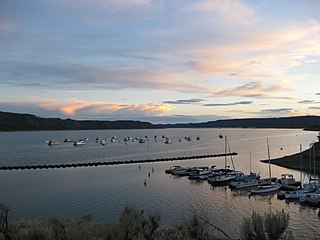The pinyon or piñon pine group grows in southwestern North America, especially in New Mexico, Arizona, and Utah. The trees yield edible nuts, which are a staple food of Native Americans, and widely eaten as a snack and as an ingredient in New Mexican cuisine. The name comes from the Spanish pino piñonero, a name used for both the American varieties and the stone pine common in Spain, which also produces edible nuts typical of Mediterranean cuisine. Harvesting techniques of the prehistoric American Indians are still used today to collect the pinyon seeds for personal use or for commercialization. The pinyon nut or seed is high in fats and calories.

Pinus cembroides, also known as pinyon pine, Mexican pinyon, Mexican nut pine, and Mexican stone pine, is a pine in the pinyon pine group, native to western North America. It grows in areas with low levels of rainfall and its range extends southwards from Arizona, Texas and New Mexico in the United States into Mexico. It typically grows at altitudes between 1,600 and 2,400 metres. It is a small pine growing to about 20 m (66 ft) with a trunk diameter of up to 50 cm (20 in). The seeds are large and form part of the diet of the Mexican jay and Abert's squirrel. They are also collected for human consumption, being the most widely used pine nut in Mexico. This is a common pine with a wide range and the International Union for Conservation of Nature has rated its conservation status as being of "least concern".

Pinus edulis, the Colorado pinyon, two-needle piñon, pinyon pine, or simply piñon, is a pine in the pinyon pine group whose ancestor was a member of the Madro-Tertiary Geoflora and is native to the United States.

Pinus monophylla, the single-leaf pinyon, is a pine in the pinyon pine group, native to North America. The range is in southernmost Idaho, western Utah, Arizona, southwest New Mexico, Nevada, eastern and southern California and northern Baja California.

Pinus quadrifolia, the Parry pinyon, is a pine in the pinyon pine group native to southernmost California in the United States and northern Baja California in Mexico, from 33° 30' N south to 30° 30' N. It occurs at moderate altitudes from 1,300 metres (4,300 ft) to 1,800 metres (5,900 ft), rarely as low as 1,200 metres (3,900 ft) and as high as 2,500 metres (8,200 ft). It is scarce and often scattered in this region, forming open woodlands, usually mixed with junipers. Other common names include nut pine and fourleaf pinyon pine.

The Pine Nut Mountains are a north–south mountain range in the Great Basin, in Douglas and Lyon counties of northwestern Nevada, United States. The highest mountain in the range is Mount Siegel at 9,456 ft.

The Sierra Madre Oriental pine–oak forests are a subtropical coniferous forest ecoregion of northeastern and Central Mexico, extending into the state of Texas in the United States.

Fortification Range Wilderness is a 30,656-acre (12,406 ha) wilderness area in Lincoln County, in the U.S. state of Nevada. The Wilderness lies approximately 50 miles (80 km) southeast of the town of Ely and is administered by the U.S. Bureau of Land Management.

The Kiavah Wilderness is a federally designated wilderness area located in the Mojave Desert, Scodie Mountains, and southern Sierra Nevada in Kern County, California, United States. California State Route 178 connects the town of Lake Isabella to State Highway 14 in the east, crossing Walker Pass at the north boundary of the wilderness.
Pinyon Pines is an unincorporated community in Riverside County, California.

The Sylvania Mountains Wilderness is a federally designated wilderness area located 30 miles (48 km) east of Bishop in the state of California. The wilderness is 18,677acres in size and is managed by the Bureau of Land Management (BLM). The California Desert Protection Act of 1994 created the Sylvania Mountains Wilderness and was added to the National Wilderness Preservation System. The wilderness is bordered by Nevada stateline on the east, Piper Mountain Wilderness on the west and Death Valley National Park to the south.

The Pinyon Mountains are a mountain range in eastern San Diego County, Southern California. The range is protected within Anza Borrego Desert State Park.

Canaan Mountain Wilderness is a 44,531-acre (180.2 km2) wilderness area in the US state of Utah. It was designated March 30, 2009, as part of the Omnibus Public Land Management Act of 2009. Located near the town of Hildale in southeastern Washington County, it borders Zion National Park to the north, Kane County to the east, and the state of Arizona to the south.

The Red Mountain Wilderness (Utah) is a 18,729-acre (75.8 km2) wilderness area in the US state of Utah. It was designated March 30, 2009, as part of the Omnibus Public Land Management Act of 2009. Located six miles northeast of St. George, it is bordered by Snow Canyon State Park to the east and the Shivwitz Indian Reservation to the southwest. Approximately one-half of the wilderness is located within the recently designated Red Cliffs National Conservation Area. Prehistoric use by the Southern Paiute Indians has been documented at seven sites in the area, and the BLM estimates archeological site densities between 4 and 40 per square mile.
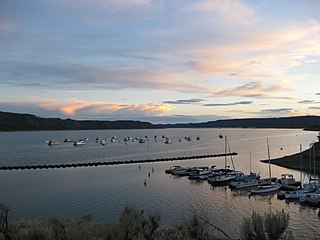
Navajo State Park is a state park of Colorado, USA, on the north shore of Navajo Lake. Touted as Colorado's answer to Lake Powell, this reservoir on the San Juan River begins in Colorado's San Juan Mountains and extends 20 miles (32 km) into New Mexico. Its area is 15,000 acres (6,100 ha), and it has 150 miles (240 km) of shoreline in two states. Park activities include boating, houseboating, fishing, camping, and wildlife viewing. There is a New Mexico state park at the southern end of the lake.

Pinyon–juniper woodland, also spelled piñon–juniper woodland, is a vegetation type (biome) of Western United States higher elevation deserts, characterized by being an open forest dominated by low, bushy, evergreen junipers, pinyon pines, and their associates which vary from region to region. The woodland's crown height may vary from less than 10 meters up to 15 meters, depending on the site. It may consist of pure stands of pinyon pine, or pure stands of juniper.

The Great Basin montane forests is an ecoregion of the Temperate coniferous forests biome, as designated by the World Wildlife Fund (WWF).

The Chino Valley of Arizona is a large, 70-mi (113 km) long valley, centered on Seligman, Arizona in northwest Yavapai County and southwest Coconino County. The valley is located at the southwest of the Coconino Plateau and lies in the extreme northwest of Arizona's transition zone.

The pinyon jay is a jay between the North American blue jay and the Eurasian jay in size. The voice is described as a rhythmic krawk-kraw-krawk repeated two or three times. It is the only member of the genus Gymnorhinus. Its overall proportions are very nutcracker-like and indeed this can be seen as convergent evolution as both birds fill similar ecological niches. The pinyon jay is a bluish-grey coloured bird with deeper head colouring and whitish throat with black bill, legs and feet.