
The Neotropical realm is one of the eight biogeographic realms constituting Earth's land surface. Physically, it includes the tropical terrestrial ecoregions of the Americas and the entire South American temperate zone.

A swamp is a forested wetland. Swamps are considered to be transition zones because both land and water play a role in creating this environment. Swamps vary in size and are located all around the world. The water of a swamp may be fresh water, brackish water, or seawater. Freshwater swamps form along large rivers or lakes where they are critically dependent upon rainwater and seasonal flooding to maintain natural water level fluctuations. Saltwater swamps are found along tropical and subtropical coastlines. Some swamps have hammocks, or dry-land protrusions, covered by aquatic vegetation, or vegetation that tolerates periodic inundation or soil saturation. The two main types of swamp are "true" or swamp forests and "transitional" or shrub swamps. In the boreal regions of Canada, the word swamp is colloquially used for what is more formally termed a bog, fen, or muskeg. Some of the world's largest swamps are found along major rivers such as the Amazon, the Mississippi, and the Congo.
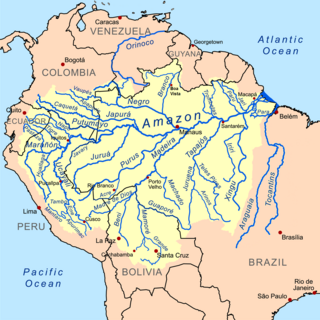
The Amazon basin is the part of South America drained by the Amazon River and its tributaries. The Amazon drainage basin covers an area of about 7,000,000 km2 (2,700,000 sq mi), or about 35.5 percent of the South American continent. It is located in the countries of Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Peru, Suriname, and Venezuela, as well as the territory of French Guiana.
A rheophile is an animal that prefers to live in fast-moving water.

Microglanis is a genus of fish in the family Pseudopimelodidae native to South America. This genus has the widest distribution within its family, with species ranging from the Guianas to Venezuela; western slope of the Andes in Ecuador and Peru to the Río de La Plata basin in Argentina. They occur eastward to the Orinoco and Amazon basins. It is also present in the eastern coastal rivers of Brazil.

Gymnogeophagus is a genus of cichlid fishes from South America, where they are known from various river basins in southern Brazil, Paraguay, Uruguay and northern Argentina. They are part of a group popularly known as eartheaters.

Laetacara is a small genus of cichlids native to freshwater habitats in tropical and subtropical South America, ranging from the upper Orinoco River basin in Venezuela to the Paraná River basin Argentina. The genus is also collectively known as the smiling acaras. Like all cichlids, Laetacara species have well-developed brood care.

Mesonauta, the flag cichlids, is a small genus of cichlids native to the Amazon, Orinoco, Essequibo, Paraná and Paraguay basins in South America. Mesonauta is included in the subfamily Cichlasomatinae. They occur in various freshwater habitats such as streams and lakes, especially in areas with little water movement and aquatic vegetation. They are generally found in small groups that stay near the water surface. To avoid predators, adults may jump out of the water and juveniles mimic leaves.
James S. Albert is a professor of Biology at the University of Louisiana at Lafayette. Dr. Albert is an author of over 100 scientific papers on the evolution and diversity of fishes, and is an expert in the systematics and biodiversity of Neotropical electric fishes (Gymnotiformes). Dr. Albert and his colleagues to date have described 50 new species.

Leporinus fasciatus, commonly known as the banded leporinus or the black-banded leporinus, is a species of characin in the family Anostomidae. L. fasciatus is native to the Amazon Basin in South America, but has been introduced into the US states of Florida and Hawaii. It has not been observed from Hawaii as of 2005; the species is thought to have been extirpated in the region.
In biogeography, geodispersal is the erosion of barriers to gene flow and biological dispersal. Geodispersal differs from vicariance, which reduces gene flow through the creation of geographic barriers. In geodispersal, the geographical ranges of individual taxa, or of whole biotas, are merged by erosion of a physical barrier to gene flow or dispersal. Multiple related geodispersal and vicariance events can be mutually responsible for differences among populations. As these geographic barriers break down, organisms of the secluded ecosystems can interact, allowing gene flow between previously separated species, creating more biological variation within a region.
Loricariichthys edentatus is a species of catfish in the family Loricariidae. It is native to South America, where it occurs in the lower Uruguay River basin in Entre Ríos Province in Argentina, and also in Brazil. It has no teeth on the premaxilla, a unique feature in the genus Loricariichthys. The species reaches 11.5 cm in standard length and is believed to be a facultative air-breather.

Mesonauta acora is a species of cichlid fish endemic to the Amazon Basin of Brazil; specifically, to blackwater in the Xingu and Tocantins River basins in South America. The species was named by François Louis de la Porte, comte de Castelnau in 1855.
Heiko Bleher is a German researcher, author, photographer, and filmmaker. He is best known in the scientific community for his contribution to the exploration of fresh and brackish water habitats worldwide. He has discovered numerous species of fish and aquatic plant, several of which carry his name or are named in honor of Bleher's family.

A whitewater river is classified based on its chemistry, sediments and water colour. Whitewater rivers have high levels of suspended sediments, giving the water a pH that is near-neutral, a high electric conductivity and a pale muddy, café au lait-like colour. Whitewater rivers are of great ecological importance and are important to local fisheries. The major seasonal Amazonian floodplains known as várzea receive their water from them.

A clearwater river is classified based on its chemistry, sediments and water colour. Clearwater rivers have a low conductivity, relatively low levels of dissolved solids, typically have a neutral to slightly acidic pH and are very clear with a greenish colour. Clearwater rivers often have fast-flowing sections.

Brachyplatystoma rousseauxii, the gilded catfish or dourada, is a species of catfish of the family Pimelodidae that is native to Amazon and Orinoco River basins and major rivers of French Guiana.

The tailspot tetra is a freshwater fish that lives in the coastal river regions of upper South America. Both its common and scientific names reference the distinct spot of color present on the tail fin, which is one of its defining characteristics. It is a small fish, reaching 4.8 in at its longest. Despite its small size, it is an active swimmer, with a preference for fast-flowing waters.

Tyttocharax madeirae, the blackedge tetra, also known as the bristly-mouthed tetra or the blue tetra, is a small freshwater fish of the family Characidae found in the Amazon basin of South America. It was first caught by Edgar A. Smith in 1912 in Brazil and described by American ichthyologist Henry Weed Fowler in 1913.

Bryconops giacopinii is a mid-sized species of freshwater fish in the family Iguanodectidae. It is the largest member of the genus Bryconops, and is therefore difficult to confuse with any of its congeners. With a diet that consists largely of land-dwelling insects, it serves as an important link between the terrestrial and aquatic aspects of its native range.















