
Maasai Mara, also sometimes spelled Masai Mara and locally known simply as The Mara, is a large national game reserve in Narok, Kenya, contiguous with the Serengeti National Park in Tanzania. It is named in honor of the Maasai people, the ancestral inhabitants of the area, who migrated to the area from the Nile Basin. Their description of the area when looked at from afar: "Mara" means "spotted" in the local Maasai language, due to the many short bushy trees which dot the landscape.

The Serengeti National Park is a large national park in northern Tanzania that stretches over 14,763 km2 (5,700 sq mi). It is located in eastern Mara Region and northeastern Simiyu Region and contains over 1,500,000 hectares of virgin savanna. The park was established in 1940.

A game reserve is a large area of land where wild animals live safely or are hunted in a controlled way for sport. If hunting is prohibited, a game reserve may be considered a nature reserve; however, the focus of a game reserve is specifically the animals (fauna), whereas a nature reserve is also, if not equally, concerned with all aspects of native biota of the area.

Nairobi National Park is a national park in Kenya that was established in 1946 about 7 km (4.3 mi) south of Nairobi. It is fenced on three sides, whereas the open southern boundary allows migrating wildlife to move between the park and the adjacent Kitengela plains. Herbivores gather in the park during the dry season. Nairobi National Park is negatively affected by increasing human and livestock populations, changing land use and poaching of wildlife. Despite its proximity to the city and its relative small size, it boasts a large and varied wildlife population, and is one of Kenya's most successful rhinoceros sanctuaries.

The Mara River is a river in that begins in Narok County (Kenya) and in ends in Mara Region (Tanzania), and lies across the migration path of ungulates in the Maasai Mara/Serengeti ecosystem.

Nanyuki is a market town in Laikipia County of Kenya lying northwest of Mount Kenya along the A2 road and at the terminus of the branch railway from Nairobi. The name is derived from Enyaanyukie Maasai word for resemblance.

Ngorongoro District is one of seven districts in western Arusha Region of Tanzania. The district is bordered to the north by Kenya, to the east by Monduli District, the northeast by Longido District, and to the south by the Karatu District. The western border is the Serengeti District in Mara Region. Ngorongoro District is home to the Ngorongoro Crater and was named after it. It covers an area of 14,036 km2 (5,419 sq mi). The district is comparable in size to the land area of Timor Leste. The administrative seat is the town of Loliondo. The district is home to the Ngorongoro Conservation Area which is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The district is also home to the third tallest mountain in the country, Mount Loolmalasin. According to the 2002 Tanzania National Census, the population of the Ngorongoro Region was 129,776. By 2012, the population of the district was 174,278.

Jonathan Scott is an English zoologist, wildlife photographer and television presenter specializing in African wildlife.

Namibia is one of few countries in the world to specifically address habitat conservation and protection of natural resources in their constitution. Article 95 states, "The State shall actively promote and maintain the welfare of the people by adopting international policies aimed at the following: maintenance of ecosystems, essential ecological processes, and biological diversity of Namibia, and utilization of living natural resources on a sustainable basis for the benefit of all Namibians, both present and future.".

Tourism in Kenya is the second-largest source of foreign exchange revenue, following agriculture. The Kenya Tourism Board is responsible for maintaining information about tourism in Kenya.
The Mara Triangle is the southwestern part of the Maasai Mara National Reserve, Kenya, and is managed by the not-for-profit organisation The Mara Conservancy on behalf of Trans-Mara County Council.
Solio Ranch or Solio Game Reserve is a privately owned wildlife conservancy located in Kenya's Central Province.

Milking the Rhino is a 2009 documentary film, produced by Kartemquin Films, that examines the relationship between the indigenous African wildlife, the villagers who live amongst this wildlife and conservationists who look to keep tourism dollars coming in. Both the Maasai of Kenya and the Ovahimba of Namibia have spent centuries as cattle farmers. With their lands being turned into protected game reserves, these ancient tribes have turned to tourism as a means of survival.

The Kigio Wildlife Conservancy is a protected Conservancy near Gilgil in the Great Rift Valley of Kenya. It is owned and operated by the local community.
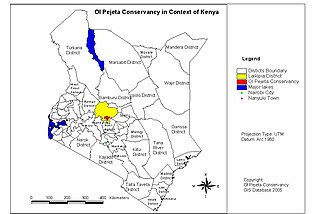
The Ol Pejeta Conservancy is a 360 km2 (140 sq mi) not-for-profit wildlife conservancy in Central Kenya's Laikipia County. It is situated on the equator west of Nanyuki, between the foothills of the Aberdares and Mount Kenya. The Ol Pejeta Conservancy works to conserve wildlife, provide a sanctuary for great apes, and generate income through wildlife tourism and complementary enterprises for re-investment in conservation and community development.
Maasai Mara University (MMU),, is a public university in Kenya.

Angama Mara is a safari lodge in the Maasai Mara in Kenya. In the Kiswahili language, "angama" means "suspended in mid-air"; the name refers to the lodge's location 300 metres (980 ft) above the floor of the Maasai Mara.
To the east and north of the Maasai Mara National Reserve, some of the former Maasai cattle-grazing areas have been converted into wildlife conservancies for tourism.
WildEarth is a British-South African broadcasting and conservation company primarily based at Djuma Game Reserve, part of the Sabi Sand Game Reserve in South Africa, who focus on connecting people with African Wildlife. The company is best known for its live drives, which take place twice a day in Sabi Sands and Pridelands. Former locations included Tswalu Kalahari, Karongwe Private Game Reserve, Phinda, Ngala and Arathusa.
Fortress conservation is a conservation model based on the belief that biodiversity protection is best achieved by creating protected areas where ecosystems can function in isolation from human disturbance. Its implementation has been criticized for human rights abuses against indigenous inhabitants when creating and maintaining protected areas.














