
The substantia nigra (SN) is a basal ganglia structure located in the midbrain that plays an important role in reward and movement. Substantia nigra is Latin for "black substance", reflecting the fact that parts of the substantia nigra appear darker than neighboring areas due to high levels of neuromelanin in dopaminergic neurons. Parkinson's disease is characterized by the loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta.
Tardive dyskinesia (TD) is a disorder that results in involuntary repetitive body movements, which may include grimacing, sticking out the tongue or smacking the lips. Additionally, there may be rapid jerking movements or slow writhing movements. In about 20% of people with TD, the disorder interferes with daily functioning.

The nigrostriatal pathway is a bilateral dopaminergic pathway in the brain that connects the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNc) in the midbrain with the dorsal striatum in the forebrain. It is one of the four major dopamine pathways in the brain, and is critical in the production of movement as part of a system called the basal ganglia motor loop. Dopaminergic neurons of this pathway release dopamine from axon terminals that synapse onto GABAergic medium spiny neurons (MSNs), also known as spiny projection neurons (SPNs), located in the striatum.
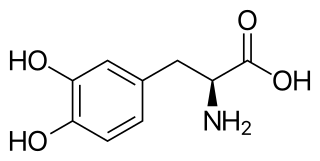
l-DOPA, also known as levodopa and l-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine, is an amino acid that is made and used as part of the normal biology of some plants and animals, including humans. Humans, as well as a portion of the other animals that utilize l-DOPA, make it via biosynthesis from the amino acid l-tyrosine. l-DOPA is the precursor to the neurotransmitters dopamine, norepinephrine (noradrenaline), and epinephrine (adrenaline), which are collectively known as catecholamines. Furthermore, l-DOPA itself mediates neurotrophic factor release by the brain and CNS. l-DOPA can be manufactured and in its pure form is sold as a psychoactive drug with the INN levodopa; trade names include Sinemet, Pharmacopa, Atamet, and Stalevo. As a drug, it is used in the clinical treatment of Parkinson's disease and dopamine-responsive dystonia.
Dyskinesia refers to a category of movement disorders that are characterized by involuntary muscle movements, including movements similar to tics or chorea and diminished voluntary movements. Dyskinesia can be anything from a slight tremor of the hands to an uncontrollable movement of the upper body or lower extremities. Discoordination can also occur internally especially with the respiratory muscles and it often goes unrecognized. Dyskinesia is a symptom of several medical disorders that are distinguished by their underlying cause.

Amantadine, sold under the brand name Gocovri among others, is a medication used to treat dyskinesia associated with parkinsonism and influenza caused by type A influenzavirus, though its use for the latter is no longer recommended due to widespread drug resistance. It acts as a nicotinic antagonist, dopamine agonist, and noncompetitive NMDA antagonist. The antiviral mechanism of action is antagonism of the influenzavirus A M2 proton channel, which prevents endosomal escape.

A dopamine antagonist, also known as an anti-dopaminergic and a dopamine receptor antagonist (DRA), is a type of drug which blocks dopamine receptors by receptor antagonism. Most antipsychotics are dopamine antagonists, and as such they have found use in treating schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and stimulant psychosis. Several other dopamine antagonists are antiemetics used in the treatment of nausea and vomiting.

Cabergoline, sold under the brand name Dostinex among others, is a dopaminergic medication used in the treatment of high prolactin levels, prolactinomas, Parkinson's disease, and for other indications. It is taken by mouth.

Apomorphine, sold under the brand name Apokyn among others, is a type of aporphine having activity as a non-selective dopamine agonist which activates both D2-like and, to a much lesser extent, D1-like receptors. It also acts as an antagonist of 5-HT2 and α-adrenergic receptors with high affinity. The compound is historically a morphine decomposition product made by boiling morphine with concentrated acid, hence the -morphine suffix. Contrary to its name, apomorphine does not actually contain morphine or its skeleton, nor does it bind to opioid receptors. The apo- prefix relates to it being a morphine derivative ("[comes] from morphine").

A dopamine agonist(DA) is a compound that activates dopamine receptors. There are two families of dopamine receptors, D2-like and D1-like, and they are all G protein-coupled receptors. D1- and D5-receptors belong to the D1-like family and the D2-like family includes D2, D3 and D4 receptors. Dopamine agonists are primarily used in the treatment of Parkinson's disease, and to a lesser extent, in hyperprolactinemia and restless legs syndrome. They are also used off-label in the treatment of clinical depression. The use of dopamine agonists is associated with impulse control disorders and dopamine agonist withdrawal syndrome (DAWS).
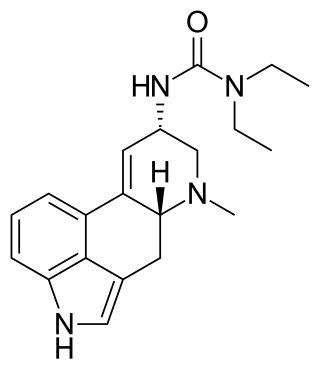
Lisuride, sold under the brand name Dopergin among others, is a monoaminergic medication of the ergoline class which is used in the treatment of Parkinson's disease, migraine, and high prolactin levels. It is taken by mouth.

