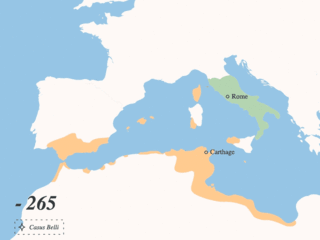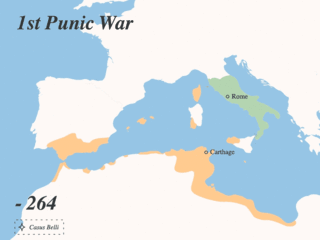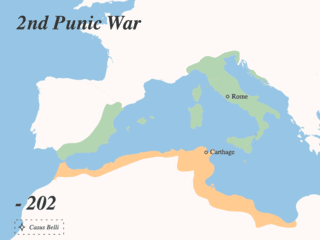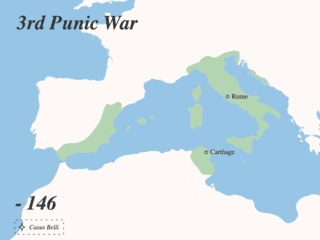
The Punic Wars were a series of wars between 264 and 146 BC fought between Rome and Carthage. Three conflicts between these states took place on both land and sea across the western Mediterranean region and involved a total of forty-three years of warfare. The Punic Wars are also considered to include the four-year-long revolt against Carthage which started in 241 BC. Each war involved immense materiel and human losses on both sides.

The Second Punic War was the second of three wars fought between Carthage and Rome, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean in the 3rd century BC. For 17 years the two states struggled for supremacy, primarily in Italy and Iberia, but also on the islands of Sicily and Sardinia and, towards the end of the war, in North Africa. After immense materiel and human losses on both sides, the Carthaginians were defeated. Macedonia, Syracuse and several Numidian kingdoms were drawn into the fighting, and Iberian and Gallic forces fought on both sides. There were three main military theatres during the war: Italy, where Hannibal defeated the Roman legions repeatedly, with occasional subsidiary campaigns in Sicily, Sardinia and Greece; Iberia, where Hasdrubal, a younger brother of Hannibal, defended the Carthaginian colonial cities with mixed success before moving into Italy; and Africa, where Rome finally won the war.
Year 218 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Scipio and Longus. The denomination 218 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Hamilcar Barca or Barcas was a Carthaginian general and statesman, leader of the Barcid family, and father of Hannibal, Hasdrubal and Mago. He was also father-in-law to Hasdrubal the Fair.
The Battle of Zama was fought in 202 BC in what is now Tunisia between a Roman army commanded by Scipio Africanus and a Carthaginian army commanded by Hannibal. The battle was part of the Second Punic War and resulted in such a severe defeat for the Carthaginians that they capitulated. The Roman army of approximately 30,000 men was outnumbered by the Carthaginians who fielded either 40,000 or 50,000; the Romans were stronger in cavalry, but the Carthaginians had 80 war elephants.

The Battle of Lake Trasimene was fought when a Carthaginian force under Hannibal ambushed a Roman army commanded by Gaius Flaminius on 21 June 217 BC, during the Second Punic War. The battle took place on the north shore of Lake Trasimene, to the south of Cortona, and resulted in a heavy defeat for the Romans.

A war elephant was an elephant that was trained and guided by humans for combat. The war elephant's main use was to charge the enemy, break their ranks, and instill terror and fear. Elephantry is a term for specific military units using elephant-mounted troops.

The Battle of Agrigentum was the first pitched battle of the First Punic War and the first large-scale military confrontation between Carthage and the Roman Republic. The battle was fought after a long siege which started in 262 BC and resulted both in a Roman victory and the beginning of Roman control of Sicily.

Hasdrubal Barca, a latinization of ʿAzrubaʿal son of Hamilcar Barca, was a Carthaginian general in the Second Punic War. He was the brother of Hannibal and Mago Barca.

The Battle of the Saw was the culminating battle of a campaign fought between a Carthaginian army led by Hamilcar Barca and a rebel force led by Spendius in 238 BC in what is now northern Tunisia. Carthage was fighting a coalition of mutinous soldiers and rebellious African cities in the Mercenary War which had started in 241 BC. The rebels had been besieging Carthage while the Carthaginian field army under Hamilcar raided their supply lines. Under this pressure the rebels pulled back to their base at Tunis and despatched their own army to prevent Hamilcar's activities and, ideally, destroy his army.

The Battle of Cissa was part of the Second Punic War. It was fought in the fall of 218 BC, near the Celtic town of Tarraco in north-eastern Iberia. A Roman army under Gnaeus Cornelius Scipio Calvus defeated an outnumbered Carthaginian army under Hanno, thus gaining control of the territory north of the Ebro River that Hannibal had just subdued a few months prior in the summer of 218 BC. This was the first battle that the Romans had ever fought in Iberia. It allowed the Romans to establish a secure base among friendly Iberian tribes, and due to the eventual success of the Scipio brothers in Spain, Hannibal looked for but never received reinforcements from Spain during the war.

