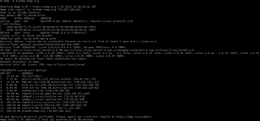
In computing, traceroute and tracert are computer network diagnostic commands for displaying possible routes (paths) and measuring transit delays of packets across an Internet Protocol (IP) network. The history of the route is recorded as the round-trip times of the packets received from each successive host in the route (path); the sum of the mean times in each hop is a measure of the total time spent to establish the connection. Traceroute proceeds unless all sent packets are lost more than twice; then the connection is lost and the route cannot be evaluated. Ping, on the other hand, only computes the final round-trip times from the destination point.
A port scanner is an application designed to probe a server or host for open ports. Such an application may be used by administrators to verify security policies of their networks and by attackers to identify network services running on a host and exploit vulnerabilities.
Network security consists of the policies, processes and practices adopted to prevent, detect and monitor unauthorized access, misuse, modification, or denial of a computer network and network-accessible resources. Network security involves the authorization of access to data in a network, which is controlled by the network administrator. Users choose or are assigned an ID and password or other authenticating information that allows them access to information and programs within their authority. Network security covers a variety of computer networks, both public and private, that are used in everyday jobs: conducting transactions and communications among businesses, government agencies and individuals. Networks can be private, such as within a company, and others which might be open to public access. Network security is involved in organizations, enterprises, and other types of institutions. It does as its title explains: it secures the network, as well as protecting and overseeing operations being done. The most common and simple way of protecting a network resource is by assigning it a unique name and a corresponding password.
In information technology, a Christmas tree packet is a packet with every single option set for whatever protocol is in use.
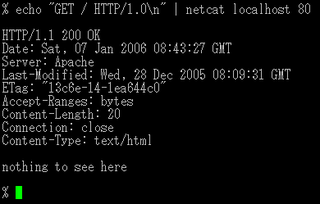
netcat is a computer networking utility for reading from and writing to network connections using TCP or UDP. The command is designed to be a dependable back-end that can be used directly or easily driven by other programs and scripts. At the same time, it is a feature-rich network debugging and investigation tool, since it can produce almost any kind of connection its user could need and has a number of built-in capabilities.

iStumbler is a utility for finding wireless networks and devices with AirPort or Bluetooth-enabled Macintosh computers.
A penetration test, colloquially known as a pentest, is an authorized simulated cyberattack on a computer system, performed to evaluate the security of the system; this is not to be confused with a vulnerability assessment. The test is performed to identify weaknesses, including the potential for unauthorized parties to gain access to the system's features and data, as well as strengths, enabling a full risk assessment to be completed.

Kismet is a network detector, packet sniffer, and intrusion detection system for 802.11 wireless LANs. Kismet will work with any wireless card which supports raw monitoring mode, and can sniff 802.11a, 802.11b, 802.11g, and 802.11n traffic. The program runs under Linux, FreeBSD, NetBSD, OpenBSD, and macOS. The client can also run on Microsoft Windows, although, aside from external drones, there's only one supported wireless hardware available as packet source.

TCP/IP stack fingerprinting is the remote detection of the characteristics of a TCP/IP stack implementation. The combination of parameters may then be used to infer the remote machine's operating system, or incorporated into a device fingerprint.

Ettercap is a free and open source network security tool for man-in-the-middle attacks on a LAN. It can be used for computer network protocol analysis and security auditing. It runs on various Unix-like operating systems including Linux, Mac OS X, BSD and Solaris, and on Microsoft Windows. It is capable of intercepting traffic on a network segment, capturing passwords, and conducting active eavesdropping against a number of common protocols. Its original developers later founded Hacking Team.
In the field of computer network administration, pcap is an application programming interface (API) for capturing network traffic. While the name is an abbreviation of packet capture, that is not the API's proper name. Unix-like systems implement pcap in the libpcap library; for Windows, there is a port of libpcap named WinPcap that is no longer supported or developed, and a port named Npcap for Windows 7 and later that is still supported.
OpenVAS is the scanner component of Greenbone Vulnerability Management (GVM), a software framework of several services and tools offering vulnerability scanning and vulnerability management.
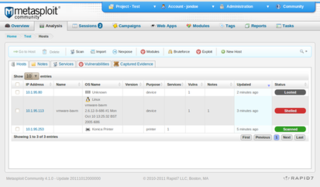
The Metasploit Project is a computer security project that provides information about security vulnerabilities and aids in penetration testing and IDS signature development. It is owned by Boston, Massachusetts-based security company Rapid7.

An idle scan is a TCP port scan method for determining what services are open on a target computer without leaving traces pointing back at oneself. This is accomplished by using packet spoofing to impersonate another computer so that the target believes it's being accessed by the zombie. The target will respond in different ways depending on whether the port is open, which can in turn be detected by querying the zombie.
In computing, a ping sweep is a method that can establish a range of IP addresses which map to live hosts.
Network enumeration is a computing activity in which usernames and info on groups, shares, and services of networked computers are retrieved. It should not be confused with network mapping, which only retrieves information about which servers are connected to a specific network and what operating system runs on them. Network enumeration is the discovery of hosts or devices on a network. Network enumeration tends to use overt discovery protocols such as ICMP and SNMP to gather information. It may also scan various ports on remote hosts for looking for well known services in an attempt to further identify the function of a remote host. The next stage of enumeration is to fingerprint the operating system of the remote host.

OpenSSH is a suite of secure networking utilities based on the Secure Shell (SSH) protocol, which provides a secure channel over an unsecured network in a client–server architecture.
Paping is a computer network administration utility used to test the reachability of a host on an Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) network and to measure the time it takes to connect to a specified port. The name is a play on the word ping, another computer network administration utility.
Avira Operations GmbH & Co. KG is a German multinational computer security software company mainly known for its Avira Free Security antivirus software. Although founded in 2006, the Avira antivirus application has been under active development since 1986 through its predecessor company H+BEDV Datentechnik GmbH. Since 2021, Avira has been owned by American software company NortonLifeLock, which also operates Norton, Avast and AVG. It was previously owned by investment firm Investcorp.

Kali Linux is a Linux distribution designed for digital forensics and penetration testing. It is maintained and funded by Offensive Security. The software is based on the Debian Testing branch: most packages Kali uses are imported from the Debian repositories.