
Itanium is a discontinued family of 64-bit Intel microprocessors that implement the Intel Itanium architecture. The Itanium architecture originated at Hewlett-Packard (HP), and was later jointly developed by HP and Intel. Launched in June 2001, Intel initially marketed the processors for enterprise servers and high-performance computing systems. In the concept phase, engineers said "we could run circles around PowerPC, that we could kill the x86." Early predictions were that IA-64 would expand to the lower-end servers, supplanting Xeon, and eventually penetrate into the personal computers, eventually to supplant RISC and complex instruction set computing (CISC) architectures for all general-purpose applications.
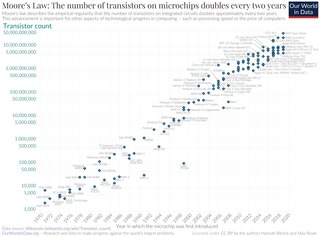
Moore's law is the observation that the number of transistors in an integrated circuit (IC) doubles about every two years. Moore's law is an observation and projection of a historical trend. Rather than a law of physics, it is an empirical relationship linked to gains from experience in production.

Leon N. Cooper is an American physicist and Nobel Prize laureate who, with John Bardeen and John Robert Schrieffer, developed the BCS theory of superconductivity. His name is also associated with the Cooper pair and co-developer of the BCM theory of synaptic plasticity.
Neuromorphic computing is an approach to computing that is inspired by the structure and function of the human brain. A neuromorphic computer/chip is any device that uses physical artificial neurons to do computations. In recent times, the term neuromorphic has been used to describe analog, digital, mixed-mode analog/digital VLSI, and software systems that implement models of neural systems. The implementation of neuromorphic computing on the hardware level can be realized by oxide-based memristors, spintronic memories, threshold switches, transistors, among others. Training software-based neuromorphic systems of spiking neural networks can be achieved using error backpropagation, e.g., using Python based frameworks such as snnTorch, or using canonical learning rules from the biological learning literature, e.g., using BindsNet.

A multi-core processor is a microprocessor on a single integrated circuit with two or more separate processing units, called cores, each of which reads and executes program instructions. The instructions are ordinary CPU instructions but the single processor can run instructions on separate cores at the same time, increasing overall speed for programs that support multithreading or other parallel computing techniques. Manufacturers typically integrate the cores onto a single integrated circuit die or onto multiple dies in a single chip package. The microprocessors currently used in almost all personal computers are multi-core.
The transistor count is the number of transistors in an electronic device. It is the most common measure of integrated circuit complexity. The rate at which MOS transistor counts have increased generally follows Moore's law, which observed that the transistor count doubles approximately every two years. However, being directly proportional to the area of a chip, transistor count does not represent how advanced the corresponding manufacturing technology is: a better indication of this is the transistor density.
An Advanced Encryption Standard instruction set is now integrated into many processors. The purpose of the instruction set is to improve the speed and security of applications performing encryption and decryption using the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES).

Intel Core is a line of streamlined midrange consumer, workstation and enthusiast computer central processing units (CPUs) marketed by Intel Corporation. These processors displaced the existing mid- to high-end Pentium processors at the time of their introduction, moving the Pentium to the entry level. Identical or more capable versions of Core processors are also sold as Xeon processors for the server and workstation markets.
In semiconductor manufacturing, the International Roadmap for Devices and Systems defines the 5 nm process as the MOSFET technology node following the 7 nm node. In 2020, Samsung and TSMC entered volume production of 5 nm chips, manufactured for companies including Apple, Marvell, Huawei and Qualcomm.
A cognitive computer is a computer that hardwires artificial intelligence and machine-learning algorithms into an integrated circuit that closely reproduces the behavior of the human brain. It generally adopts a neuromorphic engineering approach. Synonyms are neuromorphic chip and cognitive chip.

Intel Quark is a line of 32-bit x86 SoCs and microcontrollers by Intel, designed for small size and low power consumption, and targeted at new markets including wearable devices. The line was introduced at Intel Developer Forum in 2013, and discontinued in January 2019.

Movidius is a company based in San Mateo, California, that designs low-power processor chips for computer vision. The company was acquired by Intel in September 2016.
A vision processing unit (VPU) is an emerging class of microprocessor; it is a specific type of AI accelerator, designed to accelerate machine vision tasks.

Tensor Processing Unit (TPU) is an AI accelerator application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC) developed by Google for neural network machine learning, using Google's own TensorFlow software. Google began using TPUs internally in 2015, and in 2018 made them available for third party use, both as part of its cloud infrastructure and by offering a smaller version of the chip for sale.
An AI accelerator is a class of specialized hardware accelerator or computer system designed to accelerate artificial intelligence and machine learning applications, including artificial neural networks and machine vision. Typical applications include algorithms for robotics, Internet of Things, and other data-intensive or sensor-driven tasks. They are often manycore designs and generally focus on low-precision arithmetic, novel dataflow architectures or in-memory computing capability. As of 2018, a typical AI integrated circuit chip contains billions of MOSFET transistors. A number of vendor-specific terms exist for devices in this category, and it is an emerging technology without a dominant design.
Coherent Accelerator Processor Interface (CAPI), is a high-speed processor expansion bus standard for use in large data center computers, initially designed to be layered on top of PCI Express, for directly connecting central processing units (CPUs) to external accelerators like graphics processing units (GPUs), ASICs, FPGAs or fast storage. It offers low latency, high speed, direct memory access connectivity between devices of different instruction set architectures.

Apple M1 is a series of ARM-based systems-on-a-chip (SoCs) designed by Apple Inc. as a central processing unit (CPU) and graphics processing unit (GPU) for its Mac desktops and notebooks, and the iPad Pro and iPad Air tablets. The M1 chip initiated Apple's third change to the instruction set architecture used by Macintosh computers, switching from Intel to Apple silicon 14 years after they were switched from PowerPC to Intel, and 26 years after the transition from the original Motorola 68000 series to PowerPC. At the time of introduction in 2020, Apple said that the M1 had the world's fastest CPU core "in low power silicon" and the world's best CPU performance per watt. Its successor, Apple M2, was announced on June 6, 2022 at WWDC.

Apple M2 is a series of ARM-based system on a chip (SoC) designed by Apple Inc. as a central processing unit (CPU) and graphics processing unit (GPU) for its Mac desktops and notebooks, and the iPad Pro tablet. It is the second generation of ARM architecture intended for Apple's Mac computers after switching from Intel Core to Apple silicon, succeeding the M1. Apple announced the M2 on June 6, 2022, at WWDC, along with models of the MacBook Air and the 13-inch MacBook Pro using the M2. The M2 is made with TSMC's "Enhanced 5-nanometer technology" N5P process and contains 20 billion transistors, a 25% increase from the M1. Apple claims CPU improvements up to 18% and GPU improvements up to 35% compared to the M1.

BrainChip is an Australia-based technology company, founded in 2004 by Peter Van Der Made, that specializes in developing advanced artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) hardware. The company's primary products are the MetaTF development environment, which allows the training and deployment of spiking neural networks (SNN), and the AKD1000 neuromorphic processor, a hardware implementation of their spiking neural network system. BrainChip's technology is based on a neuromorphic computing architecture, which attempts to mimic the way the human brain works. The company is a part of Intel Foundry Services and Arm AI partnership.












