
Saskatchewan is a province in Western Canada, bordered on the west by Alberta, on the north by the Northwest Territories, on the east by Manitoba, to the northeast by Nunavut, and to the south by the United States. Saskatchewan and Alberta are the only landlocked provinces of Canada. In 2023, Saskatchewan's population was estimated at 1,225,493. Nearly 10% of Saskatchewan's total area of 651,900 km2 (251,700 sq mi) is fresh water, mostly rivers, reservoirs, and lakes.

Yukon is the smallest and westernmost of Canada's three territories. It is the third-least populated province or territory in Canada, with a population of 45,148 as of 2023. However, Whitehorse, the territorial capital, is the largest settlement in any of the three territories.
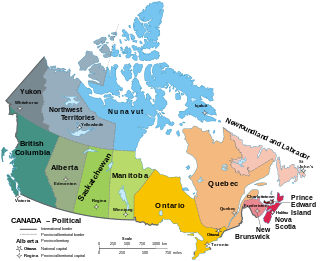
Canada has ten provinces and three territories that are sub-national administrative divisions under the jurisdiction of the Canadian Constitution. In the 1867 Canadian Confederation, three provinces of British North America—New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, and the Province of Canada —united to form a federation, becoming a fully independent country over the next century. Over its history, Canada's international borders have changed several times as it has added territories and provinces, making it the world's second-largest country by area.

Northern Canada, colloquially the North or the Territories, is the vast northernmost region of Canada, variously defined by geography and politics. Politically, the term refers to the three territories of Canada: Yukon, Northwest Territories and Nunavut. This area covers about 48 per cent of Canada's total land area, but has less than 0.5 per cent of Canada's population.

An unincorporated area is a region that is not governed by a local municipal corporation. There are many unincorporated communities and areas in the United States and Canada.
The vastness of Canada's Northwest Territories meant that for much of its history it was divided into several districts for ease of administration. The number and size of these territorial districts varied as other provinces and territories of Canada were created and expanded. The districts of the Northwest Territories were abolished in 1999 with the creation of the Nunavut territory and the contraction of the Northwest Territories to its current size.
An unorganized area or unorganized territory is any geographic region in Canada that does not form part of a municipality or Indian reserve. In these areas, the lowest level of government is provincial or territorial. In some of these areas, local service agencies may have some of the responsibilities that would otherwise be covered by municipalities.
A federal territory is an administrative division under the direct and usually exclusive jurisdiction of a federation's national government. A federal territory is a part of a federation, but not a part of any federated state. The states constitute the federation itself and share sovereignty with the federal government, while a territory does not have sovereign status and is constitutionally dependent on the federal government.

The Unorganized Borough is composed of the portions of the U.S. state of Alaska which are not contained in any of its 19 organized boroughs. While referred to as the "Unorganized Borough", it is not a borough itself, as it forgoes that level of government structure. It encompasses nearly half of Alaska's land area, 323,440 square miles (837,700 km2), and, as of the 2020 U.S. Census, it had a population of 77,157, which was 10.52% of the population of the state. The largest communities in the Unorganized Borough are the cities of Bethel, Unalaska, and Valdez.

The town is the basic unit of local government and local division of state authority in the six New England states. Most other U.S. states lack a direct counterpart to the New England town. New England towns overlay the entire area of a state, similar to civil townships in other states where they exist, but they are fully functioning municipal corporations, possessing powers similar to cities and counties in other states. New Jersey's system of equally powerful townships, boroughs, towns, and cities is the system which is most similar to that of New England. New England towns are often governed by a town meeting, an assembly of eligible town residents. The great majority of municipal corporations in New England are based on the town model; there, statutory forms based on the concept of a compact populated place are uncommon, though elsewhere in the U.S. they are prevalent. County government in New England states is typically weak at best, and in some states nonexistent. Connecticut, for example, has no county governments, nor does Rhode Island. Both of those states retain counties only as geographic subdivisions with no governmental authority, while Massachusetts has abolished eight of fourteen county governments so far. Counties serve mostly as dividing lines for the states' judicial systems and some other state services in the southern New England states, while providing varying services in the more sparsely populated three northern New England states.

Division No. 18, Saskatchewan, Canada, is one of the eighteen Statistics Canada census divisions within the province, occupying the northern half of the province. The census division is coextensive with the Northern Saskatchewan Administration District (NSAD).

The Northwest Territories is a territory in Northern Canada, specifically in Northwestern Canada between Yukon Territory and Nunavut including part of Victoria Island, Melville Island, and other islands on the western Arctic Archipelago. Originally a much wider territory enclosing most of central and northern Canada, the Northwest Territories was created in 1870 from the Hudson's Bay Company's holdings that were sold to Canada from 1869-1870. In addition, Alberta and Saskatchewan were formed from the territory in 1905. In 1999, it was divided again: the eastern portion became the new territory of Nunavut. Yellowknife stands as its largest city and capital. It has a population of 42,800 and has an area of 532,643 sq mi (1,379,540 km2). The current territory lies west of Nunavut, north of latitude 60° north, and east of Yukon.

The Stikine Region is an unincorporated area in northwestern British Columbia, Canada. It is the only area in the province that is not part of a regional district. The Stikine Region was left unincorporated following legislation that established the province's regional districts in 1968 and is not classified as a regional district. It contains no municipal governments which normally constitute the majority of seats on the boards of regional districts. There is only one local planning area, the Atlin Community Planning Area, which was combined in 2009 with the Atlin Community Improvement District to provide fire, landfill, water, streetlighting, sidewalks and advisory land use services. All other services not provided privately are administered directly by various provincial government ministries. The area around Dease Lake, formerly in the Stikine Region, is now within the boundaries of the Regional District of Kitimat–Stikine following a boundary amendment in 2008.












