
A wireless network is a computer network that uses wireless data connections between network nodes.
A location-based service (LBS) is a general term denoting software services which use geographic data and information to provide services or information to users. LBS can be used in a variety of contexts, such as health, indoor object search, entertainment, work, personal life, etc. Commonly used examples of location based services include navigation software, social networking services, location-based advertising, and tracking systems. LBS can also include mobile commerce when taking the form of coupons or advertising directed at customers based on their current location. LBS also includes personalized weather services and even location-based games.

Wardriving is the act of searching for Wi-Fi wireless networks, usually from a moving vehicle, using a laptop or smartphone. Software for wardriving is freely available on the internet.

Mobile computing is human–computer interaction in which a computer is expected to be transported during normal usage and allow for transmission of data, which can include voice and video transmissions. Mobile computing involves mobile communication, mobile hardware, and mobile software. Communication issues include ad hoc networks and infrastructure networks as well as communication properties, protocols, data formats, and concrete technologies. Hardware includes mobile devices or device components. Mobile software deals with the characteristics and requirements of mobile applications.
In computing, Internet geolocation is software capable of deducing the geographic position of a device connected to the Internet. For example, the device's IP address can be used to determine the country, city, or ZIP code, determining its geographical location. Other methods include examination of Wi-Fi hotspots, a MAC address, image metadata, or credit card information.
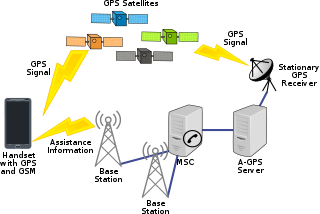
Assisted GNSS (A-GNSS) is a GNSS augmentation system that often significantly improves the startup performance—i.e., time-to-first-fix (TTFF)—of a global navigation satellite system (GNSS). A-GNSS works by providing the necessary data to the device via a radio network instead of the slow satellite link, essentially "warming up" the receiver for a fix. When applied to GPS, it is known as assisted GPS or augmented GPS. Other local names include A-GANSS for Galileo and A-Beidou for BeiDou.

Mobile phone tracking is a process for identifying the location of a mobile phone, whether stationary or moving. Localization may be affected by a number of technologies, such as the multilateration of radio signals between (several) cell towers of the network and the phone or by simply using GNSS. To locate a mobile phone using multilateration of mobile radio signals, the phone must emit at least the idle signal to contact nearby antenna towers and does not require an active call. The Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) is based on the phone's signal strength to nearby antenna masts.

Geosocial networking is a type of social networking in which geographic services and capabilities such as geocoding and geotagging are used to enable additional social dynamics. User-submitted location data or geolocation techniques can allow social networks to connect and coordinate users with local people or events that match their interests. Geolocation on web-based social network services can be IP-based or use hotspot trilateration. For mobile social networks, texted location information or mobile phone tracking can enable location-based services to enrich social networking.
Monsoon Multimedia was a company that manufactured, developed and sold video streaming and place-shifting devices that allowed consumers to view and control live television on PCs connected to a local (home) network or remotely from a broadband-connected PC or mobile phone. It was one of 5 major transformations initiated by Prabhat Jain, a Silicon Valley entrepreneur with 5 undergraduate and post graduate engineering degrees from Cal Berkeley and Univ of Vienna, Austria. On the even of Cisco acquiring Monsoon in 2017, EchoStar, the new parent of Sling sued Monsoon for patent infringement, having obtained confidential information about the date of the acquisition by Cisco from a Monsoon employee under murky circumstances. Monsoon settled the lawsuit by agreeing not to sell its products in the USA simply because it did not have the legal funds to fight mighty Echostar's legal maneuvers. EchoStar thus successfully removed its only competitor from the market place. This meant Monsoon's death knell.
Cyril Lionel Houri is a New York-based entrepreneur who has founded two geolocation technology companies: InfoSplit, Inc. and Mexens Technology Inc.. Houri has designed IP address geolocation, WiFi and cellular positioning technologies, and has testified as an expert witness on location-based technology in LICRA vs. Yahoo!.
Skyhook is a location technology company based in Boston, Massachusetts, that specializes in location positioning, context, and intelligence. Founded in 2003, Skyhook originally began by geolocating Wi-Fi access points. It has since then has been focusing on hybrid positioning technology, which incorporates with Wi-Fi, GPS, cell towers, IP address, and device sensors to improve device location.

An indoor positioning system (IPS) is a network of devices used to locate people or objects where GPS and other satellite technologies lack precision or fail entirely, such as inside multistory buildings, airports, alleys, parking garages, and underground locations.
Wi-Fi positioning system is a geolocation system that uses the characteristics of nearby Wi-Fi hotspots and other wireless access points to discover where a device is located.
Real-time geotagging refers to the automatic technique of acquiring media, associating a specific location with the media, transferring the media to an online map and publishing the media in real time. It is thus an extension of an automatic geotagging process, requiring an in-built or attached location acquisition device, but also requires communication with a wireless data transfer device. Most modern smartphones and several digital cameras already integrate camera, aGPS, and wireless data transfer into one device, thus directly producing a geotagged photograph. Real-time geotagging is sometimes referred to as "mobile geotagging" or "autogeotagging", but this does not imply the real-time publishing step.

The Palm Pre, styled as palm prē, is a multitasking smartphone that was designed and marketed by Palm with a multi-touch screen and a sliding keyboard. The smartphone was the first to use Palm's Linux-based mobile operating system, webOS. The Pre functions as a camera phone and a portable media player, and has location and navigation capabilities. The Pre also serves as a personal information manager, has a number of communication and collaboration applications, and has Bluetooth and Wi-Fi connectivity built-in.
The W3C Geolocation API is an effort by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) to standardize an interface to retrieve the geographical location information for a client-side device. It defines a set of objects, ECMAScript standard compliant, that executing in the client application give the client's device location through the consulting of Location Information Servers, which are transparent for the application programming interface (API). The most common sources of location information are IP address, Wi-Fi and Bluetooth MAC address, radio-frequency identification (RFID), Wi-Fi connection location, or device Global Positioning System (GPS) and GSM/CDMA cell IDs. The location is returned with a given accuracy depending on the best location information source available.
Trapster was a navigation social networking mobile application and website, provided for free, that maps out and alerts users in real time to the presence of live police speed traps, DUI checkpoints, traffic, red light cameras, speed cameras, and areas where police often hide. Further, it allows users to record trip data and share it via the web, including interfaces with Facebook and Twitter. Trapster was recognized by Time Magazine as one of the 10 Best iPhone Apps for Dads in June 2009. In addition, Wired listed Trapster as the number 1 application in their 10 Mobile Applications that Make the Most of Location and CNET named Trapster as their number 1 free iPhone automotive app.
A GSM Cell ID (CID) is a generally unique number used to identify each base transceiver station (BTS) or sector of a BTS within a location area code (LAC) if not within a GSM network.

WiGLE is a website for collecting information about the different wireless hotspots around the world. Users can register on the website and upload hotspot data like GPS coordinates, SSID, MAC address and the encryption type used on the hotspots discovered. In addition, cell tower data is uploaded and displayed.
Mozilla Location Service (MLS) is an open geolocation service which allows devices to find their position by processing their received signals of publicly observable radio transmitters: cellular network antennae, Wi-Fi access points, and Bluetooth beacons. The service is provided by Mozilla since 2013. The service uses Mozilla's open source software project called Ichnaea.








