Related Research Articles
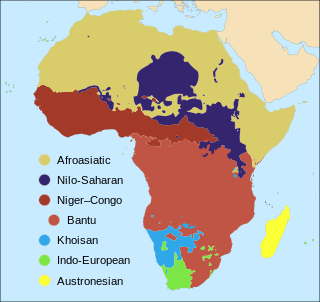
The number of languages natively spoken in Africa is variously estimated at between 1,250 and 2,100, and by some counts at over 3,000. Nigeria alone has over 500 languages, one of the greatest concentrations of linguistic diversity in the world. The languages of Africa belong to many distinct language families, among which the largest are:

The West Atlantic languages of West Africa are a major subgroup of the Niger–Congo languages.
The Lengue language, also called Molengue, Balengue, Molendji, is a Bantu language of southern Equatorial Guinea, spoken by the Lengue people between Bata and the Gabon border near the coast. The speakers have come under increasing Fang influence. The Ethnologue describes it as a member of the B subgroup of Northwest Bantu, while Echegaray is more specific, saying that it is linguistically a member of the Sheke group :

Fula, also known as Fulani or Fulah, is a Senegambian language spoken by around 36.8 million people as a set of various dialects in a continuum that stretches across some 18 countries in West and Central Africa. Along with other related languages such as Serer and Wolof, it belongs to the Atlantic geographic group within Niger–Congo, and more specifically to the Senegambian branch. Unlike most Niger-Congo languages, Fula does not have tones.

Portuguese is spoken in a number of African countries and is the official language in six African countries: Angola, Mozambique, Guinea-Bissau, Cape Verde, São Tomé and Príncipe and Equatorial Guinea. There are Portuguese-speaking communities in most countries of Southern Africa, a mixture of Portuguese settlers and Angolans and Mozambicans who left their countries during the civil wars. A rough estimate has it that there are about 14 million people who use Portuguese as their sole mother tongue across Africa, but depending on the criteria applied, the number might be considerably higher, since many Africans speak Portuguese as a second language, in countries like Angola and Mozambique, where Portuguese is an official language, but also in countries like South Africa and Senegal, thanks to migrants coming from Portuguese-speaking countries. Some statistics claim that there are over 60 million Portuguese speakers in the continent.

Guinea-Bissau Creole, also known as Kiriol or Crioulo, is a creole language whose lexicon derives mostly from Portuguese. It is spoken in Guinea Bissau, Senegal and The Gambia. It is also called by its native speakers as guinensi, kriyol, or portuguis.

Senegal is a multilingual country: Ethnologue lists 36 languages, Wolof being the most widely spoken language.

Pular (𞤆𞤵𞤤𞤢𞤪) is a Fula language spoken primarily by the Fula people of Fouta Djallon, Guinea. It is also spoken in parts of Guinea-Bissau, Sierra Leone, and Senegal. There are a small number of speakers in Mali. Pular is spoken by 4.3 million Guineans, about 55% of the national population. This makes Pular the most widely spoken indigenous language in the country. Substantial numbers of Pular speakers have migrated to other countries in West Africa, notably Senegal.
The Mankanya language is spoken by approximately 86,000 people in Guinea-Bissau, Senegal and Gambia primarily belonging to the ethnic group of the same name. It belongs to the Bak branch of the Atlantic–Congo language family.

Guinean Portuguese is the variety of Portuguese spoken in Guinea-Bissau, where it is the official language.
Bijago or Bidyogo is the language of the Bissagos Archipelago of Guinea-Bissau. There are some difficulties of grammar and intelligibility between dialects, with the Kamona dialect being unintelligible to the others.

The official language of Guinea-Bissau is Portuguese, which was spoken by 32.1% of the population according to the 2009 census. It is the language of instruction in schools, the language of literary production, the written press, legislation and administration.
Balanta is a group of two closely related Bak languages of West Africa spoken by the Balanta people.
Nalu is an Atlantic language of Guinea and Guinea-Bissau, spoken by the Nalu people, a West African people who settled the region before the arrival of the Mandinka in the 14th or 15th centuries. It is spoken predominantly by adults. It is estimated to be spoken by a range of 10,000 to 25,000 people, whereas Wilson (2007) reports that there are around 12,000 speakers. It is considered an endangered language due to its dwindling population of speakers.
Banyun (Banyum), Nyun, or Bainouk, is a Senegambian dialect cluster of Senegal and Guinea-Bissau.
Kobiana (Cobiana) or Buy (Uboi) is a Senegambian language spoken in several villages of Senegal and Guinea-Bissau. The language is referred to as gu-boy by its speakers. Speakers are shifting to Mandinka.
Manjak or Manjack or Njak is a Bak language of Guinea-Bissau and Senegal. The language is also known as Kanyop.
The Papel languages of southern Senegal, Gambia, and northwestern Guinea-Bissau are an uncontroversial cluster of the Bak languages and form a dialect continuum. All of these names are exonyms.
Kasanga (Cassanga) or Haal is a Senegambian language traditionally spoken in a few villages of Guinea-Bissau. The language is referred to as gu-haaca by its speakers. Speakers are shifting to Mandinka.
Papels, also known as Moium, Oium, Papei, Pepel or Pelels, are an ethnic group primarily located in Guinea-Bissau, though are also found in Casamance (Senegal) and Guinea. Their population in Guinea-Bissau is about 183,000, with 9,000 living outside of the country. They traditionally engaged in hunting and agriculture.