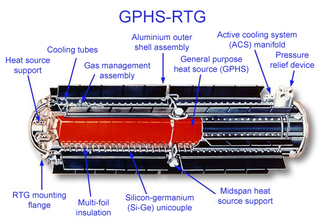
A radioisotope thermoelectric generator, sometimes referred to as a radioisotope power system (RPS), is a type of nuclear battery that uses an array of thermocouples to convert the heat released by the decay of a suitable radioactive material into electricity by the Seebeck effect. This type of generator has no moving parts and is ideal for deployment in remote and harsh environments for extended periods with no risk of parts wearing out or malfunctioning.

The Nimbus satellites were second-generation U.S. robotic spacecraft launched between 1964 and 1978 used for meteorological research and development. The spacecraft were designed to serve as stabilized, Earth-oriented platforms for the testing of advanced systems to sense and collect atmospheric science data. Seven Nimbus spacecraft have been launched into near-polar, Sun-synchronous orbits beginning with Nimbus 1 on August 28, 1964. On board the Nimbus satellites are various instrumentation for imaging, sounding, and other studies in different spectral regions. The Nimbus satellites were launched aboard Thor-Agena rockets and Delta rockets.

SNAP-10A was a US experimental nuclear powered satellite launched into space in 1965 as part of the SNAPSHOT program. The test marked both the world's first operation of a nuclear reactor in orbit, and the first operation of an ion thruster system in orbit. It is the only fission reactor power system launched into space by the United States. The reactor stopped working after just 43 days due to a non-nuclear electrical component failure. The Systems Nuclear Auxiliary Power Program reactor was specifically developed for satellite use in the 1950s and early 1960s under the supervision of the U.S. Atomic Energy Commission.

The Orbiting Carbon Observatory (OCO) is a NASA satellite mission intended to provide global space-based observations of atmospheric carbon dioxide. The original spacecraft was lost in a launch failure on 24 February 2009, when the payload fairing of the Taurus rocket which was carrying it failed to separate during ascent. The added mass of the fairing prevented the satellite from reaching orbit. It subsequently re-entered the atmosphere and crashed into the Indian Ocean near Antarctica. The replacement satellite, Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2, was launched 2 July 2014 aboard a Delta II rocket. The Orbiting Carbon Observatory-3, a stand-alone payload built from the spare OCO-2 flight instrument, was installed on the International Space Station's Kibō Exposed Facility in May 2019.
The Systems Nuclear Auxiliary POWER (SNAP) program was a program of experimental radioisotope thermoelectric generators (RTGs) and space nuclear reactors flown during the 1960s by NASA.
The Polar-orbiting Operational Environmental Satellite (POES) is a constellation of polar orbiting weather satellites funded by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and the European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites (EUMETSAT) with the intent of improving the accuracy and detail of weather analysis and forecasting. The spacecraft were provided by NASA and the European Space Agency (ESA), and NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center oversaw the manufacture, integration and test of the NASA-provided TIROS satellites. The first polar-orbiting weather satellite launched as part of the POES constellation was the Television Infrared Observation Satellite-N (TIROS-N), which was launched on 13 October 1978. The final spacecraft, NOAA-19, was launched on 6 February 2009. The ESA-provided MetOp satellite operated by EUMETSAT utilize POES-heritage instruments for the purpose of data continuity. The Joint Polar Satellite System, which was launched on 18 November 2017, is the successor to the POES Program.

The multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) is a type of radioisotope thermoelectric generator (RTG) developed for NASA space missions such as the Mars Science Laboratory (MSL), under the jurisdiction of the United States Department of Energy's Office of Space and Defense Power Systems within the Office of Nuclear Energy. The MMRTG was developed by an industry team of Aerojet Rocketdyne and Teledyne Energy Systems.

