Related Research Articles
An orphan drug is a pharmaceutical agent developed to treat medical conditions which, because they are so rare, would not be profitable to produce without government assistance. The conditions are referred to as orphan diseases.
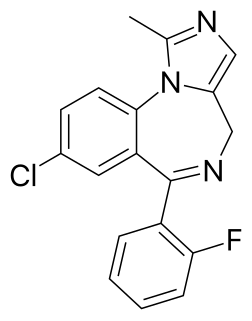
Midazolam, sold under the brand name Versed, among others, is a benzodiazepine medication used for anesthesia, procedural sedation, trouble sleeping, and severe agitation. It works by inducing sleepiness, decreasing anxiety, and causing a loss of ability to create new memories. It is important to note that this drug does not cause an individual to become unconscious, merely be sedated. It is also useful for the treatment of seizures. Midazolam can be given by mouth, intravenously, by injection into a muscle, by spraying into the nose, or through the cheek. When given intravenously, it typically begins working within five minutes; when injected into a muscle, it can take fifteen minutes to begin working. Effects last between one and six hours.
Rimonabant (also known as SR141716; trade names Acomplia, Zimulti) is an anorectic antiobesity drug that was first approved in Europe in 2006 but was withdrawn worldwide in 2008 due to serious psychiatric side effects; it was never approved in the United States. Rimonabant is an inverse agonist for the cannabinoid receptor CB1 and was the first drug approved in that class.

The European Medicines Agency (EMA) is an agency of the European Union (EU) in charge of the evaluation and supervision of medicinal products. Prior to 2004, it was known as the European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products or European Medicines Evaluation Agency (EMEA).
Stiripentol, sold under the brand name Diacomit, is an anticonvulsant medication used for the treatment of Dravet syndrome - a serious genetic brain disorder.
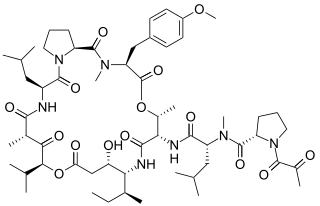
Plitidepsin is a chemical compound extracted from the ascidian Aplidium albicans. It is currently undergoing clinical trial testing. It is a member of the class of compounds known as didemnins.
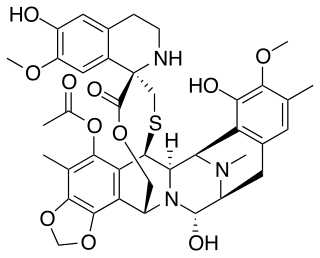
Trabectedin, sold under the brand name Yondelis, is an antitumor chemotherapy medication for the treatment of advanced soft-tissue sarcoma and ovarian cancer.
Ofatumumab is a fully human monoclonal antibody to CD20, which appears to inhibit early-stage B lymphocyte activation. Under the brand name Arzerra, it is approved for the treatment of certain types of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) in the United States. Under the brand name Kesimpta, it is approved for the treatment of multiple sclerosis in the United States as well as in the EU and other regions.
A biosimilar is a biologic medical product that is almost an identical copy of an original product that is manufactured by a different company. Biosimilars are officially approved versions of original "innovator" products and can be manufactured when the original product's patent expires. Reference to the innovator product is an integral component of the approval.

Garenoxacin (INN) is a quinolone antibiotic for the treatment of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacterial infections.

Flupirtine is an aminopyridine that functions as a centrally acting non-opioid analgesic that was originally used as an analgesic for acute and chronic pain but in 2013 due to issues with liver toxicity, the European Medicines Agency restricted its use to acute pain, for no more than two weeks, and only for people who cannot use other painkillers. In March 2018, marketing authorisations for flupirtine were withdrawn following a European Medicines Agency recommendation based on the finding that the restrictions introduced in 2013 had not been sufficiently followed in clinical practice, and cases of serious liver injury still occurred including liver failure.
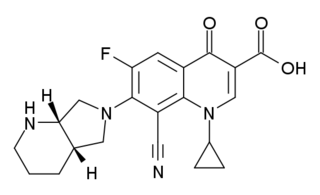
Pradofloxacin is a 3rd generation enhanced spectrum veterinary antibiotic of the fluoroquinolone class. It was developed by Bayer HealthCare AG, Animal Health GmbH, and received approval from the European Commission in April 2011 for prescription-only use in veterinary medicine for the treatment of bacterial infections in dogs and cats.
Olaratumab, sold under the brand name Lartruvo, is a monoclonal antibody medication developed by Eli Lilly and Company for the treatment of solid tumors. It is directed against the platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha.

Ingenol mebutate, sold under the brand name Picato, is a substance that is found in the sap of the plant Euphorbia peplus, commonly known as milkweed, and is an inducer of cell death. A gel formulation of the drug has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and by the European Medicines Agency (EMA) for the topical treatment of actinic keratosis. Two different strengths of the gel have been approved for use on either the face and scalp (0.015%) or the trunk and extremities (0.05%), respectively. In 2020 the drug was withdrawn from the market in the EU.
Evinacumab, sold under the brand name Evkeeza, is a monoclonal antibody medication for the treatment of homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HoFH).
Obiltoxaximab, sold under the brand name Anthim, is a monoclonal antibody medication designed for the treatment of exposure to Bacillus anthracis spores.

Lorlatinib, sold under the brand name Lorbrena in the United States, Canada, and Japan, and Lorviqua in the European Union, is an anti-cancer drug developed by Pfizer. It is an orally administered inhibitor of ALK and ROS1, two enzymes that play a role in the development of cancer.
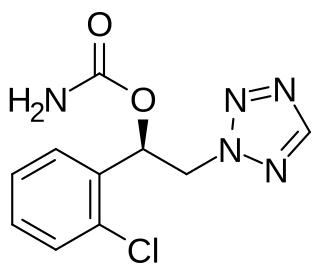
Cenobamate, sold under the brand names Xcopri (US) and Ontozry (EU), is a medication used for the treatment of partial-onset seizures, a kind of epilepsy, in adults. It is taken by mouth.

SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, was isolated in late 2019. Its genetic sequence was published on 11 January 2020, triggering the urgent international response to prepare for an outbreak and hasten development of a preventive COVID-19 vaccine. Since 2020, vaccine development has been expedited via unprecedented collaboration in the multinational pharmaceutical industry and between governments. By June 2020, tens of billions of dollars were invested by corporations, governments, international health organizations, and university research groups to develop dozens of vaccine candidates and prepare for global vaccination programs to immunize against COVID‑19 infection. According to the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations (CEPI), the geographic distribution of COVID‑19 vaccine development shows North American entities to have about 40% of the activity, compared to 30% in Asia and Australia, 26% in Europe, and a few projects in South America and Africa.
Regdanvimab, sold under the brand name Regkirona, is a human monoclonal antibody used for the treatment of COVID-19. The antibody is directed against the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2. It is developed by Celltrion. The medicine is given by infusion (drip) into a vein.
References
- ↑ "Questions and answers on the paediatric use marketing authorisation (PUMA)" (PDF). European Medicines Agency. 13 September 2011.
- ↑ "Monthly Report" (PDF). Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP). 5 July 2011. p. 1.
- ↑ PR Newswire (6 September 2011). "ViroPharma's Buccolam (Midazolam, Oromucosal Solution) Granted European Marketing Authorization for Treatment of Acute Seizures".