
U.S. Route 1 or U.S. Highway 1 (US 1) is a major north–south United States Numbered Highway that serves the East Coast of the United States. It runs 2,370 miles (3,810 km) from Key West, Florida, north to Fort Kent, Maine, at the Canadian border, making it the longest north–south road in the United States. US 1 is generally paralleled by Interstate 95 (I-95), though US 1 is significantly farther west (inland) between Jacksonville, Florida, and Petersburg, Virginia, while I-95 is closer to the coastline. In contrast, US 1 in Maine is much closer to the coast than I-95, which runs farther inland than US 1. The route connects most of the major cities of the East Coast from the Southeastern United States to New England, including Miami, Jacksonville, Raleigh, Richmond, Washington D.C., Baltimore, Philadelphia, New York City, and Boston.

Interstate 95 (I-95) is the main north–south Interstate Highway on the East Coast of the United States, running from U.S. Route 1 (US 1) in Miami, Florida, north to the Houlton–Woodstock Border Crossing between Maine and the Canadian province of New Brunswick. The highway largely parallels the Atlantic coast and US 1, except for the portion between Savannah, Georgia, and Washington, D.C., and the portion between Portland and Houlton in Maine, both of which follow a more direct inland route.

The East Coast Greenway is a 3,000-mile (4,800 km) pedestrian and bicycle route between Maine and Florida along the East Coast of the United States. The nonprofit East Coast Greenway Alliance was created in 1991 with the goal to use the entire route with off-road, shared-use paths; as of 2021, over 1,000 mi (1,600 km) of the route (35%) meets this criteria. In 2020, the Greenway received over 50 million visits.

The Cape May–Lewes Ferry is a ferry system in the United States that traverses a 17-mile (27 km) crossing of the Delaware Bay connecting North Cape May, New Jersey with Lewes, Delaware. The ferry constitutes a portion of U.S. Route 9 and is the final crossing of the Delaware River-Delaware Bay waterway before it meets the Atlantic Ocean.
E-ZPass is an electronic toll collection system used on toll roads, toll bridges, and toll tunnels in the Eastern United States, Midwestern United States, and Southern United States. The E-ZPass Interagency Group (IAG) consists of member agencies in several states, which use the same technology and allow travelers to use the same transponder on toll roads throughout the network.

U.S. Route 17 or U.S. Highway 17 (US 17), also known as the Coastal Highway, is a north–south United States Numbered Highway that spans in the Southeastern United States. It runs close to the Atlantic Coast for much of its length, with the exception of the portion between Punta Gorda and Jacksonville, Florida, and the portion from Fredericksburg to Winchester, Virginia, both of which follow a more inland route. Major metropolitan areas served along US 17's route include the Punta Gorda, Greater Orlando, and Jacksonville metropolitan areas in Florida, the Brunswick and Savannah metropolitan areas in Georgia, the Charleston and Myrtle Beach metropolitan areas in South Carolina, the Cape Fear and New Bern metropolitan areas in North Carolina, and the Hampton Roads and Winchester metropolitan areas in Virginia.

U.S. Route 13 or U.S. Highway 13 (US 13) is a north–south United States Numbered Highway established in 1926 that runs for 518 miles (834 km) from Interstate 95 (I-95) just north of Fayetteville, North Carolina, to US 1 in the northeastern suburbs of Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, near Morrisville. In all, it traverses five states in the Atlantic coastal plain region. It follows the Atlantic coast more closely than does the main north–south U.S. Highway of the region, US 1. Due to this, its number is out of place on the general U.S. Highway numbering grid, as it should be running west of US 11 but does not. Its routing is largely rural, the notable exceptions being the Hampton Roads area in Virginia and the northern end of the highway in Delaware and Pennsylvania. It is also notable for being the main thoroughfare for the Delmarva Peninsula and carrying the Chesapeake Bay Bridge–Tunnel to it in Virginia.

The Chesapeake Bay Bridge–Tunnel is a 17.6-mile (28.3 km) bridge–tunnel that crosses the mouth of the Chesapeake Bay between Delmarva and Hampton Roads in the U.S. state of Virginia. It opened in 1964, replacing ferries that had operated since the 1930s. A major project to dualize its bridges was completed in 1999, and a similar project to dualize one of its tunnels is currently underway.

U.S. Route 301 (US 301) is a spur of U.S. Route 1 running through the South Atlantic States. It runs 1,099 miles (1,769 km) from Biddles Corner, Delaware, at Delaware Route 1 to Sarasota, Florida, at U.S. Route 41. It passes through the states of Delaware, Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, Georgia, and Florida. It goes through the cities of Middletown, Delaware; Annapolis, Maryland; Richmond and Petersburg, Virginia; Rocky Mount, Wilson, and Fayetteville, North Carolina; Florence, South Carolina; Statesboro and Jesup, Georgia; and Ocala, Zephyrhills, and Sarasota, Florida.

