
The Game Boy Advance (GBA) is a 32-bit handheld game console developed, manufactured and marketed by Nintendo as the successor to the Game Boy Color. It was released in Japan on March 21, 2001, in North America on June 11, 2001, in the PAL region on June 22, 2001, and in mainland China as iQue Game Boy Advance on June 8, 2004. The GBA is part of the sixth generation of video game consoles. The original model does not have an illuminated screen; Nintendo addressed that with the release of a redesigned model with a frontlit screen, the Game Boy Advance SP, in 2003. A newer revision of the redesign was released in 2005, with a backlit screen. Around the same time, the final redesign, the Game Boy Micro, was released in September 2005.

Nintendo Co., Ltd. is a Japanese multinational video game company headquartered in Kyoto, Japan. It develops video games and video game consoles.

Mario Bros. is a 1983 arcade game developed and published for arcades by Nintendo. It was designed by Shigeru Miyamoto and Gunpei Yokoi, Nintendo's chief engineer. Italian twin brother plumbers Mario and Luigi exterminate creatures emerging from the sewers by knocking them upside-down and kicking them away. The Famicom/Nintendo Entertainment System version is the first game produced by Intelligent Systems. It is part of the Mario franchise, but originally began as a spin-off from the Donkey Kong series.

The Nintendo DS is a handheld game console produced by Nintendo, released globally across 2004 and 2005. The DS, an initialism for "Developers' System" or "Dual Screen", introduced distinctive new features to handheld games: two LCD screens working in tandem, a built-in microphone and support for wireless connectivity. Both screens are encompassed within a clamshell design similar to the Game Boy Advance SP. The Nintendo DS also features the ability for multiple DS consoles to directly interact with each other over Wi-Fi within a short range without the need to connect to an existing wireless network. Alternatively, they could interact online using the now-defunct Nintendo Wi-Fi Connection service. Its main competitor was Sony's PlayStation Portable during the seventh generation of video game consoles.
Homebrew, when applied to video games, refers to games produced by hobbyists for proprietary video game consoles which are not intended to be user-programmable. The official documentation is often only available to licensed developers, and these systems may use storage formats that make distribution difficult, such as ROM cartridges or encrypted CD-ROMs. Many consoles have hardware restrictions to prevent unauthorized development. A non-professional developer for a system intended to be user-programmable, like the Commodore 64, is simply called a hobbyist.

Pokémon is a series of video games developed by Game Freak and published by Nintendo and The Pokémon Company under the Pokémon media franchise. It was created by Satoshi Tajiri with assistance from Ken Sugimori, the first games, Pocket Monsters Red and Green, were released in 1996 in Japan for the Game Boy, later released outside of Japan as Pokémon Red and Blue. The main series of role-playing video games (RPGs), referred as the "core series" by their developers, have continued on each generation of Nintendo's handhelds. The most recently released core series game, Pokémon Scarlet and Violet, was released on November 18, 2022, for the Nintendo Switch.

Official Nintendo Magazine, or ONM, was a British video game magazine that ran from 2006 to 2014 that covered the Nintendo DS, Nintendo 3DS, Wii, and Wii U video game consoles released by Nintendo.

PlayStation Magazine, also known by the acronym PSM, is an Italian video game magazine specializing in all Sony video game consoles and handheld gaming platforms. The magazine features previews, reviews, and cheat codes for Sony games.

Nintendo Gamer was a magazine published in the United Kingdom which mainly covered Nintendo video game consoles and software. It was the successor publication to N64 Magazine, later renamed NGC Magazine (1997–2006), and Super Play (1992–1996), continuing the unique style of those magazines. The publication was originally known as NGamer, with the first issue being released on 13 July 2006. From issue 71 onward, released on 5 January 2012, the magazine was renamed Nintendo Gamer and was significantly reformatted. On 30 August 2012, it was announced that issue 80 was to be the magazine's final issue.

Dengeki Nintendo is a Japanese gaming magazine published by ASCII Media Works. The magazine mainly covers information pertaining Nintendo games and consoles.

The Wii system software is a discontinued set of updatable firmware versions and a software frontend on the Wii home video game console. Updates, which could be downloaded over the Internet or read from a game disc, allowed Nintendo to add additional features and software, as well as to patch security vulnerabilities used by users to load homebrew software. When a new update became available, Nintendo sent a message to the Wii Message Board of Internet-connected systems notifying them of the available update.
Two Tribes B.V. is an independent video game developer based in Harderwijk, Netherlands. Founded in 2001 by Martijn Reuvers and Collin van Ginkel, it develops its own intellectual property and games for franchises. As announced on 10 March 2016, the office closed in September 2016, after the release of Rive. However, Two Tribes continues development of the Nintendo Switch version of Rive, as well as supporting older games.

The Japanese multinational consumer electronics company Nintendo has developed seven home video game consoles and multiple portable consoles for use with external media, as well as dedicated consoles and other hardware for their consoles. As of September 30, 2021, in addition to Nintendo Switch, Nintendo has sold over 863.07 million hardware units.

The Nintendo 3DS is a handheld game console produced by Nintendo. It was announced in March 2010 and unveiled at E3 2010 as the successor to the Nintendo DS. The system features backward compatibility with Nintendo DS video games. As an eighth-generation console, its primary competitor was Sony's PlayStation Vita.

The Nintendo 3DS system software is the updatable operating system used by the Nintendo 3DS.
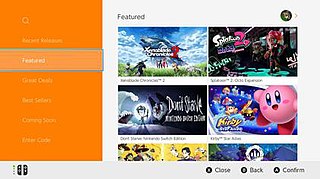
The Nintendo eShop is a digital distribution service powered by the Nintendo Network for the Wii U and Nintendo 3DS, and by a dedicated online infrastructure for the Nintendo Switch. Launched in June 2011 on the Nintendo 3DS, the eShop was enabled by the release of a system update that added the functionality to the Nintendo 3DS's HOME Menu. It is the successor to both the Wii Shop Channel and DSi Shop. Unlike on the Nintendo 3DS, the eShop was made available on the launch date of the Wii U, although a system update is required in order to access it. It is also a multitasking application, which means it is easily accessible even when a game is already running in the background through the system software, though this feature is exclusive to the Wii U and the Nintendo Switch. The Nintendo eShop features downloadable games, demos, applications, streaming videos, consumer rating feedback, and other information on upcoming game releases.
The eighth generation of video game consoles began in 2012, and consists of four home video game consoles: the Wii U released in 2012, the PlayStation 4 family in 2013, the Xbox One family in 2013, and the Nintendo Switch family in 2017.
The video game developer and publisher Nintendo has engaged in a variety of marketing campaigns, ranging from early efforts to appeal to teenagers with "Play It Loud!" to the more open-ended "Who Are You?" campaign. Nintendo also sometimes markets its various consoles and games with lavish promotions.

Majesco Entertainment Company is an American video game publisher and distributor based in Hazlet, New Jersey. The company was founded as Majesco Sales in Edison, New Jersey in 1986, and was a privately held company until acquiring operation-less company ConnectivCorp in a reverse merger takeover, becoming its subsidiary and thus a public company on December 5, 2003. ConnectivCorp later changed its name to Majesco Holdings Inc. on April 13, 2004.

Mario vs. Donkey Kong is a sub-series of the Mario and Donkey Kong series, based on puzzle video games, marking the return of Pauline and the rivalry between Mario and Donkey Kong.
