The Joint Polar Satellite System (JPSS) is the latest generation of U.S. polar-orbiting, non-geosynchronous, environmental satellites. JPSS will provide the global environmental data used in numerical weather prediction models for forecasts, and scientific data used for climate monitoring. JPSS will aid in fulfilling the mission of the U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), an agency of the Department of Commerce. Data and imagery obtained from the JPSS will increase timeliness and accuracy of public warnings and forecasts of climate and weather events, thus reducing the potential loss of human life and property and advancing the national economy. The JPSS is developed by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), who is responsible for operation of JPSS. Three to five satellites are planned for the JPSS constellation of satellites. JPSS satellites will be flown, and the scientific data from JPSS will be processed, by the JPSS – Common Ground System (JPSS-CGS).

Nuclear power in space is the use of nuclear power in outer space, typically either small fission systems or radioactive decay for electricity or heat. Another use is for scientific observation, as in a Mössbauer spectrometer. The most common type is a radioisotope thermoelectric generator, which has been used on many space probes and on crewed lunar missions. Small fission reactors for Earth observation satellites, such as the TOPAZ nuclear reactor, have also been flown. A radioisotope heater unit is powered by radioactive decay and can keep components from becoming too cold to function, potentially over a span of decades.

Nimbus 7 was a meteorological satellite. It was the seventh and last in a series of the Nimbus program.

Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) is a NASA Earth-observing satellite mission that will continue and advance observations of global ocean color, biogeochemistry, and ecology, as well as the carbon cycle, aerosols and clouds. PACE will be used to identify the extent and duration of phytoplankton blooms and improve understanding of air quality. These and other uses of PACE data will benefit the economy and society, especially sectors that rely on water quality, fisheries and food security.

NOAA-21, designated JPSS-2 prior to launch, is the second of the United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA)'s latest generation of U.S. polar-orbiting, non-geosynchronous, environmental satellites called the Joint Polar Satellite System. NOAA-21 was launched on 10 November 2022 and join NOAA-20 and Suomi NPP in the same orbit. Circling the Earth from pole-to-pole, it will cross the equator about 14 times daily, providing full global coverage twice a day. It was launched with LOFTID.

NOAA-20, designated JPSS-1 prior to launch, is the first of the United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's latest generation of U.S. polar-orbiting, non-geosynchronous, environmental satellites called the Joint Polar Satellite System. NOAA-20 was launched on 18 November 2017 and joined the Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership satellite in the same orbit. NOAA-20 operates about 50 minutes behind Suomi NPP, allowing important overlap in observational coverage. Circling the Earth from pole-to-pole, it crosses the equator about 14 times daily, providing full global coverage twice a day. This gives meteorologists information on "atmospheric temperature and moisture, clouds, sea-surface temperature, ocean color, sea ice cover, volcanic ash, and fire detection" so as to enhance weather forecasting including hurricane tracking, post-hurricane recovery by detailing storm damage and mapping of power outages.

TIROS-8 was a spin-stabilized meteorological satellite. It was the eighth in a series of Television Infrared Observation Satellites.

Nimbus 1 was a meteorological satellite. It was the first in a series of the Nimbus program.
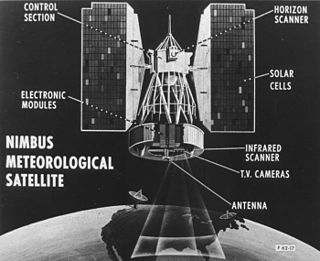
Nimbus 2 was a meteorological satellite. It was the second in a series of the Nimbus program.
Nimbus 3 was a meteorological satellite. It was the third in a series of the Nimbus program.

Nimbus 4 was a meteorological satellite. It was the fourth in a series of the Nimbus program.

Nimbus 6 was a meteorological satellite. It was the sixth in a series of the Nimbus program.

NOAA-5, also known as ITOS-H was a weather satellite operated by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). It was part of a series of satellites called ITOS, or improved TIROS, being the last of the series. NOAA-5 was launched on a Delta rocket on July 29, 1976.



















