
A melanocytic nevus is a type of melanocytic tumor that contains nevus cells. Some sources equate the term mole with "melanocytic nevus", but there are also sources that equate the term mole with any nevus form.

Nevus is a nonspecific medical term for a visible, circumscribed, chronic lesion of the skin or mucosa. The term originates from nævus, which is Latin for "birthmark"; however, a nevus can be either congenital or acquired. Common terms, including mole, birthmark, and beauty mark, are used to describe nevi, but these terms do not distinguish specific types of nevi from one another.

A dysplastic nevus or atypical mole is a nevus (mole) whose appearance is different from that of common moles. In 1992, the NIH recommended that the term "dysplastic nevus" be avoided in favor of the term "atypical mole". An atypical mole may also be referred to as an atypical melanocytic nevus, atypical nevus, B-K mole, Clark's nevus, dysplastic melanocytic nevus, or nevus with architectural disorder.

Dysplastic nevus syndrome, also known as familial atypical multiple mole–melanoma (FAMMM) syndrome, is an inherited cutaneous condition described in certain families, and characterized by unusual nevi and multiple inherited melanomas. First described in 1820, the condition is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern, and caused by mutations in the CDKN2A gene. In addition to melanoma, individuals with the condition are at increased risk for pancreatic cancer.

The congenital melanocytic nevus is a type of melanocytic nevus found in infants at birth. This type of birthmark occurs in an estimated 1% of infants worldwide; it is located in the area of the head and neck 15% of the time.

A lentigo is a small pigmented spot on the skin with a clearly defined edge, surrounded by normal-appearing skin. It is a harmless (benign) hyperplasia of melanocytes which is linear in its spread. This means the hyperplasia of melanocytes is restricted to the cell layer directly above the basement membrane of the epidermis where melanocytes normally reside. This is in contrast to the "nests" of multi-layer melanocytes found in moles. Because of this characteristic feature, the adjective "lentiginous" is used to describe other skin lesions that similarly proliferate linearly within the basal cell layer.

A blue nevus is a type of coloured mole, typically a single well-defined blue-black bump.
Phakomatosis pigmentovascularis is a rare neurocutanous condition where there is coexistence of a capillary malformation with various melanocytic lesions, including dermal melanocytosis, nevus spilus, and nevus of Ota.

Fibrous papule of the nose is a harmless small bump on or near the nose. It is typically dome-shaped, skin-colored, white or reddish, smooth and firm. Less frequently it can occur elsewhere on the face. Sometimes there are a few. It may be shiny and remains unchanged for life. There may be a central hair.
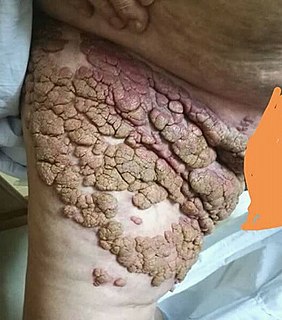
Nevus lipomatosus (cutaneous) superficialis is characterized by soft, yellowish papules or cerebriform plaques, usually of the buttock or thigh, less often of the ear or scalp, with a wrinkled rather than warty surface. It is usually congenital in origin or appears within the first three decades.
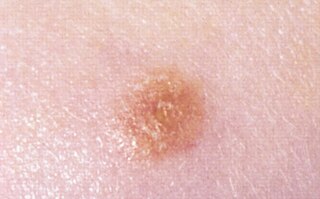
A Spitz nevus is a benign skin lesion. A type of melanocytic nevus, it affects the epidermis and dermis.
Epidermal nevus syndrome is a rare disease that was first described in 1968 and consists of extensive epidermal nevi with abnormalities of the central nervous system (CNS), skeleton, skin, cardiovascular system, genitourinary system and eyes. However, since the syndrome's first description, a broader concept for the "epidermal nevus" syndrome has been proposed, with at least six types being described:
Phakomatosis pigmentokeratotica is a rare neurocutanous condition characterized by the combination of an organoid sebaceous nevus and speckled lentiginous nevus. It is an unusual variant of epidermal naevus syndrome. It was first described by Happle et al. It is often associated with neurological or skeletal anomalies such as hemiatrophy, dysaesthesia and hyperhidrosis in a segmental pattern, mild mental retardation, seizures, deafness, ptosis and strabismus.
A benign melanocytic nevus is a cutaneous condition characterised by well-circumscribed, pigmented, round or ovoid lesions, generally measuring from 2 to 6 mm in diameter. A benign melanocytic nevus may feature hair or pigmentation as well.

Balloon cell nevus is a benign nevus. It appears like a melanocytic nevus.
Oral pigmentation is asymptomatic and does not usually cause any alteration to the texture or thickness of the affected area. The colour can be uniform or speckled and can appear solitary or as multiple lesions. Depending on the site, depth, and quantity of pigment, the appearance can vary considerably.

An acral nevus is a cutaneous condition of the palms, soles, fingers, or toes, characterized by a skin lesion that is usually macular or only slightly elevated, and may display a uniform brown or dark brown color, often with linear striations.
Zosteriform speckled lentiginous nevus is a skin lesion that may be the result of a potentially lethal mutation.
Kamino bodies are eosinophilic globoids. Kamino bodies are commonly observed microscopically with the condition spitz nevi, a benign melanocytic nevus, a type of skin lesion, affecting the epidermis and dermis.

A pigmented spindle cell nevus is a skin condition characterized by a dark brown to black macule or papule, usually less than 6 mm.













