Related Research Articles
Health insurance or medical insurance is a type of insurance that covers the whole or a part of the risk of a person incurring medical expenses. As with other types of insurance, risk is shared among many individuals. By estimating the overall risk of health risk and health system expenses over the risk pool, an insurer can develop a routine finance structure, such as a monthly premium or payroll tax, to provide the money to pay for the health care benefits specified in the insurance agreement. The benefit is administered by a central organization, such as a government agency, private business, or not-for-profit entity.
General practice is the name given in various nations, such as the United Kingdom, India, Australia, New Zealand and South Africa to the services provided by general practitioners. In some nations, such as the US, similar services may be described as family medicine or primary care. The term Primary Care in the UK may also include services provided by community pharmacy, optometrist, dental surgery and community hearing care providers. The balance of care between primary care and secondary care - which usually refers to hospital based services - varies from place to place, and with time. In many countries there are initiatives to move services out of hospitals into the community, in the expectation that this will save money and be more convenient.

Two-tier healthcare is a situation in which a basic government-provided healthcare system provides basic care, and a secondary tier of care exists for those who can pay for additional, better quality or faster access. Most countries have both publicly and privately funded healthcare, but the degree to which it creates a quality differential depends on the way the two systems are managed, funded, and regulated.

Axa S.A. is a French multinational insurance company headquartered in the 8th arrondissement of Paris. It also provides investment management and other financial services.
Health care in Ireland is delivered through public and private healthcare. The public health care system is governed by the Health Act 2004, which established a new body to be responsible for providing health and personal social services to everyone living in Ireland – the Health Service Executive. The new national health service came into being officially on 1 January 2005; however the new structures are currently in the process of being established as the reform programme continues. In addition to the public-sector, there is also a large private healthcare market.
The Voluntary Health Insurance Board — which trades under the brand name Vhi Healthcare, and is still commonly referred to in Ireland as "The Vhi" – is the largest health insurance company in Ireland. It is a statutory corporation whose members are appointed by the Minister for Health. It is regulated by the Health Insurance Authority.
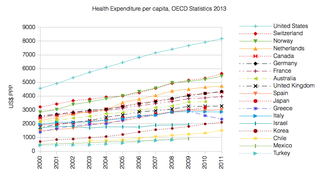
Switzerland has universal health care, regulated by the Swiss Federal Law on Health Insurance. There are no free state-provided health services, but private health insurance is compulsory for all persons residing in Switzerland.

Laya Healthcare is a health insurance company in Ireland. Its headquarters are in Little Island, County Cork. It is regulated by the Health Insurance Authority.

The National Health Service (NHS) is the publicly funded healthcare system in England, and one of the four National Health Service systems in the United Kingdom. It is the second largest single-payer healthcare system in the world after the Brazilian Sistema Único de Saúde. Primarily funded by the government from general taxation, and overseen by the Department of Health and Social Care, the NHS provides healthcare to all legal English residents and residents from other regions of the UK, with most services free at the point of use for most people. The NHS also conducts research through the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR).

Healthcare in the Netherlands is differentiated along three dimensions (1) level (2) physical versus mental and (3) short term versus long term care.
Healthcare in England is mainly provided by the National Health Service (NHS), a public body that provides healthcare to all permanent residents in England, that is free at the point of use. The body is one of four forming the UK National Health Service as health is a devolved matter; there are differences with the provisions for healthcare elsewhere in the United Kingdom, and in England it is overseen by NHS England. Though the public system dominates healthcare provision in England, private health care and a wide variety of alternative and complementary treatments are available for those willing and able to pay.

Healthcare in Singapore is under the purview of the Ministry of Health of the Government of Singapore. It mainly consists of a government-run publicly funded universal healthcare system as well as a significant private healthcare sector. Financing of healthcare costs is done through a mixture of direct government subsidies, compulsory comprehensive savings, national healthcare insurance, and cost-sharing.

The British United Provident Association Limited, trading as Bupa, is a British multinational health insurance and healthcare company with over 43 million customers worldwide.

Guardian Royal Exchange Assurance plc was a large British insurance company. It was listed on the London Stock Exchange and was a constituent of the FTSE 100 Index.

Healthcare in Belgium is composed of three parts. Firstly there is a primarily publicly funded healthcare and social security service run by the federal government, which organises and regulates healthcare; independent private/public practitioners, university/semi-private hospitals and care institutions. There are a few private hospitals. Secondly is the insurance coverage provided for patients. Finally, industry coverage; which covers the production and distribution of healthcare products for research and development. The primary aspect of this research is done in universities and hospitals.

Spire Healthcare Group plc is the second-largest provider of private healthcare in the United Kingdom. It is listed on the London Stock Exchange and is a constituent of the FTSE 250 Index.

Private healthcare in the UK, where universal state-funded healthcare is provided by the National Health Service, is a niche market.
Now Healthcare Group was a health technology company founded in 2014 based in Salford. Lee Dentith is the founder and chief executive.
Simplyhealth is a provider of health cash plans in the United Kingdom. The scheme is an amalgamation of a number of schemes, with the earliest dating from 1872. Members can claim back cash costs from various services from the NHS or private provision, such as dental care, optical care, prescriptions and physiotherapy, as well as having access to services such as remote telehealth consultations with a general practitioner.
References
- 1 2 3 "Open Referral: one year on" (PDF). Buck Consultants. December 2012.
- ↑ Murphy, Fiona (2013-07-01). "Aviva launches open referral plan for large corporates". Cover Magazine. Incisive Media Investments Limited.
- 1 2 3 "Private Healthcare Market Study (OFT1396)" (PDF). Office of Fair Trading. December 2011.
- ↑ "Open Referral". Universal Provident. 2013-09-29.
- ↑ Tirbutt, Edmund (2013-10-02). "Key points about private medical insurance open referral". Centaur Communications Ltd.
- 1 2 "Open Referral schemes explained". BUPA. Archived from the original on 2014-07-14.
- ↑ Gray, Alistair (13 March 2014). "Bupa's 'open referral' system stems exodus of customers". Financial Times. Retrieved 5 July 2020.
- 1 2 "Consultants´ attitude to ´open referral´". wpa.org.uk. WPA. Archived from the original on 2014-07-14.