
In organic chemistry, an alkane, or paraffin, is an acyclic saturated hydrocarbon. In other words, an alkane consists of hydrogen and carbon atoms arranged in a tree structure in which all the carbon–carbon bonds are single. Alkanes have the general chemical formula CnH2n+2. The alkanes range in complexity from the simplest case of methane, where n = 1, to arbitrarily large and complex molecules, like pentacontane or 6-ethyl-2-methyl-5-(1-methylethyl) octane, an isomer of tetradecane.

Paraffin wax is a soft colorless solid derived from petroleum, coal, or oil shale that consists of a mixture of hydrocarbon molecules containing between 20 and 40 carbon atoms. It is solid at room temperature and begins to melt above approximately 37 °C (99 °F), and its boiling point is above 370 °C (698 °F). Common applications for paraffin wax include lubrication, electrical insulation, and candles; dyed paraffin wax can be made into crayons. It is distinct from kerosene and other petroleum products that are sometimes called paraffin.
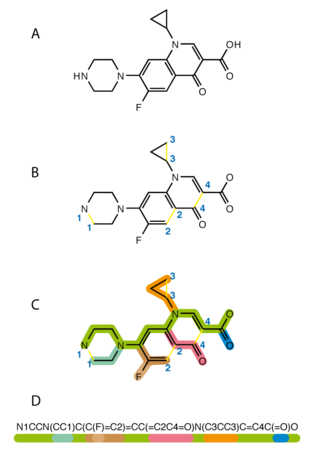
The simplified molecular-input line-entry system (SMILES) is a specification in the form of a line notation for describing the structure of chemical species using short ASCII strings. SMILES strings can be imported by most molecule editors for conversion back into two-dimensional drawings or three-dimensional models of the molecules.
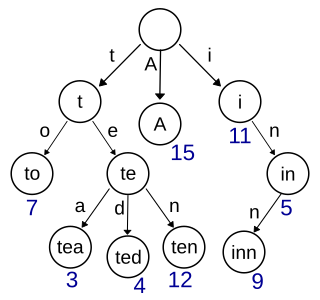
In computer science, a trie, also called digital tree or prefix tree, is a type of k-ary search tree, a tree data structure used for locating specific keys from within a set. These keys are most often strings, with links between nodes defined not by the entire key, but by individual characters. In order to access a key, the trie is traversed depth-first, following the links between nodes, which represent each character in the key.

Iodoform is the organoiodine compound with the chemical formula CHI3. It is a pale yellow, crystalline, volatile substance, with a penetrating and distinctive odor and, analogous to chloroform, sweetish taste. It is occasionally used as a disinfectant.

In computing, SQL injection is a code injection technique used to attack data-driven applications, in which malicious SQL statements are inserted into an entry field for execution. SQL injection must exploit a security vulnerability in an application's software, for example, when user input is either incorrectly filtered for string literal escape characters embedded in SQL statements or user input is not strongly typed and unexpectedly executed. SQL injection is mostly known as an attack vector for websites but can be used to attack any type of SQL database.
A chemical database is a database specifically designed to store chemical information. This information is about chemical and crystal structures, spectra, reactions and syntheses, and thermophysical data.

The Entrez Global Query Cross-Database Search System is a federated search engine, or web portal that allows users to search many discrete health sciences databases at the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) website. The NCBI is a part of the National Library of Medicine (NLM), which is itself a department of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), which in turn is a part of the United States Department of Health and Human Services. The name "Entrez" was chosen to reflect the spirit of welcoming the public to search the content available from the NLM.
A query string is a part of a uniform resource locator (URL) that assigns values to specified parameters. A query string commonly includes fields added to a base URL by a Web browser or other client application, for example as part of an HTML document, choosing the appearance of a page, or jumping to positions in multimedia content.
In chemistry, dehydrogenation is a chemical reaction that involves the removal of hydrogen, usually from an organic molecule. It is the reverse of hydrogenation. Dehydrogenation is important, both as a useful reaction and a serious problem. At its simplest, it is useful way of converting alkanes, which are relatively inert and thus low-valued, to olefins, which are reactive and thus more valuable. Alkenes are precursors to aldehydes, alcohols, polymers, and aromatics. As a problematic reaction, the fouling and inactivation of many catalysts arises via coking, which is the dehydrogenative polymerization of organic substrates.
The International Chemical Identifier is a textual identifier for chemical substances, designed to provide a standard way to encode molecular information and to facilitate the search for such information in databases and on the web. Initially developed by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) and National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) from 2000 to 2005, the format and algorithms are non-proprietary. Since May 2009, it has been developed by the InChI Trust, a nonprofit charity from the United Kingdom which works to implement and promote the use of InChI.

