
Kiwi are flightless birds endemic to New Zealand of the order Apterygiformes. The five extant species fall into the family Apterygidae and genus Apteryx. Approximately the size of a domestic chicken, kiwi are the smallest living ratites.

Moa are an extinct group of flightless birds formerly endemic to New Zealand. During the Late Pleistocene-Holocene, there were nine species. The two largest species, Dinornis robustus and Dinornis novaezelandiae, reached about 3.6 metres (12 ft) in height with neck outstretched, and weighed about 230 kilograms (510 lb) while the smallest, the bush moa, was around the size of a turkey. Estimates of the moa population when Polynesians settled New Zealand circa 1300 vary between 58,000 and approximately 2.5 million.

A ratite is any of a diverse group of flightless, large, long-necked, and long-legged birds of the infraclass Palaeognathae. Kiwi, the exception, are much smaller and shorter-legged and are the only nocturnal extant ratites.

Tinamous form an order of birds called Tinamiformes, comprising a single family called Tinamidae, divided into two distinct subfamilies, containing 46 species found in Mexico, Central America, and South America. The word "tinamou" comes from the Galibi term for these birds, tinamu. Tinamous have traditionally been regarded as the sister group of the flightless ratites, but recent work places them well within the ratite radiation, implying basal ratites could fly. Tinamous first appear in the fossil record in the Miocene epoch. They are generally sedentary, ground-dwelling and, though not flightless, when possible avoid flight in favour of hiding or running away from danger. They are found in a variety of habitats, ranging from semi-arid alpine grasslands to tropical rainforests. The two subfamilies are broadly divided by habitat, with the Nothurinae referred to as steppe or open country tinamous, and the Tinaminae known as forest tinamous.

Elephant birds are extinct flightless birds belonging to the order Aepyornithiformes that were native to the island of Madagascar. They are thought to have become extinct by around 1260 CE, probably as a result of human activity. Elephant birds comprised three species, one in the genus Mullerornis, and two in Aepyornis.Aepyornis maximus is possibly the largest bird to have ever lived, with their eggs being the largest known for any amniote. Elephant birds are palaeognaths, and their closest living relatives are kiwi, suggesting that ratites did not diversify by vicariance during the breakup of Gondwana but instead convergently evolved flightlessness from ancestors that dispersed more recently by flying.

Flightless birds are birds that, through evolution, lost the ability to fly. There are over 60 extant species, including the well known ratites and penguins. The smallest flightless bird is the Inaccessible Island rail. The largest flightless bird, which is also the largest living bird in general, is the ostrich.

The brown tinamou is a brownish ground bird found in humid lowland and montane forest in tropical and subtropical South America.

The great spotted kiwi, great grey kiwi or roroa is a species of kiwi endemic to the South Island of New Zealand. The great spotted kiwi, as a member of the ratites, is flightless. It is the largest of the kiwi. The rugged topography and harsh climate of the high altitude alpine part of its habitat render it inhospitable to a number of introduced mammalian predators, which include dogs, ferrets, cats, and stoats. Because of this, populations of this species have been less seriously affected by the predations of these invasive species compared to other kiwi. Nonetheless, there has been a 43% decline in population in the past 45 years, due to these predators and habitat destruction. This has led it to be classified as vulnerable. There are less than 16,000 great spotted kiwis in total, almost all in the more mountainous parts of northwest Nelson, the northwest coast, and the Southern Alps. A minority live on island reserves.

Palaeognathae is a infraclass of birds, called paleognaths or palaeognaths, within the class Aves of the clade Archosauria. It is one of the two extant infraclasses of birds, the other being Neognathae, both of which form Neornithes. Palaeognathae contains five extant branches of flightless lineages, termed ratites, and one flying lineage, the Neotropic tinamous. There are 47 species of tinamous, five of kiwis (Apteryx), three of cassowaries (Casuarius), one of emus (Dromaius), two of rheas (Rhea) and two of ostriches (Struthio). Recent research has indicated that paleognaths are monophyletic but the traditional taxonomic split between flightless and flighted forms is incorrect; tinamous are within the ratite radiation, meaning flightlessness arose independently multiple times via parallel evolution.

