Microsoft Windows is a product line of proprietary graphical operating systems developed and marketed by Microsoft. It is grouped into families and sub-families that cater to particular sectors of the computing industry -- Windows (unqualified) for a consumer or corporate workstation, Windows Server for a server and Windows IoT for an embedded system. Defunct families include Windows 9x, Windows Mobile, Windows Phone, and Windows Embedded Compact.

Windows 2000 is a major release of the Windows NT operating system developed by Microsoft and designed for businesses. It was the direct successor to Windows NT 4.0, and was released to manufacturing on December 15, 1999, and was officially released to retail on February 17, 2000 and September 26, 2000 for Windows 2000 Datacenter Server. It was Microsoft's business operating system until the introduction of Windows XP Professional in 2001.
Distributed Component Object Model (DCOM) is a proprietary Microsoft technology for communication between software components on networked computers. DCOM, which originally was called "Network OLE", extends Microsoft's COM, and provides the communication substrate under Microsoft's COM+ application server infrastructure.

Novell, Inc. was an American software and services company headquartered in Provo, Utah, that existed from 1980 until 2014. Its most significant product was the multi-platform network operating system known as Novell NetWare.
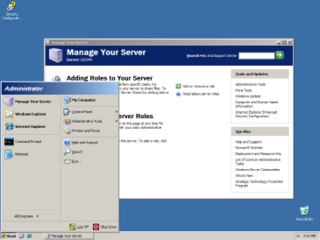
Windows Server 2003, codenamed "Whistler Server", is the second version of the Windows Server operating system produced by Microsoft. It is part of the Windows NT family of operating systems and was released to manufacturing on March 28, 2003 and generally available on April 24, 2003. Windows Server 2003 is the successor to the Server editions of Windows 2000 and the predecessor to Windows Server 2008. An updated version, Windows Server 2003 R2, was released to manufacturing on December 6, 2005. Windows Server 2003 is based on Windows XP.
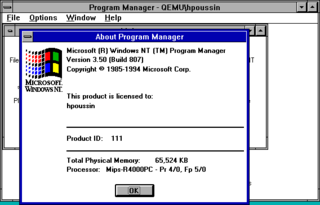
Windows NT 3.5 is a major release of the Windows NT operating system developed by Microsoft and oriented towards businesses. It was released on September 21, 1994, as the successor to Windows NT 3.1 and the predecessor to Windows NT 3.51.
Interix was an optional, POSIX-conformant Unix subsystem for Windows NT operating systems. Interix was a component of Windows Services for UNIX, and a superset of the Microsoft POSIX subsystem. Like the POSIX subsystem, Interix was an environment subsystem for the NT kernel. It included numerous open source utility software programs and libraries. Interix was originally developed and sold as OpenNT until purchased by Microsoft in 1999.
Windows Server is a group of operating systems (OS) for servers that Microsoft has been developing since 1993. The first OS that was released for this platform is Windows NT 3.1 Advanced Server. With the release of Windows Server 2003, the brand name was changed to Windows Server. The latest release of Windows Server is Windows Server 2022, which was released in 2021.

Microsoft Internet Explorer 6 (IE6) is a graphical web browser developed by Microsoft for Windows operating systems. Released on August 24, 2001, it is the sixth, and by now discontinued, version of Internet Explorer and the successor to Internet Explorer 5. It was the default browser in Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 and can replace previous versions of Internet Explorer on Windows NT 4.0, Windows 98, Windows 2000 and Windows ME but unlike version 5, this version does not support Windows 95 or earlier versions. IE6 SP2+ and IE7 were only included in or available (IE7) for Windows XP SP2+.
An internet leak is the unauthorized release of information over the internet. Various types of information and data can be, and have been, "leaked" to the Internet, the most common being personal information, computer software and source code, and artistic works such as books or albums. For example, a musical album is leaked if it has been made available to the public on the Internet before its official release date.
The development of Windows Vista began in May 2001, prior to the release of Microsoft's Windows XP operating system, and continuing until November 2006.
MinWin is a term used informally by Microsoft to describe the kernel and operating system components that form the basis of releases of Microsoft Windows starting with Windows Vista. The term was first used in 2003 to describe approximately 95% of the common components of the operating system, but has over time come to refer to a significantly smaller portion. Its most recent and most well-known variation was a minimalistic, self-contained set of Windows components that shipped as part of Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2.
Windows NT is a proprietary graphical operating system produced by Microsoft as part of its Windows product line, the first version of which was released on July 27, 1993, and it lives on today since the latest version of Windows, 11, includes its technology.
Windows Interface Source Environment was a licensing program from Microsoft which allowed developers to recompile and run Windows-based applications on UNIX and Macintosh platforms.

Mainsoft is a software company, founded in 1993, that develops interoperability software products for Microsoft Windows and Linux/Unix platforms.

Microsoft started development on the .NET Framework in the late 1990s originally under the name of Next Generation Windows Services (NGWS). By late 2001 the first beta versions of .NET Framework 1.0 were released. The first version of .NET Framework was released on 13 February 2002, bringing managed code to Windows NT 4.0, 98, 2000, ME and XP.

The Nokia X family was a range of budget smartphones that was produced and marketed by Microsoft Mobile, originally introduced in February 2014 by Nokia. The smartphones run on the Nokia X platform, a Linux-based operating system which was a fork of Android. Nokia X is also known generally as the Nokia Normandy. It is regarded as Nokia's first Android device during the company's Microsoft partnership and was in the process of selling its mobile phone business to Microsoft, which eventually happened two months later.
Microsoft, a technology company historically known for its opposition to the open source software paradigm, turned to embrace the approach in the 2010s. From the 1970s through 2000s under CEOs Bill Gates and Steve Ballmer, Microsoft viewed the community creation and sharing of communal code, later to be known as free and open source software, as a threat to its business, and both executives spoke negatively against it. In the 2010s, as the industry turned towards cloud, embedded, and mobile computing—technologies powered by open source advances—CEO Satya Nadella led Microsoft towards open source adoption although Microsoft's traditional Windows business continued to grow throughout this period generating revenues of 26.8 billion in the third quarter of 2018, while Microsoft's Azure cloud revenues nearly doubled.









