| Public finance |
|---|
 |
Non-tax revenue or non-tax receipts are government revenue not generated from taxes. For example - bond issues and profits of state-owned companies.
| Public finance |
|---|
 |
Non-tax revenue or non-tax receipts are government revenue not generated from taxes. For example - bond issues and profits of state-owned companies.
Non-tax revenues can fluctuate significantly from one year to another. Indeed, their value is correlated with changing economic circumstances, repayments and interest on loans may be renegotiated, a record fine in the field of competition can significantly vary the profits of fines and penalties. Moreover, some years are marked by exceptional events: for example, in France in 2012, the sale of "4G" radio frequencies resulted in the collection of nearly €1.3 billion in non-tax revenues.
A tax is a compulsory financial charge or some other type of levy imposed on a taxpayer by a governmental organization in order to collectively fund government spending, public expenditures, or as a way to regulate and reduce negative externalities. Tax compliance refers to policy actions and individual behaviour aimed at ensuring that taxpayers are paying the right amount of tax at the right time and securing the correct tax allowances and tax relief. The first known taxation took place in Ancient Egypt around 3000–2800 BC. Taxes consist of direct or indirect taxes and may be paid in money or as its labor equivalent.
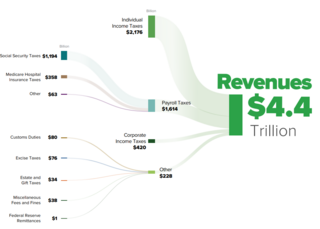
The United States has separate federal, state, and local governments with taxes imposed at each of these levels. Taxes are levied on income, payroll, property, sales, capital gains, dividends, imports, estates and gifts, as well as various fees. In 2020, taxes collected by federal, state, and local governments amounted to 25.5% of GDP, below the OECD average of 33.5% of GDP.
In the United States, a 401(k) plan is an employer-sponsored, defined-contribution, personal pension (savings) account, as defined in subsection 401(k) of the U.S. Internal Revenue Code. Periodic employee contributions come directly out of their paychecks, and may be matched by the employer. This legal option is what makes 401(k) plans attractive to employees, and many employers offer this option to their (full-time) workers. 401(k) payable is a general ledger account that contains the amount of 401(k) plan pension payments that an employer has an obligation to remit to a pension plan administrator. This account is classified as a payroll liability, since the amount owed should be paid within one year.
A television licence or broadcast receiving licence is a payment required in many countries for the reception of television broadcasts or the possession of a television set. In some countries, a licence is also required to own a radio or receive radio broadcasts. In such countries, some broadcasts are funded in full or in part by the licence fees. Licence fees are effectively a hypothecated tax to fund public broadcasting.

Public finance is the study of the role of the government in the economy. It is the branch of economics that assesses the government revenue and government expenditure of the public authorities and the adjustment of one or the other to achieve desirable effects and avoid undesirable ones. The purview of public finance is considered to be threefold, consisting of governmental effects on:

A fee is the price one pays as remuneration for rights or services. Fees usually allow for overhead, wages, costs, and markup. Traditionally, professionals in the United Kingdom receive a fee in contradistinction to a payment, salary, or wage, and often use guineas rather than pounds as units of account. Under the feudal system, a Knight's fee was what was given to a knight for his service, usually the usage of land. A contingent fee is an attorney's fee which is reduced or not charged at all if the court case is lost by the attorney.
In many states with political systems derived from the Westminster system, a consolidated fund or consolidated revenue fund is the main bank account of the government. General taxation is taxation paid into the consolidated fund, and general spending is paid out of the consolidated fund.

A taxpayer is a person or organization subject to pay a tax. Modern taxpayers may have an identification number, a reference number issued by a government to citizens or firms.
A 529 plan, also called a Qualified Tuition Program, is a tax-advantaged investment vehicle in the United States designed to encourage saving for the future higher education expenses of a designated beneficiary. In 2017, K–12 public, private, and religious school tuition were included as qualified expenses for 529 plans along with post-secondary education costs after passage of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act.