Aepyornis is an extinct genus of elephant bird formerly endemic to Madagascar. The genus had two species, the smaller A. hildebrandti and the larger A. maximus. A. maximus is one of, and possibly the largest bird to have ever lived. Its closest living relative is the New Zealand kiwi. They became extinct sometime around 1000 CE, probably as a result of human activity.

The grey-legged tinamou, alternatively, the gray-legged tinamou, is a small ground-dwelling bird endemic to the neotropics. It is a rarely seen bird due to its small size and discreet appearance.
Diogenornis is an extinct genus of ratites, that lived during the Early Eocene. It was described in 1983 by Brazilian scientist Herculano Marcos Ferraz de Alvarenga based on fossils found in the Itaboraí Formation in southeastern Brazil. The type species is D. fragilis. While initially considered a member of the family Opisthodactylidae, further examination of the fossil remains showed that it was more similar to the modern rhea. According to Gerald Mayr, Diogenornis is best considered a stem-group member of the Rheidae. It grew to about two thirds the size of the modern greater rhea, at about 90 centimetres (3.0 ft) of height.

The crested moa is an extinct species of moa. It is one of the 9 known species of moa to have existed.
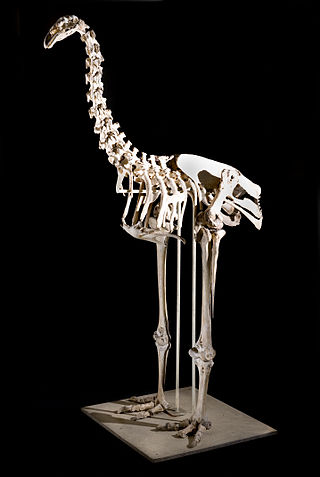
The South Island giant moa is an extinct species of moa in the genus Dinornis. It was the tallest-known bird species to walk the Earth, exceeded in weight only by the heavier but shorter elephant bird of Madagascar.

Lithornithidae is an extinct, possibly paraphyletic group of early paleognath birds. They are known from fossils dating to the Upper Paleocene through the Middle Eocene of North America and Europe, with possible Late Cretaceous representatives. All are extinct today; the youngest specimen is the currently unnamed SGPIMH MEV1 specimen from the mid-Eocene Messel Pit site.
Eremopezus is a prehistoric bird genus, possibly a palaeognath. It is known only from the fossil remains of a single species, the huge and presumably flightless Eremopezus eocaenus. This was found in Upper Eocene Jebel Qatrani Formation deposits around the Qasr el Sagha escarpment, north of the Birket Qarun lake near Faiyum in Egypt. The rocks its fossils occur in were deposited in the Priabonian, with the oldest dating back to about 36 million years ago (Ma) and the youngest not less than about 33 Ma.
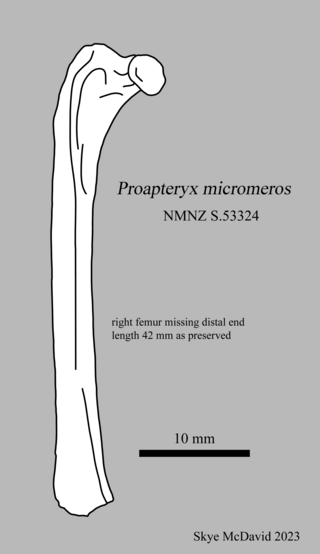
Proapteryx micromeros is an extinct kiwi known from the 16–19 million-year-old early Miocene sediments of the St Bathans Fauna of Otago, New Zealand.

Novaeratitae is a clade that was originally defined to contain the recent common ancestors of the orders Casuariiformes and Apterygiformes (kiwis). Recently it has been determined that the elephant birds of the extinct order Aepyornithiformes were the closest relatives of the kiwis, and therefore are part of this group. The implication is that ratites had lost flight independently in each group, as the elephant birds are the only novaeratites found outside Oceania.


















