
p53, also known as Tumor protein P53, cellular tumor antigen p53, or transformation-related protein 53 (TRP53) is a regulatory protein that is often mutated in human cancers. The p53 proteins are crucial in vertebrates, where they prevent cancer formation. As such, p53 has been described as "the guardian of the genome" because of its role in conserving stability by preventing genome mutation. Hence TP53 is classified as a tumor suppressor gene.
Myc is a family of regulator genes and proto-oncogenes that code for transcription factors. The Myc family consists of three related human genes: c-myc (MYC), l-myc (MYCL), and n-myc (MYCN). c-myc was the first gene to be discovered in this family, due to homology with the viral gene v-myc.
Biopolymers and Cell is a scientific journal issued by the National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine and Institute of Molecular Biology and Genetics of NASU. It was established in January 1985, and its ISSN numbers are ISSN 0233-7657 for the print version and ISSN 1993-6842 for the online version.

CHEK2 is a tumor suppressor gene that encodes the protein CHK2, a serine-threonine kinase. CHK2 is involved in DNA repair, cell cycle arrest or apoptosis in response to DNA damage. Mutations to the CHEK2 gene have been linked to a wide range of cancers.
Suzanne Cory is an Australian molecular biologist. She has worked on the genetics of the immune system and cancer and has lobbied her country to invest in science. She is married to fellow scientist Jerry Adams, also a WEHI scientist, whom she met while studying for her PhD at the University of Cambridge, England.
Activating transcription factor, ATF, is a group of bZIP transcription factors, which act as homodimers or heterodimers with a range of other bZIP factors. First, they have been described as members of the CREB/ATF family, whereas it turned out later that some of them might be more similar to AP-1-like factors such as c-Jun or c-Fos. In general, ATFs are known to respond to extracellular signals and this suggests an important role that they have in maintaining homeostasis. Some of these ATFs, such as ATF3, ATF4, and ATF6 are known to play a role in stress responses. Another example of ATFs function would be ATFx that can suppress apoptosis.

Retinoblastoma-like protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RBL2 gene.

CDC34 is a gene that in humans encodes the protein Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 R1. This protein is a member of the ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme family, which catalyzes the covalent attachment of ubiquitin to other proteins.

Cornelia Isabella "Cori" Bargmann is an American neurobiologist. She is known for her work on the genetic and neural circuit mechanisms of behavior using C. elegans, particularly the mechanisms of olfaction in the worm. She has been elected to the National Academy of Sciences and had been a Howard Hughes Medical Institute investigator at UCSF and then Rockefeller University from 1995 to 2016. She was the Head of Science at the Chan Zuckerberg Initiative from 2016 to 2022. In 2012 she was awarded the $1 million Kavli Prize, and in 2013 the $3 million Breakthrough Prize in Life Sciences.
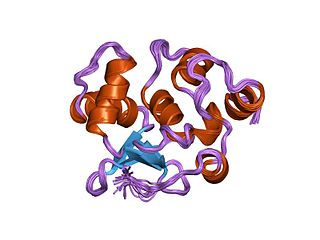
In the field of molecular biology, the ETSfamily is one of the largest families of transcription factors and is unique to animals. There are 29 genes in humans, 28 in the mouse, 10 in Caenorhabditis elegans and 9 in Drosophila. The founding member of this family was identified as a gene transduced by the leukemia virus, E26. The members of the family have been implicated in the development of different tissues as well as cancer progression.

Genes & Development is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering molecular biology, molecular genetics, cell biology, and development. It was established in 1987 and is published twice monthly by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press in association with The Genetics Society.

Clinical Cancer Research is a peer-reviewed medical journal on oncology, including the cellular and molecular characterization, prevention, diagnosis, and therapy of human cancer, medical and hematological oncology, radiation therapy, pediatric oncology, pathology, surgical oncology, and clinical genetics. The applications of the disciplines of pharmacology, immunology, cell biology, and molecular genetics to intervention in human cancer are also included. One of the main interests of Clinical Cancer Research is on clinical trials that evaluate new treatments together with research on pharmacology and molecular alterations or biomarkers that predict response or resistance to treatment. Another priority for Clinical Cancer Research is laboratory and animal studies of new drugs as well as molecule-targeted agents with the potential to lead to clinical trials, and studies of targetable mechanisms of oncogenesis, progression of the malignant phenotype, and metastatic disease. The journal is published by the American Association for Cancer Research.

Genesis: The Journal of Genetics and Development is a peer-reviewed scientific journal of genetics and developmental biology. It was established as Developmental Genetics in 1979 and obtained its current title in 2000. In addition to original research articles, the journal also publishes letters to the editor and technology reports relevant to the understanding of the functions of genes. The editor-in-chief is Sally A. Moody.

Clifford James Tabin is chairman of the Department of Genetics at Harvard Medical School.

Douglas Green, is an American biologist. He holds the Peter C. Doherty Endowed Chair of Immunology in St. Jude Children's Research Hospital. His research has focused on the process of active cell death and cell survival, extending from the role of cell death in cancer regulation and immune responses in the whole organism to the molecular events directing the death of the cell. Green was editor in chief of the journal Oncogene from 2009-2016, is a Deputy Editor of the journal "Science Advances" and the author of the book Cell Death, Means To An End.
Communications Biology is a peer-reviewed open access scientific journal covering research in biology. It was established in 2018 and is published by Nature Portfolio. It is a sister journal to Communications Physics and Communications Chemistry.
In academic publishing, a sister journal, mirror journal or companion journal is a newer academic journal that is affiliated with an older, better-established journal in the same field.
Oncogenesis is a peer-reviewed open access medical journal covering the molecular biology of cancer. It was established in 2012 by Douglas R. Green as a sister journal to Oncogene, of which Green was then editor-in-chief. New articles are published exclusively online by Nature Publishing Group on a weekly basis. The editor-in-chief is Jan Paul Medema. According to the Journal Citation Reports, the journal has a 2020 impact factor of 7.485, ranking it 40th out of 242 journals in the category "Oncology".

Justin Stebbing is Editor-in-Chief of Nature’s cancer journal Oncogene, a visiting Professor of Cancer Medicine and Oncology at Imperial College, London and a Professor of Biomedical Sciences at ARU, Cambridge. He works at the Phoenix Hospital Group in London to provide medical services to patients for the management of cancer, in person and remotely. He specialises in a range of solid malignancies including difficult cases with few conventional options and has published over 700 papers, the majority regarding new therapeutic and translational approaches including use of immunotherapies in clinical trials, many in the world's best journals.













