
Foster care is a system in which a minor has been placed into a ward, group home, or private home of a state-certified caregiver, referred to as a "foster parent", or with a family member approved by the state. The placement of a "foster child" is normally arranged through the government or a social service agency. The institution, group home, or foster parent is compensated for expenses unless with a family member. In some states, relative or "Kinship" caregivers of children who are wards of the state are provided with a financial stipend.

John Lester Hubbard Chafee was an American politician and officer in the United States Marine Corps. A member of the Republican Party, he served as the 66th Governor of Rhode Island, as the Secretary of the Navy, and as a United States Senator.
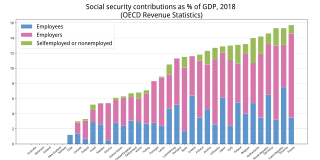
Social insurance is a form of social welfare that provides insurance against economic risks. The insurance may be provided publicly or through the subsidizing of private insurance. In contrast to other forms of social assistance, individuals' claims are partly dependent on their contributions, which can be considered insurance premiums to create a common fund out of which the individuals are then paid benefits in the future.
Foster children in Canada are known as permanent wards. A ward is someone, in this case a child, placed under protection of a legal guardian and are the legal responsibility of the government. Census data from 2011 counted children in foster care for the first time, counting 47,885 children in care. The majority of foster children – 29,590, or about 62% – were aged 14 and under. The wards remain under the care of the government until they "age out of care." This age is different depending on the province.
Kinship care is a term used in the United States and Great Britain for the raising of children by grandparents, other extended family members, and unrelated adults with whom they have a close family-like relationship such as godparents and close family friends because biological parents are unable to do so for whatever reason. Legal custody of a child may or may not be involved, and the child may be related by blood, marriage, or adoption. This arrangement is also known as "kincare" or "relative care." Kinship placement may reduce the number of home placements children experience; allow children to maintain connections to communities, schools, and family members; and increase the likelihood of eventual reunification with birth parents. It is less costly to taxpayers than formal foster care and keeps many children out of the foster care system. "Grandfamily" is a recently coined term in the United States that refers to families engaged in kinship care.

The North Carolina Department of Health and Human Services is a large state government agency in the U.S. state of North Carolina, somewhat analogous to the United States Department of Health and Human Services. The NCDHHS has more than 19,000 employees. The NCDHHS has its origins in the former North Carolina Department of Human Resources (DHR). The head of NCDHHS (Secretary) is appointed by the Governor of North Carolina and is a member of the North Carolina Cabinet in the executive branch of the North Carolina government. The NCDHHS was created in 1971.
Transitional age youth can reference both a developmental period and be a descriptor regarding eligibility for certain services. While there are variations in definitions, the age ranges do consistently overlap and include late adolescence to early adulthood. This range is considered a critical period in human development characterized by several changes socially, environmentally, and cognitively. During this time, individuals can experience changes in their social roles and function, family and peer supports, exposure to substance use, educational and vocational programs, as well as changes in healthcare providers from pediatric to adult settings.
Aging out is American popular culture vernacular used to describe anytime a youth leaves a formal system of care designed to provide services below a certain age level.
Early Head Start is a federally funded community-based program for low-income families with pregnant women, infants, and toddlers up to age 3. It is a program that came out of Head Start. The program was designed in 1994 by an Advisory Committee on Services for Families with Infants and Toddlers formed by the Secretary of Health and Human Services. "In addition to providing or linking families with needed services—medical, mental health, nutrition, and education—Early Head Start can provide a place for children to experience consistent, nurturing relationships and stable, ongoing routines."

Cherry Hospital is an inpatient regional referral psychiatric hospital located in Goldsboro, North Carolina, United States. As one of three psychiatric hospitals operated by the North Carolina Department of Health and Human Services, it provides services to 38 counties in the eastern region of North Carolina. It is part of the Division of State Operated Healthcare Facilities within the Department of Health and Human Services, which oversees and manages 14 state-operated healthcare facilities that treat adults and children with mental illness, developmental disabilities, and substance use disorders. The Division's psychiatric hospitals provide comprehensive inpatient mental health services to people with psychiatric illness who cannot be safely treated at a lower level of care.