Rose oil is the essential oil extracted from the petals of various types of rose. Rose ottos are extracted through steam distillation, while rose absolutes are obtained through solvent extraction, the absolute being used more commonly in perfumery. The production technique originated in Greater Iran. Even with their high price and the advent of organic synthesis, rose oils are still perhaps the most widely used essential oil in perfumery.
SPARQL is an RDF query language—that is, a semantic query language for databases—able to retrieve and manipulate data stored in Resource Description Framework (RDF) format. It was made a standard by the RDF Data Access Working Group (DAWG) of the World Wide Web Consortium, and is recognized as one of the key technologies of the semantic web. On 15 January 2008, SPARQL 1.0 was acknowledged by W3C as an official recommendation, and SPARQL 1.1 in March, 2013.
The DrugBank database is a comprehensive, freely accessible, online database containing information on drugs and drug targets created and maintained by the University of Alberta and The Metabolomics Innovation Centre located in Alberta, Canada. As both a bioinformatics and a cheminformatics resource, DrugBank combines detailed drug data with comprehensive drug target information. DrugBank has used content from Wikipedia; Wikipedia also often links to Drugbank, posing potential circular reporting issues.
ChemSpider is a freely accessible online database of chemicals owned by the Royal Society of Chemistry. It contains information on more than 100 million molecules from over 270 data sources, each of them receiving a unique identifier called ChemSpider Identifier.

In computing, POST is a request method supported by HTTP used by the World Wide Web. By design, the POST request method requests that a web server accept the data enclosed in the body of the request message, most likely for storing it. It is often used when uploading a file or when submitting a completed web form.
The BitterDB is a database of compounds that were reported to taste bitter to humans. The aim of the BitterDB database is to gather information about bitter-tasting natural and synthetic compounds, and their cognate bitter taste receptors.
The Yeast Metabolome Database (YMDB) is a comprehensive, high-quality, freely accessible, online database of small molecule metabolites found in or produced by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The YMDB was designed to facilitate yeast metabolomics research, specifically in the areas of general fermentation as well as wine, beer and fermented food analysis. YMDB supports the identification and characterization of yeast metabolites using NMR spectroscopy, GC-MS spectrometry and Liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. The YMDB contains two kinds of data: 1) chemical data and 2) molecular biology/biochemistry data. The chemical data includes 2027 metabolite structures with detailed metabolite descriptions along with nearly 4000 NMR, GC-MS and LC/MS spectra.
The E. coli Metabolome Database (ECMDB) is a comprehensive, high-quality, freely accessible, online database of small molecule metabolites found in or produced by Escherichia coli. Escherichia coli is perhaps the best studied bacterium on earth and has served as the "model microbe" in microbiology research for more than 60 years. The ECMDB is essentially an E. coli "omics" encyclopedia containing detailed data on E. coli's genome, proteome and its metabolome. ECMDB is part of a suite of organism-specific metabolomics databases that includes DrugBank, HMDB, YMDB and SMPDB. As a metabolomics resource, the ECMDB is designed to facilitate research in the area gut/microbiome metabolomics and environmental metabolomics. The ECMDB contains two kinds of data: 1) chemical data and 2) molecular biology and/or biochemical data. The chemical data includes more than 2700 metabolite structures with detailed metabolite descriptions along with nearly 5000 NMR, GC-MS and LC-MS spectra corresponding to these metabolites. The biochemical data includes nearly 1600 protein sequences and more than 3100 biochemical reactions that are linked to these metabolite entries. Each metabolite entry in the ECMDB contains more than 80 data fields with approximately 65% of the information being devoted to chemical data and the other 35% of the information devoted to enzymatic or biochemical data. Many data fields are hyperlinked to other databases. The ECMDB also has a variety of structure and pathway viewing applets. The ECMDB database offers a number of text, sequence, spectral, chemical structure and relational query searches. These are described in more detail below.
Microsoft Azure Cognitive Search, formerly known as Azure Search, is a component of the Microsoft Azure Cloud Platform providing indexing and querying capabilities for data uploaded to Microsoft servers. The Search as a service framework is intended to provide developers with complex search capabilities for mobile and web development while hiding infrastructure requirements and search algorithm complexities. Azure Search is a recent addition to Microsoft's Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) approach.









