Related Research Articles

Windows 2000 is a major release of the Windows NT operating system developed by Microsoft and designed for businesses. It was the direct successor to Windows NT 4.0, and was released to manufacturing on December 15, 1999, and was officially released to retail on February 17, 2000 and September 26, 2000 for Windows 2000 Datacenter Server. It was Microsoft's business operating system until the introduction of Windows XP Professional in 2001.
ext3, or third extended filesystem, is a journaled file system that is commonly used by the Linux kernel. It used to be the default file system for many popular Linux distributions. Stephen Tweedie first revealed that he was working on extending ext2 in Journaling the Linux ext2fs Filesystem in a 1998 paper, and later in a February 1999 kernel mailing list posting. The filesystem was merged with the mainline Linux kernel in November 2001 from 2.4.15 onward. Its main advantage over ext2 is journaling, which improves reliability and eliminates the need to check the file system after an unclean shutdown. Its successor is ext4.

In the maintenance of file systems, defragmentation is a process that reduces the degree of fragmentation. It does this by physically organizing the contents of the mass storage device used to store files into the smallest number of contiguous regions. It also attempts to create larger regions of free space using compaction to impede the return of fragmentation. Some defragmentation utilities try to keep smaller files within a single directory together, as they are often accessed in sequence.

Microsoft Windows XP Professional x64 Edition, released on April 25, 2005, is an edition of Windows XP for x86-64 personal computers. It is designed to use the expanded 64-bit memory address space provided by the x86-64 architecture.

Windows NT 4.0 is a major release of the Windows NT operating system developed by Microsoft and oriented towards businesses. It is the direct successor to Windows NT 3.51, and was released to manufacturing on July 31, 1996, and then to retail in September 1996. It was Microsoft's primary business-oriented operating system until the introduction of Windows 2000. Workstation, server and embedded editions were sold, and all editions feature a graphical user interface similar to that of Windows 95, which was superseded by Windows 98 and could still be directly upgraded by either Windows 2000 Professional or Windows Me.
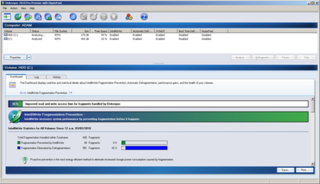
Diskeeper is a discontinued defragmentation app, designed for Microsoft Windows. It was developed by Executive Software International, Inc., which later changed its name to Diskeeper Corporation, and is now called Condusiv Technologies. The final version of Diskeeper was released in March 2020. All of Diskeeper's features and functionality are now included in Condusiv's data performance software DymaxIO.
A registry cleaner is a class of third-party utility software designed for the Microsoft Windows operating system, whose purpose is to remove redundant items from the Windows Registry.
As the next version of Windows NT after Windows 2000, as well as the successor to Windows Me, Windows XP introduced many new features but it also removed some others.

Microsoft Drive Optimizer is a utility in Microsoft Windows designed to increase data access speed by rearranging files stored on a disk to occupy contiguous storage locations, a technique called defragmentation. Defragmenting a disk minimizes head travel, which reduces the time it takes to read files from and write files to the disk. As a result of the decreased read and write times, Microsoft Drive Optimizer decreases system startup times for systems starting from magnetic storage devices such as a hard drive. However, defragmentation is not helpful on storage devices such as solid state drives, USB drives or SD cards that use flash memory to increase speeds, as these drives do not use a head. Defragmentation may decrease lifespan for certain technologies, e.g. solid state drives. Microsoft Drive Optimizer was first officially shipped with Windows XP.
Contig is a command line defragmentation utility for Windows developed by Microsoft as part of the Sysinternals Suite.
Windows Vista contains a range of new technologies and features that are intended to help network administrators and power users better manage their systems. Notable changes include a complete replacement of both the Windows Setup and the Windows startup processes, completely rewritten deployment mechanisms, new diagnostic and health monitoring tools such as random access memory diagnostic program, support for per-application Remote Desktop sessions, a completely new Task Scheduler, and a range of new Group Policy settings covering many of the features new to Windows Vista. Subsystem for UNIX Applications, which provides a POSIX-compatible environment is also introduced.
O&O Defrag is a Windows defragmentation utility sold by German software developer O&O Software. It has won several awards by PC journals and magazines, and is certified by Microsoft for all its current NTFS-based operating systems, including Windows 2000, Server 2003, Vista, 7, and 10.

Vopt is a Windows defragmentation utility sold by Golden Bow Systems. It is one of the oldest defragmentation products, and has supported MS-DOS and all versions of Microsoft Windows. The convenience of quick processing time is offset by less optimal performance, but when used in conjunction with the built-in optimization of the Windows prefetch folder, system performance is maintained without major reorganization of all the files on the drive.
Defraggler is a freemium defragmentation utility developed by Piriform Software, which can defragment individual files or groups of files on computer memory systems. Defraggler runs on Microsoft Windows; it has support for all versions since Windows XP. It includes support for both IA-32 and x64 versions of these operating systems.
UltraDefrag is a disk defragmentation utility for Microsoft Windows. Prior to version 8.0.0 it was released under the GNU General Public License. The only other Windows-based defragmentation utility licensed under the GNU GPL was JkDefrag, discontinued in 2008.
Windows XP, which is the next version of Windows NT after Windows 2000 and the successor to the consumer-oriented Windows Me, has been released in several editions since its original release in 2001.

JkDefrag is a free open-source disk defragmenting utility computer program for Windows. It was developed by Jeroen Kessels beginning in 2004 and was released under the GNU General Public License. Since version 4 of 2008, much changed from previous versions, JkDefrag was renamed MyDefrag by its developer; earlier JkDefrag versions continued to be available. MyDefrag, which was closed source freeware, was discontinued, with the last version being v4.3.1, file date 21 May 2010; for several years the MyDefrag website has been a redirect to the still-existing JkDefrag site, but links to downloadable JKdefrag files are dead.
UltimateDefrag is a retail file-system defragmentation utility made by DiskTrix. An older version of the program is available as the UltimateDefrag Freeware Edition.
The following is a comparison of notable file system defragmentation software:
Auslogics Disk Defrag is a freemium software application for Microsoft Windows intended to defragment files and folders on a hard drive, consolidate free space and optimize file placement using different criteria. It has an estimated 10 It is available in both free and "Pro" versions.
References
- ↑ Official forum moderator promised in January 2009 to try to get the website corrected.