Related Research Articles

Costa Rica, officially the Republic of Costa Rica, is a country in the Central American region of North America. Costa Rica is bordered by Nicaragua to the north, the Caribbean Sea to the northeast, Panama to the southeast, and the Pacific Ocean to the southwest, as well as maritime border with Ecuador to the south of Cocos Island. It has a population of around five million in a land area of 51,060 km2 (19,710 sq mi). An estimated 333,980 people live in the capital and largest city, San José, with around two million people in the surrounding metropolitan area.

San José is the capital and largest city of Costa Rica, and the capital of the province of the same name. It is in the center of the country, in the mid-west of the Central Valley, within San José Canton. San José is Costa Rica's seat of national government, focal point of political and economic activity, and major transportation hub. San José Canton's population was 288,054 in 2011, and San José's municipal land area is 44.2 square kilometers, with an estimated 333,980 residents in 2015. Together with several other cantons of the central valley, including Alajuela, Heredia and Cartago, it forms the country's Greater Metropolitan Area, with an estimated population of over 2 million in 2017. The city is named in honor of Joseph of Nazareth.
The colón is the currency of Costa Rica. It was named after Christopher Columbus, known as Cristóbal Colón in Spanish. A colón is divided into one hundred céntimos.
Hawaiʻi Sign Language or Hawaiian Sign Language, also known as Hoailona ʻŌlelo, Old Hawaiʻi Sign Language and Hawaiʻi Pidgin Sign Language, is an indigenous sign language native to Hawaiʻi. Historical records document its presence on the islands as early as the 1820s, but HSL was not formally recognized by linguists until 2013.
Providence Island Sign Language is a village sign language of the small island community of Providence Island in the Western Caribbean, off the coast of Nicaragua but belonging to Colombia. The island is about 15 square miles (39 km2) and the total population is about 5000, of which an unusual proportion are deaf.

The Bribri are an Indigenous people in eastern Costa Rica and northern Panama. Today, most Bribri people speak the Bribri language or Spanish.

Thai Sign Language (TSL), or Modern Standard Thai Sign Language (MSTSL), is the national sign language of Thailand's deaf community and is used in most parts of the country by the 20 percent of the estimated 56,000 pre-linguistically deaf people who go to school.
Guatemalan Sign Language or "Lengua de Señas de Guatemala" is the proposed national deaf sign language of Guatemala, formerly equated by most users and most literature equates with the sign language known by the acronymic abbreviations LENSEGUA, Lensegua, and LenSeGua. Recent legal initiatives have sought to define the term more inclusively, so that it encompasses all the distinctive sign languages and sign systems native to the country.

Televisora de Costa Rica S.A., known as Teletica, is a Costa Rican television broadcaster, founded in 1958. It operates Teletica Canal 7, XperTV Canal 33, and since 1991 CableTica.
Costa Rica's official and predominant language is Spanish. The variety spoken there, Costa Rican Spanish, is a form of Central American Spanish.

Costa Rican Spanish is the form of the Spanish language spoken in Costa Rica. It is one of the dialects of Central American Spanish. Nevertheless, because the country was more remote than its neighbors, the development of this variety of Spanish followed a distinct path.
The French Sign Language or Francosign family is a language family of sign languages which includes French Sign Language and American Sign Language.

Heiner Mora Mora is a Costa Rican professional footballer who plays for A.D. Municipal Pérez Zeledón as a wingback.

Italian Costa Ricans are Costa Rican-born citizens who are fully or partially of Italian descent, whose ancestors were Italians who emigrated to Costa Rica during the Italian diaspora, or Italian-born people in Costa Rica. Most of them reside in San Vito, the capital city of the Coto Brus Canton. Both Italians and their descendants are referred to in the country as tútiles. There were over 380,000 Costa Ricans of Italian descent, corresponding to about 7.5% of Costa Rica's population, while there were around 2,300 Italian citizens.

Costa Ricans are the citizens of Costa Rica, a multiethnic, Spanish-speaking nation in Central America. Costa Ricans are predominantly Castizos, other ethnic groups people of Indigenous, European, African and Asian descent.
Chiangmai Sign Language is a deaf-community sign language of Thailand that arose among deaf people who migrated to Chiang Mai for work or family. The language is moribund, with all speakers born before 1960. Younger generations have switched to Thai Sign Language.
Bribri Sign Language was a village sign language of an indigenous Bribri community in southern Costa Rica. It is unrelated to Costa Rican Sign Language.
Brunca Sign Language is a village sign language of an indigenous Brunca community in southern Costa Rica. It is unrelated to Costa Rican Sign Language.
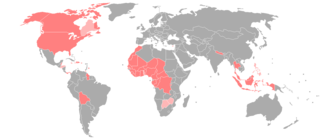
American Sign Language (ASL) developed in the United States, starting as a blend of local sign languages and French Sign Language (FSL). Local varieties have developed in many countries, but there is little research on which should be considered dialects of ASL and which have diverged to the point of being distinct languages.

Costa Rica–Spain relations are the diplomatic relations between Costa Rica and Spain. Both nations are members of the Association of Academies of the Spanish Language and the Organization of Ibero-American States.
References
Bibliography
- Woodward, James (1991). "Sign Language Varieties in Costa Rica". Sign Language Studies (73): 329–346. doi: 10.1353/sls.1991.0022 . JSTOR 26204768.