
Freenet is a peer-to-peer platform for censorship-resistant communication. It uses a decentralized distributed data store to keep and deliver information, and has a suite of free software for publishing and communicating on the Web without fear of censorship. Both Freenet and some of its associated tools were originally designed by Ian Clarke, who defined Freenet's goal as providing freedom of speech on the Internet with strong anonymity protection.
In software engineering, multitier architecture or multilayered architecture is a client–server architecture in which presentation, application processing and data management functions are physically separated. The most widespread use of multitier architecture is the three-tier architecture.

Peer-to-peer (P2P) computing or networking is a distributed application architecture that partitions tasks or workloads between peers. Peers are equally privileged, equipotent participants in the application. They are said to form a peer-to-peer network of nodes.

A Wiki software is collaborative software that runs a wiki, which allows users to create and collaboratively edit pages or entries via a web browser. A wiki system is usually a web application that runs on one or more web servers. The content, including previous revisions, is usually stored in either a file system or a database. Wikis are a type of web content management system, and the most commonly supported off-the-shelf software that web hosting facilities offer.
Uploading refers to transmitting data from one computer system to another through means of a network. Common methods of uploading include: uploading via web browsers, FTP clients], and terminals (SCP/SFTP). Uploading can be used in the context of clients that send files to a central server. While uploading can also be defined in the context of sending files between distributed clients, such as with a peer-to-peer (P2P) file-sharing protocol like BitTorrent, the term file sharing is more often used in this case. Moving files within a computer system, as opposed to over a network, is called file copying.
A web portal is a specially designed website that brings information from diverse sources, like emails, online forums and search engines, together in a uniform way. Usually, each information source gets its dedicated area on the page for displaying information ; often, the user can configure which ones to display. Variants of portals include mashups and intranet "dashboards" for executives and managers. The extent to which content is displayed in a "uniform way" may depend on the intended user and the intended purpose, as well as the diversity of the content. Very often design emphasis is on a certain "metaphor" for configuring and customizing the presentation of the content and the chosen implementation framework or code libraries. In addition, the role of the user in an organization may determine which content can be added to the portal or deleted from the portal configuration.
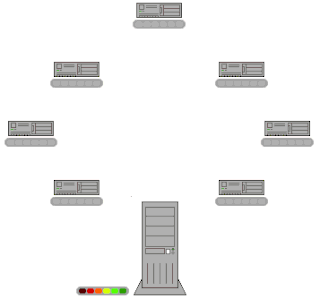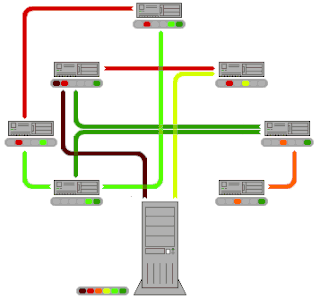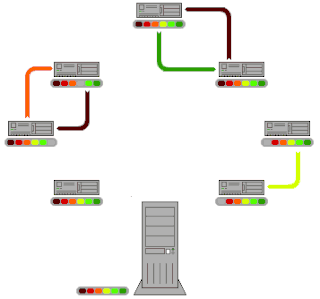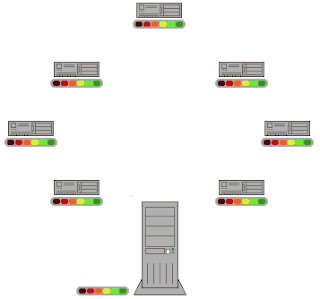
BitTorrent is a communication protocol for peer-to-peer file sharing (P2P), which enables users to distribute data and electronic files over the Internet in a decentralized manner.
An anonymous P2P communication system is a peer-to-peer distributed application in which the nodes, which are used to share resources, or participants are anonymous or pseudonymous. Anonymity of participants is usually achieved by special routing overlay networks that hide the physical location of each node from other participants.
The Invisible Internet Project (I2P) is an anonymous network layer that allows for censorship resistant, peer to peer communication. Anonymous connections are achieved by encrypting the user's traffic, and sending it through a volunteer-run network of roughly 55,000 computers distributed around the world. Given the high number of possible paths the traffic can transit, a third party watching a full connection is unlikely. The software that implements this layer is called an "I2P router", and a computer running I2P is called an "I2P node". I2P is free and open source, and is published under multiple licenses.

WebGUI is an open-source content management system written in Perl and released under the GNU General Public License.
In computer science and networking in particular, a session is a temporary and interactive information interchange between two or more communicating devices, or between a computer and user. A session is established at a certain point in time, and then ‘torn down’ - brought to an end - at some later point. An established communication session may involve more than one message in each direction. A session is typically stateful, meaning that at least one of the communicating parties needs to hold current state information and save information about the session history in order to be able to communicate, as opposed to stateless communication, where the communication consists of independent requests with responses.

A content delivery network, or content distribution network (CDN), is a geographically distributed network of proxy servers and their data centers. The goal is to provide high availability and performance by distributing the service spatially relative to end users. CDNs came into existence in the late 1990s as a means for alleviating the performance bottlenecks of the Internet, even as the Internet was starting to become a mission-critical medium for people and enterprises. Since then, CDNs have grown to serve a large portion of the Internet content today, including web objects, downloadable objects, applications, live streaming media, on-demand streaming media, and social media sites.
A web content management system is a software content management system (CMS) specifically for web content. It provides website authoring, collaboration, and administration tools that help users with little knowledge of web programming languages or markup languages create and manage website content. A WCMS provides the foundation for collaboration, providing users the ability to manage documents and output for multiple author editing and participation. Most systems use a content repository or a database to store page content, metadata, and other information assets the system needs.
Cumulus is a digital asset management software designed as a client/server system developed by Canto Software. The product line includes editions targeted to smaller organizations and larger enterprises. The product makes use of metadata for indexing, organizing, and searching.

Syndie is an open-source cross-platform computer application to syndicate (re-publish) data over a variety of anonymous and non-anonymous computer networks.
Geo-replication systems are designed to improve the distribution of data across geographically distributed data networks. This is intended to improve the response time for applications such as web portals. Geo-replication can be achieved using software, hardware or a combination of the two.

Open Cobalt is a free and open-source software platform for constructing, accessing, and sharing virtual worlds both on local area networks or across the Internet, with no need for centralized servers.
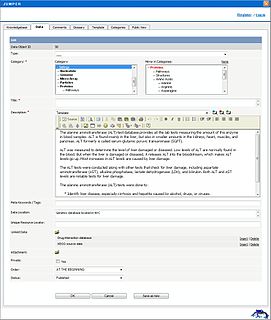
ApexKB, is a discontinued free and open-source script for collaborative search and knowledge management powered by a shared enterprise bookmarking engine that is a fork of KnowledgebasePublisher. It was publicly announced on 29 September 2008. A stable version of Jumper was publicly released under the GNU General Public License and made available on Sourceforge on 26 March 2009.
Marlin is a DRM platform, created by an open-standards community initiative called the Marlin Developer Community (MDC). The MDC develops the necessary technology, partners, and services for enabling the creation of interoperable digital content distribution services.
IBM API Management is an API Management platform for use in the API Economy. IBM API Connect enables users to create, assemble, manage, secure and socialize web application programming interfaces (APIs).