The Battle of Ibera, also known as the Battle of Dertosa, was fought in the spring of 215 BC on the south bank of the Ebro River near the town of Ibera and was part of the Second Punic War. A Roman army, under the command of the brothers Gnaeus and Publius Scipio, defeated a similarly sized Carthaginian army under Hasdrubal Barca. The Romans, under Gnaeus Scipio, had invaded Iberia in late 218 BC and established a foothold after winning the Battle of Cissa. This lodgement, on the north-east Iberian coast, between the Ebro and the Pyrenees, blocked the route of any reinforcements from Iberia for the army of Hannibal, who had invaded Italy from Iberia earlier in the year. Hasdrubal attempted to evict the Romans in 217 BC, but this ended in defeat when the Carthaginian naval contingent was mauled at the Battle of Ebro River.
The military of Carthage was one of the largest military forces in the ancient world. Although Carthage's navy was always its main military force, the army acquired a key role in the spread of Carthaginian power over the native peoples of northern Africa and southern Iberian Peninsula from the 6th century BC and the 3rd century BC. Carthage's military also allowed it to expand into Sardinia and the Balearic Islands. This expansion transformed the military from a body of citizen-soldiers into a multinational force composed of a combination of allies, citizens and foreign mercenary units.

The city of Carthage was founded in the 9th century BC on the coast of Northwest Africa, in what is now Tunisia, as one of a number of Phoenician settlements in the western Mediterranean created to facilitate trade from the city of Tyre on the coast of what is now Lebanon. The name of both the city and the wider republic that grew out of it, Carthage developed into a significant trading empire throughout the Mediterranean. The date from which Carthage can be counted as an independent power cannot exactly be determined, and probably nothing distinguished Carthage from the other Phoenician colonies in Northwest Africa and the Mediterranean during 800–700 BC. By the end of the 7th century BC, Carthage was becoming one of the leading commercial centres of the West Mediterranean region. After a long conflict with the emerging Roman Republic, known as the Punic Wars, Rome finally destroyed Carthage in 146 BC. A Roman Carthage was established on the ruins of the first. Roman Carthage was eventually destroyed—its walls torn down, its water supply cut off, and its harbours made unusable—following its conquest by Arab invaders at the close of the 7th century. It was replaced by Tunis as the major regional centre, which has spread to include the ancient site of Carthage in a modern suburb.

The Battle of the Rhône Crossing was a battle during the Second Punic War in September of 218 BC. Hannibal marched on the Italian Alps, and an army of Gallic Volcae attacked the Carthaginian army on the east bank of the Rhône. The Roman army camped near Massalia. The Volcae tried to prevent the Carthaginians from crossing the Alps and invading Italy.

Ancient Carthage was an ancient Semitic civilization centered in North Africa. Initially a settlement in present-day Tunisia, it later became a city-state and then an empire. Founded by the Phoenicians in the ninth century BC, Carthage reached its height in the fourth century BC as one of the largest metropolises in the world. It was the centre of the Carthaginian Empire, a major power led by Punic people who dominated the ancient western and central Mediterranean Sea. Following the Punic Wars, Carthage was destroyed by the Romans in 146 BC, who later rebuilt the city lavishly.

Surus was believed to be the last war elephant of Carthaginian general Hannibal's army in Italy.
During the siege of Tunis in October 238 BC a rebel army under Mathos was besieged by a Carthaginian force under Hamilcar Barca and Hannibal. The Carthaginian army, which had served on Sicily during the First Punic War, mutinied in late 241 BC in the wake of Carthage's defeat, starting the Mercenary War. After three years of increasingly bitter war, the Carthaginians defeated the rebel field army at the Battle of the Saw, capturing its leaders. The Carthaginians then moved to besiege the rebels' strongest remaining stronghold at Tunis.
Hamilcar's victory with Naravas took place in 240 BC in what is now north-west Tunisia. A Carthaginian army led by Hamilcar Barca defeated a rebel army led by Spendius and Autaritus, after 2,000 Numidian cavalry led by Naravas defected from the rebels to Carthage. The precise location location of the battle is unknown. Carthage was fighting a coalition of mutinous soldiers and rebellious African cities in the Mercenary War which had started in 241 BC.
The Battle of Oroscopa was fought between a Carthaginian army of more than 30,000 men commanded by the general Hasdrubal and a Numidian force of unknown size under its king, Masinissa. It took place in late 151 BC near the ancient town of Oroscopa in what is now north western Tunisia. The battle resulted in a heavy Carthaginian defeat.