In the United Kingdom, taxation may involve payments to at least three different levels of government: central government, devolved governments and local government. Central government revenues come primarily from income tax, National Insurance contributions, value added tax, corporation tax and fuel duty. Local government revenues come primarily from grants from central government funds, business rates in England, Council Tax and increasingly from fees and charges such as those for on-street parking. In the fiscal year 2014–15, total government revenue was forecast to be £648 billion, or 37.7 per cent of GDP, with net taxes and National Insurance contributions standing at £606 billion.
Road tax, known by various names around the world, is a tax which has to be paid on, or included with, a motorised vehicle to use it on a public road.
In France, taxation is determined by the yearly budget vote by the French Parliament, which determines which kinds of taxes can be levied and which rates can be applied.

Fund accounting is an accounting system for recording resources whose use has been limited by the donor, grant authority, governing agency, or other individuals or organisations or by law. It emphasizes accountability rather than profitability, and is used by Nonprofit organizations and by governments. In this method, a fund consists of a self-balancing set of accounts and each are reported as either unrestricted, temporarily restricted or permanently restricted based on the provider-imposed restrictions.
The tax system of the Russian Federation is a complex of relationships between fiscal authorities and taxpayers in the field of all existing taxes and fees. It implies continuous communication of all its members and related objects: payers; legislative framework; oversight authorities; types of mandatory payments. The Russian Tax Code is the primary tax law for the Russian Federation. The Code was created, adopted and implemented in three stages.
The Oklahoma Tax Commission (OTC) is the Oklahoma state government agency that collects taxes and enforces the taxation and revenue laws of the state. The Commission is composed of three members appointed by the Governor of Oklahoma and confirmed by the Oklahoma Senate. The Commissioners are charged with oversight of the agency but appoint an Executive Director to serve as the chief administrative officer of the Commission and to oversee the general practices of the Commission.

Government revenue or national revenue is money received by a government from taxes and non-tax sources to enable it, assuming full resource employment, to undertake non-inflationary public expenditure. Government revenue as well as government spending are components of the government budget and important tools of the government's fiscal policy. The collection of revenue is the most basic task of a government, as the resources released via the collection of revenue are necessary for the operation of government, provision of the common good and enforcement of its laws; this necessity of revenue was a major factor in the development of the modern bureaucratic state.
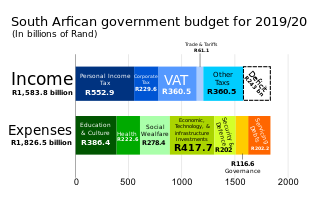
Taxation may involve payments to a minimum of two different levels of government: central government through SARS or to local government. Prior to 2001 the South African tax system was "source-based", where in income is taxed in the country where it originates. Since January 2001, the tax system was changed to "residence-based" wherein taxpayers residing in South Africa are taxed on their income irrespective of its source. Non residents are only subject to domestic taxes.

The Moving Ahead for Progress in the 21st Century Act (MAP-21) is a funding and authorization bill to govern United States federal surface transportation spending. It was passed by Congress on June 29, 2012, and President Barack Obama signed it on July 6. The vote was 373–52 in the House of Representatives and 74–19 in the Senate.
In Malaysia, federal budgets are presented annually by the Government of Malaysia to identify proposed government revenues and spending and forecast economic conditions for the upcoming year, and its fiscal policy for the forward years. The federal budget includes the government's estimates of revenue and spending and may outline new policy initiatives. Federal budgets are usually released in October, before the start of the fiscal year. All of the Malaysian states also present budgets. Since state finances are dependent on money from the federal government, these budgets are usually released after the federal one.

On November 8, 2016, Illinois voters approved the Illinois Transportation Taxes and Fees Lockbox Amendment, a legislatively referred constitutional amendment that prohibits lawmakers from using transportation funds for anything other than their stated purpose.