
Sodium benzoate also known as benzoate of soda is the sodium salt of benzoic acid, widely used as a food preservative (with an E number of E211) and a pickling agent. It appears as a white crystalline chemical with the formula C6H5COONa.

4-Methylaminorex is a stimulant drug of the 2-amino-5-aryloxazoline class that was first synthesized in 1960 by McNeil Laboratories. It is also known by its street name "U4Euh" ("Euphoria"). It is banned in many countries as a stimulant.

Hordenine is an alkaloid of the phenethylamine class that occurs naturally in a variety of plants, taking its name from one of the most common, barley. Chemically, hordenine is the N-methyl derivative of N-methyltyramine, and the N,N-dimethyl derivative of the well-known biogenic amine tyramine, from which it is biosynthetically derived and with which it shares some pharmacological properties. As of September 2012, hordenine is widely sold as an ingredient of nutritional supplements, with the claims that it is a stimulant of the central nervous system, and has the ability to promote weight loss by enhancing metabolism. In experimental animals, given sufficiently large doses parenterally, hordenine does produce an increase in blood pressure, as well as other disturbances of the cardiovascular, respiratory, and nervous systems. These effects are generally not reproduced by oral administration of the drug in test animals, and virtually no scientific reports of the effects of hordenine in human beings have been published.
This is the list of extremely hazardous substances defined in Section 302 of the U.S. Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act. The list can be found as an appendix to 40 C.F.R. 355. Updates as of 2006 can be seen on the Federal Register, 71 FR 47121.

Creatine methyl ester is the methyl ester derivative of the amino acid creatine. It can be prepared by the esterification of creatine with methanol.
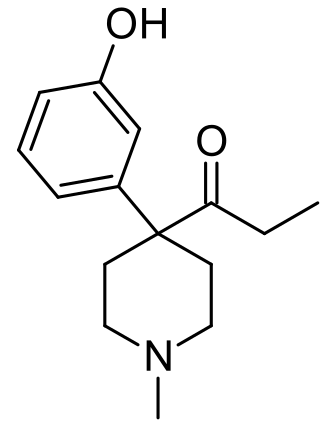
Ketobemidone, sold under the brand name Ketogan among others, is a powerful synthetic opioid painkiller. Its effectiveness against pain is in the same range as morphine, and it also has some NMDA-antagonist properties imparted, in part, by its metabolite norketobemidone. This may make it useful for some types of pain that do not respond well to other opioids. It is marketed in Denmark, Iceland, Norway and Sweden and is used for severe pain.

β-Methylphenethylamine is an organic compound of the phenethylamine class, and a positional isomer of the drug amphetamine, with which it shares some properties. In particular, both amphetamine and β-methylphenethylamine are human TAAR1 agonists. In appearance, it is a colorless or yellowish liquid.

Etaqualone is a quinazolinone-class GABAergic and is an analogue of methaqualone that was developed in the 1960s and marketed mainly in France and some other European countries. It has sedative, hypnotic, muscle relaxant and central nervous system depressant properties resulting from its agonist activity at the β-subtype of the GABAA receptor, and was used for the treatment of insomnia.

Bornaprine is a synthetic anticholinergic medication that is primarily used to treat Parkinson's disease. Additionally, bornaprine has been used to treat other disorders, including hyperhidrosis.

N-Methylphenethylamine (NMPEA) is a naturally occurring trace amine neuromodulator in humans that is derived from the trace amine, phenethylamine (PEA). It has been detected in human urine and is produced by phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase with phenethylamine as a substrate, which significantly increases PEA's effects. PEA breaks down into phenylacetaldehyde which is further broken down into phenylacetic acid by monoamine oxidase. When this is inhibited by monoamine oxidase inhibitors, it allows more of the PEA to be metabolized into nymphetamine (NMPEA) and not wasted on the weaker inactive metabolites.