Rotigotine, sold under the brand name Neupro among others, is a dopamine agonist of the non-ergoline class of medications indicated for the treatment of Parkinson's disease and restless legs syndrome. It is formulated as a once-daily transdermal patch which provides a slow and constant supply of the drug over the course of 24 hours.
Extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS) are symptoms that are archetypically associated with the extrapyramidal system of the brain's cerebral cortex. When such symptoms are caused by medications or other drugs, they are also known as extrapyramidal side effects (EPSE). The symptoms can be acute (short-term) or chronic (long-term). They include movement dysfunction such as dystonia, akathisia, parkinsonism characteristic symptoms such as rigidity, bradykinesia, tremor, and tardive dyskinesia. Extrapyramidal symptoms are a reason why subjects drop out of clinical trials of antipsychotics; of the 213 (14.6%) subjects that dropped out of one of the largest clinical trials of antipsychotics, 58 (27.2%) of those discontinuations were due to EPS.
Li, Xuening; Gao, Zixuan; Yu, Huasen; Gu, Yan; Yang, Guang (2022). "Effect of Long-term Exercise Therapy on Motor Symptoms in Parkinson Disease Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials". American Journal of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation. 101 (10): 905–912. doi:10.1097/PHM.0000000000002052. PMID 35695530. S2CID 252225251 – via Ovid.

Mesulergine (INN) (developmental code name CU-32085) is a drug of the ergoline group which was never marketed. It acts on serotonin and dopamine receptors. Specifically, it is an agonist of dopamine D2-like receptors and serotonin 5-HT6 receptors and an antagonist of serotonin 5-HT2A, 5-HT2B, 5-HT2C, and 5-HT7 receptors. It also has affinity for the 5-HT1A, 5-HT1B, 5-HT1D, 5-HT1F, and 5-HT5A receptors. The compound had entered clinical trials for the treatment of Parkinson's disease; however, further development was halted due to adverse histological abnormalities in rats. It was also investigated for the treatment of hyperprolactinemia (high prolactin levels).

Dopamine dysregulation syndrome (DDS) is a dysfunction of the reward system observed in some individuals taking dopaminergic medications for an extended length of time. It typically occurs in people with Parkinson's disease (PD) who have taken dopamine agonist medications for an extended period of time. It is characterized by self-control problems such as addiction to medication, gambling, or sexual behavior.

Parkinson's disease (PD), or simply Parkinson's, is a long-term degenerative disorder of the central nervous system that mainly affects the motor system. The symptoms usually emerge slowly, and as the disease worsens, non-motor symptoms become more common. The most obvious early symptoms are tremor, rigidity, slowness of movement, and difficulty with walking. Cognitive and behavioral problems may also occur with depression, anxiety, and apathy occurring in many people with PD. Parkinson's disease dementia becomes common in the advanced stages of the disease. Those with Parkinson's can also have problems with their sleep and sensory systems. The motor symptoms of the disease result from the death of cells in the substantia nigra, a region of the midbrain, leading to a dopamine deficit. The cause of this cell death is poorly understood, but involves the build-up of misfolded proteins into Lewy bodies in the neurons. Collectively, the main motor symptoms are also known as parkinsonism or a parkinsonian syndrome.

A-86929 is a synthetic compound that acts as a selective dopamine receptor D1 agonist. It was developed as a possible treatment for Parkinson's disease, as well as for other applications such as treatment of cocaine addiction, but while it had reasonable efficacy in humans it also caused dyskinesias and has not been continued. It has mainly been used as its diacetate ester prodrug adrogolide (ABT-431), which has better bioavailability.
Levodopa-induced dyskinesia (LID) is a form of dyskinesia associated with levodopa (l-DOPA), used to treat Parkinson's disease. It often involves hyperkinetic movements, including chorea, dystonia, and athetosis.

UWA-101 is a phenethylamine derivative invented by Dr Matthew Piggott at the University of Western Australia, and researched as a potential treatment for Parkinson's disease. Its chemical structure is very similar to that of the illegal drug MDMA, the only difference being the replacement of the α-methyl group with an α-cyclopropyl group. MDMA has been found in animal studies and reported in unauthorised human self-experiments to be effective in the short-term relief of side-effects of Parkinson's disease therapy, most notably levodopa-induced dyskinesia. However the illegal status of MDMA and concerns about its potential for recreational use, neurotoxicity and potentially dangerous side effects mean that it is unlikely to be investigated for medical use in this application, and so alternative analogues were investigated.















