Related Research Articles
Bankruptcy is a legal process through which people or other entities who cannot repay debts to creditors may seek relief from some or all of their debts. In most jurisdictions, bankruptcy is imposed by a court order, often initiated by the debtor.

The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is a major financial agency of the United Nations, and an international financial institution, headquartered in Washington, D.C., consisting of 190 countries. Its stated mission is "working to foster global monetary cooperation, secure financial stability, facilitate international trade, promote high employment and sustainable economic growth, and reduce poverty around the world." Formed in 1944, started on December 27, 1945, at the Bretton Woods Conference, primarily by the ideas of Harry Dexter White and John Maynard Keynes, it came into formal existence in 1945 with 29 member countries and the goal of reconstructing the international monetary system. It now plays a central role in the management of balance of payments difficulties and international financial crises. Countries contribute funds to a pool through a quota system, from which countries experiencing balance of payments problems can borrow money. As of 2016, the fund had SDR 477 billion. The IMF is regarded as the global lender of last resort.

In finance, a loan is the transfer of money by one party to another with an agreement to pay it back. The recipient, or borrower, incurs a debt and is usually required to pay interest for the use of the money.
The national debt of the United States is the total national debt owed by the federal government of the United States to Treasury security holders. The national debt at any point in time is the face value of the then-outstanding Treasury securities that have been issued by the Treasury and other federal agencies. The terms "national deficit" and "national surplus" usually refer to the federal government budget balance from year to year, not the cumulative amount of debt. In a deficit year the national debt increases as the government needs to borrow funds to finance the deficit, while in a surplus year the debt decreases as more money is received than spent, enabling the government to reduce the debt by buying back some Treasury securities. In general, government debt increases as a result of government spending and decreases from tax or other receipts, both of which fluctuate during the course of a fiscal year. There are two components of gross national debt:
A country's gross external debt is the liabilities that are owed to nonresidents by residents. The debtors can be governments, corporations or citizens. External debt may be denominated in domestic or foreign currency. It includes amounts owed to private commercial banks, foreign governments, or international financial institutions such as the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the World Bank.

A country's gross government debt is the financial liabilities of the government sector. Changes in government debt over time reflect primarily borrowing due to past government deficits. A deficit occurs when a government's expenditures exceed revenues. Government debt may be owed to domestic residents, as well as to foreign residents. If owed to foreign residents, that quantity is included in the country's external debt.

In accounting, insolvency is the state of being unable to pay the debts, by a person or company (debtor), at maturity; those in a state of insolvency are said to be insolvent. There are two forms: cash-flow insolvency and balance-sheet insolvency.
In corporate finance, a leveraged recapitalization is a change of the company's capital structure, usually substitution of debt for equity.
Restructuring is the corporate management term for the act of reorganizing the legal, ownership, operational, or other structures of a company for the purpose of making it more profitable, or better organized for its present needs. Other reasons for restructuring include a change of ownership or ownership structure, demerger, or a response to a crisis or major change in the business such as bankruptcy, repositioning, or buyout. Restructuring may also be described as corporate restructuring, debt restructuring and financial restructuring.

Monetary policy pertains to the regulation, availability, and cost of credit, while Fiscal policy deals with government expenditures, taxes, and debt. Through management of these areas, the Ministry of Finance regulated the allocation of resources in the economy, affected the distribution of income and wealth among the citizenry, stabilized the level of economic activities, and promoted economic growth and welfare.
Réseau ferré de France was a French company which owned and maintained the French national railway network from 1997 to 2014. The company was formed with the rail assets of SNCF in 1997. Afterwards, the trains were operated by the SNCF, the national railway company, but due to European Union Directive 91/440, the Government of France was required to separate train operations from the railway infrastructure. On 1 January 2015, RFF became SNCF Réseau, the operational assets of SNCF became SNCF Mobilités, and both groups were placed under the control of SNCF.
Ecological debt refers to the accumulated debt seen by some campaigners as owed by the Global North to Global South countries, due to the net sum of historical environmental injustice, especially through resource exploitation, habitat degradation, and pollution by waste discharge. The concept was coined by Global Southerner non-governmental organizations in the 1990s and its definition has varied over the years, in several attempts of greater specification.
The Private Sector Survey on Cost Control (PSSCC), commonly referred to as the Grace Commission, was an investigation requested by United States President Ronald Reagan, authorized in Executive Order 12369 on June 30, 1982. In doing so President Reagan used the now famous phrase, "Drain the swamp". The focus was waste and inefficiency in the US Federal government. The head of the commission, businessman J. Peter Grace, asked the members of that commission to "Be bold and work like tireless bloodhounds, don't leave any stone unturned in your search to root out inefficiency."
Venture debt or venture lending is a type of debt financing provided to venture-backed companies by specialized banks or non-bank lenders to fund working capital or capital expenses, such as purchasing equipment. Venture debt can complement venture capital and provide value to fast growing companies and their investors. Unlike traditional bank lending, venture debt is available to startups and growth companies that do not have positive cash flows or significant assets to give as collateral. Venture debt providers combine their loans with warrants, or rights to purchase equity, to compensate for the higher risk of default, although this is not always the case.


The European debt crisis, often also referred to as the eurozone crisis or the European sovereign debt crisis, was a multi-year debt crisis that took place in the European Union (EU) from 2009 until the mid to late 2010s. Several eurozone member states were unable to repay or refinance their government debt or to bail out over-indebted banks under their national supervision without the assistance of third parties like other eurozone countries, the European Central Bank (ECB), or the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
Fiscal policy are "measures employed by governments to stabilize the economy, specifically by manipulating the levels and allocations of taxes and government expenditures". In the Philippines, this is characterized by continuous and increasing levels of debt and budget deficits, though there were improvements in the last few years of the first decade of the 21st century.
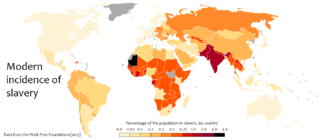
Debt bondage in India or Bandhua Mazdoori was legally abolished in 1976 but remains prevalent due to weak enforcement by the government. Bonded labour is a system in which lenders force their borrowers to repay loans through labor. Additionally, these debts often take a large amount of time to pay off and are unreasonably high, propagating a cycle of generational inequality. This is due to the typically high interest rates on the loans given out by employers. Although debt bondage is considered to be a voluntary form of labor, people are forced into this system by social situations.

Diplomatic relations between the People's Republic of China and the Maldives were established in 1972. China has an embassy in Malé which opened in November 2011, and the Maldives has an embassy in Beijing which opened in 2009.