Tilidine, Leart or tilidate is a synthetic opioid painkiller, used mainly in Belgium, Bulgaria, Germany, Luxembourg, South Africa and Switzerland for the treatment of moderate to severe pain, both acute and chronic. Its onset of pain relief after oral administration is about 10–15 minutes and peak relief from pain occurs about 25–50 minutes after oral administration.

Omega-3-acid ethyl esters are a mixture of ethyl eicosapentaenoic acid and ethyl docosahexaenoic acid, which are ethyl esters of the omega-3 fatty acids eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) found in fish oil. Together with dietary changes, they are used to treat high blood triglycerides which may reduce the risk of pancreatitis. They are generally less preferred than statins, and use is not recommended by NHS Scotland as the evidence does not support a decreased risk of heart disease. Omega-3-acid ethyl esters are taken by mouth.

Deoxyepinephrine, also known by the common names N-methyldopamine and epinine, is an organic compound and natural product that is structurally related to the important neurotransmitters dopamine and epinephrine. All three of these compounds also belong to the catecholamine family. The pharmacology of epinine largely resembles that of its "parent", dopamine. Epinine has been found in plants, insects and animals. It is also of significance as the active metabolic breakdown product of the prodrug ibopamine, which has been used to treat congestive heart failure.

Phenylethanolamine, or β-hydroxyphenethylamine, is a trace amine with a structure similar to those of other trace phenethylamines as well as the catecholamine neurotransmitters dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine. As an organic compound, phenylethanolamine is a β-hydroxylated phenethylamine that is also structurally related to a number of synthetic drugs in the substituted phenethylamine class. In common with these compounds, phenylethanolamine has strong cardiovascular activity and, under the name Apophedrin, has been used as a drug to produce topical vasoconstriction.

Buphedrone, also known as α-methylamino-butyrophenone (MABP), is a stimulant of the phenethylamine and cathinone chemical classes that was first synthesized in 1928. It is legal in most countries as a research chemical, as long as it is not intended for human consumption.

N,N-Dimethyldopamine (DMDA) is an organic compound belonging to the phenethylamine family. It is related structurally to the alkaloid epinine (N-methyldopamine) and to the major neurotransmitter dopamine (of which it is the N,N-dimethylated analog). Because of its structural relationship to dopamine, DMDA has been the subject of a number of pharmacological investigations. DMDA has been detected in Acacia rigidula.

Halostachine is a natural product, an alkaloid first isolated from the Asian shrub Halostachys caspica, and structurally a β-hydroxy-phenethylamine related to its better-known "parent" biogenic amine, phenylethanolamine, to the adrenergic drug synephrine, and to the alkaloid ephedrine. The pharmacological properties of halostachine have some similarity to those of these structurally-related compounds, and Halostachys caspica extracts have been included as a constituent of certain OTC dietary supplements, but halostachine has never been developed as a prescription drug. Although it is found in nature as a single stereoisomer, halostachine is more commonly available as a synthetic product in the form of its racemate. In appearance it is a colorless solid.

βk-2C-B is a novel psychedelic substance. It is the beta (β) ketone structural analogue of 2C-B, a psychedelic drug of the 2C family. It is used as a recreational drug, usually taken orally. βk-2C-B is a controlled substance in Canada, Germany, Switzerland, and the United Kingdom.

4-Methylcyclohexanemethanol (MCHM, systematic name 4-methylcyclohexylmethanol) is an organic compound with the formula CH3C6H10CH2OH. Classified as a saturated higher alicyclic primary alcohol. Both cis and trans isomers exist, depending on the relative positions of the methyl (CH3) and hydroxymethyl (CH2OH) groups on the cyclohexane ring. Commercial samples of MCHM consists of a mixture of these isomers as well as other components that vary with the supplier.

4-Amino-2-methyl-1-naphthol is a menadione analog. Its water-soluble hydrochloride (HCl) salt is often called vitamin K5. The HCl salt has been used as a medicine for vitamin K deficiency under tradenames such as Synkamin, which was sold by Parke-Davis, but has since been discontinued.



















