rick Nolan finishing in third place in the Democratic-Farmer-Labor primary.
Mortgage discrimination or mortgage lending discrimination is the practice of banks, governments or other lending institutions denying loans to one or more groups of people primarily on the basis of race, ethnic origin, sex or religion.
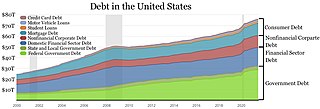
In the United States, student loans are a form of financial aid intended to help students access higher education. In 2018, 70 percent of higher education graduates had used loans to cover some or all of their expenses. With notable exceptions, student loans must be repaid, in contrast to other forms of financial aid such as scholarships, which are not repaid, and grants, which rarely have to be repaid. Student loans may be discharged through bankruptcy, but this is difficult. Research shows that access to student loans increases credit-constrained students' degree completion, later-life earnings, and student loan repayment while having no impact on overall debt.

The State Bar of Michigan is the governing body for lawyers in the State of Michigan. Membership is mandatory for attorneys who practice law in Michigan. The organization's mission is to aid in promoting improvements in the administration of justice and advancements in jurisprudence, improving relations between the legal profession and the public, and promoting the interests of the legal profession in Michigan.
Consumer protection is the practice of safeguarding buyers of goods and services, and the public, against unfair practices in the marketplace. Consumer protection measures are often established by law. Such laws are intended to prevent businesses from engaging in fraud or specified unfair practices to gain an advantage over competitors or to mislead consumers. They may also provide additional protection for the general public which may be impacted by a product even when they are not the direct purchaser or consumer of that product. For example, government regulations may require businesses to disclose detailed information about their products—particularly in areas where public health or safety is an issue, such as with food or automobiles.

The Credit Card Accountability Responsibility and Disclosure (CARD) Act of 2009 is a federal statute passed by the United States Congress and signed by U.S. President Barack Obama on May 22, 2009. It is a comprehensive credit card reform legislation that aims "to establish fair and transparent practices relating to the extension of credit under an open end consumer credit plan, and for other purposes." The bill was passed with bipartisan support by both the House of Representatives and the Senate.
Peter Bowman "Bo" Rutledge is the Dean and the Herman E. Talmadge Chair of Law at the University of Georgia School of Law in Athens, Georgia. An American attorney, academic and a specialist in international business transactions, international dispute resolution, litigation, arbitration, and the U.S. Supreme Court, he served as a law clerk for Associate U.S. Supreme Court Justice Clarence Thomas in 1998.

A payday loan is a small, short-term unsecured loan, "regardless of whether repayment of loans is linked to a borrower's payday." The loans are also sometimes referred to as "cash advances," though that term can also refer to cash provided against a prearranged line of credit such as a credit card. Payday advance loans rely on the consumer having previous payroll and employment records. Legislation regarding payday loans varies widely between different countries and, within the United States, between different states.
Credit scoring systems in the United States have garnered considerable criticism from various media outlets, consumer law organizations, government officials, debtors unions, and academics. Racial bias, discrimination against prospective employees, discrimination against medical and student debt holders, poor risk predictability, manipulation of credit scoring algorithms, inaccurate reports, and overall immorality are some of the concerns raised regarding the system. Danielle Citron and Frank Pasquale list three major flaws in the current credit-scoring system:
- Disparate impacts: The algorithms systematize biases that have been measured externally and are known to impact disadvantaged groups such as racial minorities and women. Because the algorithms are proprietary, they cannot be tested for built-in human bias.
- Arbitrary: Research shows that there is substantial variation in scoring based on audits. Responsible financial behavior can be penalized.
- Opacity: credit score technology is not transparent so consumers are unable to know why their credit scores are affected.
The Student Borrower Protection Center is a nonprofit organization aimed at protecting borrowers of student loans and improving the student loan system.








