
The illegal drug trade, drug trafficking, or narcotrafficking is a global black market dedicated to the cultivation, manufacture, distribution and sale of prohibited drugs. Most jurisdictions prohibit trade, except under license, of many types of drugs through the use of drug prohibition laws. The think tank Global Financial Integrity's Transnational Crime and the Developing World report estimates the size of the global illicit drug market between US$426 and US$652 billion in 2014 alone. With a world GDP of US$78 trillion in the same year, the illegal drug trade may be estimated as nearly 1% of total global trade. Consumption of illegal drugs is widespread globally, and it remains very difficult for local authorities to reduce the rates of drug consumption.

Child prostitution is prostitution involving a child, and it is a form of commercial sexual exploitation of children. The term normally refers to prostitution of a minor, or person under the legal age of consent. In most jurisdictions, child prostitution is illegal as part of general prohibition on prostitution.
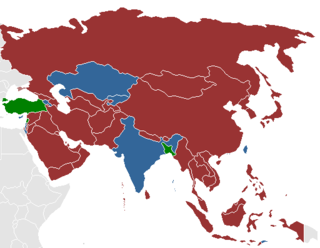
Prostitution is legal in India, but a number of related activities including soliciting, kerb crawling, owning or managing a brothel, prostitution in a hotel, child prostitution, pimping and pandering are illegal. There are, however, many brothels illegally operating in Indian cities including Mumbai, Delhi, Kolkata, Pune, and Nagpur, among others. UNAIDS estimate there were 657,829 prostitutes in the country as of 2016. Other unofficial estimates have calculated India has roughly 3 million prostitutes. India is widely regarded as having one of the world's largest commercial sex industry. It has emerged as a global hub of sex tourism, attracting sex tourists from wealthy countries. The sex industry in India is a multi-billion dollar one, and one of the fastest growing.
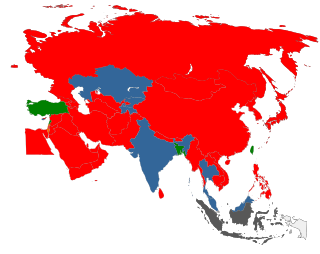
The legality of prostitution in Asia varies by country. There is often a significant difference in Asia between prostitution laws and the practice of prostitution. In 2011, the Asian Commission on AIDS estimated there were 10 million sex workers in Asia and 75 million male customers.

Since its independence in 1947, India has accepted various groups of refugees from neighbouring countries, including partition refugees from former British Indian territories that now constitute Pakistan and Bangladesh, Tibetan refugees that arrived in 1959, Chakma refugees from present day Bangladesh in early 1960s, other Bangladeshi refugees in 1965 and 1971, Sri Lankan Tamil refugees from the 1980s and most recently Rohingya refugees from Myanmar. In 1992, India was seen to be hosting 400,000 refugees from eight countries. According to records with the Union Ministry of Home Affairs, as on January 1,2021, there were 58,843 Sri Lankan refugees staying in 108 refugee camps in Tamil Nadu and 54 in Odisha and 72,312 Tibetan refugees have been living in India.
Ethnic relations in India have historically been complex. India is ethnically diverse, with more than 2,000 different ethnic groups. There is also significant diversity within regions, and almost every state and several districts has its own distinct mixture of ethnicities, traditions, and culture. Throughout the history of India, ethnic relations have been both positive and negative.
Organised crime in Nigeria includes activities by fraudsters, bandits, drug traffickers and racketeers, which have spread across Western Africa. Nigerian criminal gangs rose to prominence in the 1980s, owing much to the globalisation of the world's economies and the high level of lawlessness and corruption in the country.
Crime in India has been recorded since the British Raj, with comprehensive statistics now compiled annually by the National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB), under the Ministry of Home Affairs (India).

Prostitution is legal and regulated in Bangladesh. Prostitutes must register and state an affidavit stating that they are entering prostitution of their own free choice and that they are unable to find any other work. Bangladeshi prostitutes often suffer poor social conditions and are frequently socially degraded.
The 13 September 2008 Delhi bombings were a series of five synchronised bomb blasts that took place within the span of a few minutes on Saturday, 13 September 2008 at various locations in Delhi, India. The first bomb exploded at 18:07 IST, and four other blasts followed in succession, with at least 20 people killed and over 90 injured.

The legal status of prostitution in Africa varies widely. It is frequently common in practice, partially driven by the widespread poverty in many sub-Saharan African countries, and is one of the drivers for the prevalence of AIDS in Africa. Senegal and Côte d'Ivoire permit the operations of brothels. In other countries, prostitution may be legal, but brothels are not allowed to operate. In some countries where prostitution is illegal, the law is rarely enforced.