Saint Georges is an unincorporated town and former municipality situated on the Chesapeake and Delaware Canal in New Castle County, Delaware, United States, approximately midway between the Delaware River and Chesapeake Bay.

Maryland Route 213 (MD 213) is a 68.25-mile (109.84 km) state highway located on the Eastern Shore of Maryland in the United States. The route runs from MD 662 in Wye Mills, Queen Anne's County, north to the Pennsylvania border in Cecil County, where the road continues into that state as Pennsylvania Route 841 (PA 841). The route, which is a two-lane undivided highway most of its length, passes through mainly rural areas as well as the towns of Centreville, Chestertown, Galena, Cecilton, Chesapeake City, and Elkton. MD 213 intersects many routes including U.S. Route 50 (US 50) near Wye Mills, US 301 near Centreville, and US 40 in Elkton. It crosses over the Chesapeake & Delaware Canal in Chesapeake City on the Chesapeake City Bridge. MD 213 is designated by the state as the Chesapeake Country Scenic Byway between the southern terminus and Chesapeake City with the portion north of MD 18 in Centreville a National Scenic Byway. In addition, the route is also considered part of the Atlantic to Appalachians Scenic Byway between Chesapeake City and MD 273 in Fair Hill.

Maryland Route 404 (MD 404) is a major highway on Maryland's Eastern Shore in the United States. Signed east-west, it runs 24.61 miles (39.61 km) from MD 662 in Wye Mills on the border of Queen Anne's and Talbot counties, southeast to the Delaware state line in Caroline County, where the road continues as Delaware Route 404 (DE 404) to the Five Points intersection near Rehoboth Beach. The Maryland and Delaware state highways together cross the width of the Delmarva Peninsula and serve to connect the Baltimore–Washington Metropolitan Area by way of the Chesapeake Bay Bridge and U.S. Route 50 (US 50) with the Delaware Beaches. Along the way, MD 404 passes through mostly farmland and woodland as well as the towns of Queen Anne, Hillsboro, and Denton. The route is a four-lane divided highway between US 50 and east of Denton, with the remainder of the route a two-lane undivided road.
The National Register of Historic Places in the United States is a register including buildings, sites, structures, districts, and objects. The Register automatically includes all National Historic Landmarks as well as all historic areas administered by the U.S. National Park Service. Since its introduction in 1966, more than 90,000 separate listings have been added to the register.

Transportation in the Commonwealth of Virginia is by land, sea and air. Virginia's extensive network of highways and railroads were developed and built over a period almost 400 years, beginning almost immediately after the founding of Jamestown in 1607, and often incorporating old established trails of the Native Americans.

State Route 168 is a primary state highway in the South Hampton Roads region of the U.S. state of Virginia. It runs from the border with North Carolina through the independent cities of Chesapeake and Norfolk where it ends in the Ocean View area near the Hampton Roads Bridge-Tunnel.

U.S. Route 50 is a major east–west route of the U.S. Highway system, stretching just over 3,000 miles (4,800 km) from West Sacramento, California, east to Ocean City, Maryland, on the Atlantic Ocean. In the U.S. state of Maryland, US 50 exists in two sections. The longer of these serves as a major route connecting Washington, D.C., with Ocean City; the latter is the eastern terminus of the highway. The other section passes through the southern end of Garrett County for less than 10 miles (16 km) as part of the Northwestern Turnpike, entering West Virginia at both ends. One notable section of US 50 is the dual-span Chesapeake Bay Bridge across the Chesapeake Bay, which links the Baltimore–Washington metropolitan area with the Eastern Shore region, allowing motorists to reach Ocean City and the Delaware Beaches.
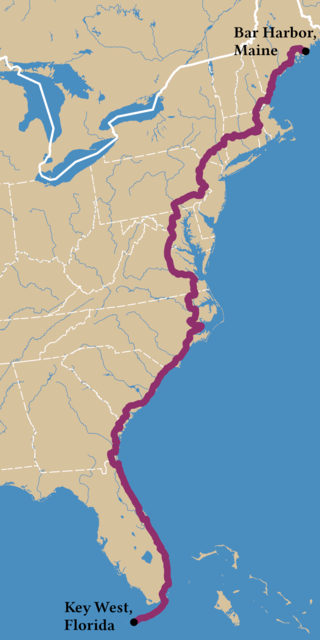
Adventure Cycling Association's Atlantic Coast Bicycle Route is a 2,615-mile-long (4,208 km) bicycle touring route traversing the East Coast of the United States. The route has two connecting segments, extending nearly the entire length of the nation's eastern margin. The northern section of the route features historic New England coastal villages and towns, rural countrysides, and Amish farmlands. The route's southern section begins after the Mason–Dixon Line and is notable for the Civil War battlefields in Fredericksburg, Virginia, and the city of Richmond, Virginia. The northern section of the route can be ridden between late spring and late fall, and the southern section can be ridden year-round.
