The Foster Care Independence Act of 1999 aims to assist youth aging out of foster care in the United States in obtaining and maintaining independent living skills. Youth aging out of foster care, or transitioning out of the formal foster care system, are one of the most vulnerable and disadvantaged populations. As youth age out of the foster care system at age 18, they are expected to become self-sufficient immediately, even though on average youth in the United States are not expected to reach self-sufficiency until age 26.
The Pennsylvania Department of Aging is a cabinet-level agency charged with providing aid to Pennsylvania's approximately three million individuals age 60 and older. Although the bureau operates some services directly, such as the Pharmaceutical Contact for the Elderly (PACE) prescription drug program, it generally serves as a clearinghouse of funding and information for county-level Area Agencies on Aging. The department was formed under the governorship of Milton Shapp.
Disability benefits are funds provided from public or private sources to a person who is ill or who has a disability.
The Fostering Connections to Success and Increasing Adoptions Act of 2008 was an Act of Congress in the United States signed into law by President George W. Bush on October 7, 2008. It was previously unanimously passed in both the House of Representatives and in the Senate. The law made numerous changes to the child welfare system, mostly to Title IV-E of the Social Security Act, which covers federal payments to states for foster care and adoption assistance. According to child welfare experts and advocates, the law made the most significant federal improvements to the child welfare system in over a decade.
The state of North Carolina is undertaking a comprehensive policy shift on how the government budgets for and manages resources for mental health, developmental disability, and substance abuse services. The 1915 (b)(c) Medicaid Waiver Program was chosen by the North Carolina Department of Health & Human Services, Division of Medical Assistance as a way to control and more accurately budget for the rising costs of Medicaid funded services. The 1915 (b)(c) Waiver Program was initially implemented at one pilot site in 2005 and evaluated for several years. Two expansion sites were then added in 2012. Full statewide implementation is expected by July 1, 2013.

Foster care is the term used for a system in which a minor who has been made a ward is placed in an institution, group home, relative placement, or private home of a state certified caregiver. The placement of the child is usually arranged through the government or a social-service agency. The institution, group home, or foster parent is paid. The state via the family court and child protection agency stand in loco parentis to the minor, making all legal decisions, while the foster parent is responsible for the day-to-day care of the minor. The foster parent is remunerated by the state for their services.
Taiwan Fund for Children and Families is a nonprofit organization in Taiwan that provides services to vulnerable children and families who are below 18 years of age. “Livelihood Supports” and “Child Protection” are its two main target programs. Regardless of race, religion and gender, TFCF was founded in 1950 with a helping hand from Christian Children's Fund, a NGO from Virginia, United States. It went independent during 1985. Presently, it has 24 branch offices, 1 Ta-Tung Children's Home and other 11 Affiliates, 3 Non-profit Kindergartens as well as 7 overseas branch offices in Mongolia, Kyrgyzstan, Kingdom of Eswatini, Vietnam, Cambodia, Jordan, and Philippines. They also collaborate with ChildFund International USA, Children Believe, ChildFund Australia, and PLAN BØRNEfonden to provide children sponsorship program to help over 50,000 needy children across 34 countries.

The COVID-19 pandemic was confirmed to have reached the U.S. state of North Carolina on March 3, 2020.

Mandy Krauthamer Cohen is an American internist, public health official, and healthcare executive serving as the director of the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) since July 10, 2023. She was previously the executive vice president at Aledade and chief executive officer of Aledade Care Solution, a healthcare company.
The Delaware Student Excellence Equals Degree Program Scholarship is intended to provide free college tuition to Delaware residents seeking to earn an Associate degree at in-state colleges Delaware Tech and the University of Delaware. Any Delaware high school graduate after 2006 is eligible to apply given certain criteria.