Sunitha Krishnan is an Indian social activist and chief functionary and co-founder of Prajwala, a non-governmental organization that rescues, rehabilitates and reintegrates sex-trafficked victims into society. She was awarded India's fourth highest civilian award the Padma Shri in 2016.

India has a very high volume of child trafficking. As many as one child disappears every eight minutes, according to the National Crime Records Bureau. In some cases, children are taken from their homes to be bought and sold in the market. In other cases, children are tricked into the hands of traffickers by being presented an opportunity for a job, when in reality, upon arrival they become enslaved. In India, there are many children trafficked for various reasons such as labor, begging, and sexual exploitation. Because of the nature of this crime, it is hard to track; due to the poor enforcement of laws, it is difficult to prevent. As such, there are only vague estimates of figures regarding the issue. India is a prime area for child trafficking to occur, as many of those trafficked are from, travel through or destined to go to India. Though most of the trafficking occurs within the country, there is also a significant number of children trafficked from Nepal and Bangladesh. There are many different causes that lead to child trafficking, with the primary reasons being poverty, weak law enforcement, and a lack of good quality public education. The traffickers that take advantage of children can be from another area in India, or could even know the child personally. Children who return home after being trafficked often face shame in their communities, rather than being welcomed home.
Prostitution in Bahrain is illegal but it has gained a reputation in the Middle East as major destination for sex tourism.

Crime in Thailand has been a defining issue in the country for decades, inspiring years of policy and international criticism. Drug use and corruption make up the majority of the crime in Thailand and due to this, many Thai administrations attempted to curtail the drug trade, most notably Thaksin Shinawatra with the 2003 War on Drugs. Since 2003 crime has been decreasing with the crime rate decreasing from 9.97 to 2.58. Despite this, juvenile delinquency has been increasing in recent years.

Somnath Bharti is an Indian lawyer who has become a politician representing the Aam Aadmi Party (AAP). As a lawyer, he practised at the Supreme Court of India and Delhi High Court. He was elected as the AAP candidate for the Malviya Nagar constituency in the 2013 Delhi state assembly elections and was Minister of Law, Tourism, Administrative Reforms, Art & Culture in the Government of Delhi, from 28 December 2013 to 14 February 2014, at which time the AAP government resigned. He has served as MLA from Malviya Nagar Constituency from February 2015 - February 2020. He served as Chairman, Committee on Privileges of Delhi Legislative Assembly for the year 2016–17. On 10 August 2018, Delhi Legislative Assembly appointed him as chairman, Committee to examine the Stray Dog and Monkey Menace in Delhi. He won the 2020 Delhi Elections by 18,144 votes. By Delhi Legislative Assembly he was appointed Chairman, Public Accounts Committee, Chairman, House Committee on Violation of Protocol Norms and Contemptuous Behaviour By Government Officers with MLAs, Members of Standing Committee on Education and Committee on Govt Undertakings.
An illegal immigrant in India is a foreigner who has entered India either without valid documents or who initially had a valid document, but has overstayed beyond the permitted time, as per the general provisions of the Citizenship Act as amended in 2003. Such persons are not eligible for citizenship by registration or naturalisation. They are also liable to be imprisoned for 2–8 years and fined.
Riots broke out in Kaliachak, Malda district in West Bengal, India on 3 January 2016. The Muslims were protesting the remark of political leaders Kamlesh Tiwari, But the protest turned into riots, when Muslim mob of more than 1 lakh people attacked the police and vandalised the police station of Kaliachak area.
The Citizenship (Amendment) Act, 2019 (CAA) was passed by the Parliament of India on 11 December 2019. It amended the Citizenship Act, 1955 by providing an accelerated pathway to Indian citizenship for persecuted religious minorities from Afghanistan, Bangladesh and Pakistan who arrived in India by 2014. The eligible minorities were stated as Hindus, Sikhs, Buddhists, Jains, Parsis or Christians. The law does not grant such eligibility to Muslims from these countries. The act was the first time that religion had been overtly used as a criterion for citizenship under Indian law, and it attracted global criticism.
Illicit drug trafficking in the West Indian Ocean (WIO) has increasingly become a major security concern for many States in the region, and is gaining international attention. The Indian Ocean borders 24 states, and accounts for a third of the world’s ocean area. Until recently, other challenges, such as piracy off the coast of Somalia, has been at the forefront of international action. However, the utilisation of the Southern route by drug traffickers, and the consequent issues this has caused, has led to increased focus on how to tackle this issue.










