In pharmacology, bioavailability is a subcategory of absorption and is the fraction (%) of an administered drug that reaches the systemic circulation.

Bioequivalence is a term in pharmacokinetics used to assess the expected in vivo biological equivalence of two proprietary preparations of a drug. If two products are said to be bioequivalent it means that they would be expected to be, for all intents and purposes, the same.

Piperacillin is a broad-spectrum β-lactam antibiotic of the ureidopenicillin class. The chemical structure of piperacillin and other ureidopenicillins incorporates a polar side chain that enhances penetration into Gram-negative bacteria and reduces susceptibility to cleavage by Gram-negative beta lactamase enzymes. These properties confer activity against the important hospital pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Thus piperacillin is sometimes referred to as an "anti-pseudomonal penicillin".

Trazodone, sold under many brand names, is an antidepressant medication. It is used to treat major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, and, with other medications, alcohol dependence. It is taken by mouth.
In medicine and pharmacology, a trough level or trough concentration (Ctrough) is the concentration reached by a drug immediately before the next dose is administered, often used in therapeutic drug monitoring. The name comes from the idea that on a graph of concentration versus time, the line forms a U-shaped trough at the lowest region, before a new dose sends it higher again. The usual criterion is concentration in the blood serum, although in some instances local concentration within tissues is relevant. It is pharmacokinetically normal that with every passing minute and hour, the drug molecules are being metabolized or cleared by the body, so the concentration of drug that remains available is dropping. In a medicine that is administered periodically, the trough level should be measured just before the administration of the next dose in order to avoid overdosing. A trough level is contrasted with a "peak level" (Cmax), which is the highest level of the medicine in the body, and the "average level", which is the mean level over time. It is widely used in clinical trials for newer medicines for its therapeutic effectiveness and safety.
Biological half-life of a biological substance such as medication is the time it takes from its maximum concentration (Cmax) to half of its maximum concentration in the blood plasma, and is denoted by the abbreviation .

Acebutolol, sold under the brand names Sectral among others, is a beta blocker for the treatment of hypertension and arrhythmias. Acebutolol is a cardioselective beta-1 blocker and has intrinsic sympathetic activity. It is commonly used in the treatment of angina.

Phenprocoumon is a long-acting blood thinner drug to be taken by mouth, and a derivative of coumarin. It acts as a vitamin K antagonist and inhibits blood clotting (coagulation) by blocking synthesis of coagulation factors II, VII, IX and X. It is used for the prophylaxis and treatment of thromboembolic disorders such as heart attacks and pulmonary (lung) embolism. The most common adverse effect is bleeding. The drug interacts with a large number of other medications, including aspirin and St John's Wort. It is the standard coumarin used in Germany, Austria, and other European countries.

Acecainide is an antiarrhythmic drug. Chemically, it is the N-acetylated metabolite of procainamide. It is a Class III antiarrhythmic agent, whereas procainamide is a Class Ia antiarrhythmic drug. It is only partially as active as procainamide; when checking levels, both must be included in the final calculation.

Sparfloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic used in the treatment of bacterial infections. It has a controversial safety profile.
Pharmacokinetics, sometimes abbreviated as PK, is a branch of pharmacology dedicated to determine the fate of substances administered to a living organism. The substances of interest include any chemical xenobiotic such as: pharmaceutical drugs, pesticides, food additives, cosmetics, etc. It attempts to analyze chemical metabolism and to discover the fate of a chemical from the moment that it is administered up to the point at which it is completely eliminated from the body. Pharmacokinetics is the study of how an organism affects a drug, whereas pharmacodynamics (PD) is the study of how the drug affects the organism. Both together influence dosing, benefit, and adverse effects, as seen in PK/PD models.

Deramciclane (EGIS-3886) is a non-benzodiazepine-type anxiolytic drug to treat various types of anxiety disorders. Deramciclane is a unique alternative to current anxiolytics on the market because it has a novel chemical structure and target. It acts as an antagonist at the 5-HT2A receptor, as an inverse agonist at the 5-HT2C receptor, and as a GABA reuptake inhibitor. The two serotonin receptors are G protein-coupled receptors and are two of the main excitatory serotonin receptor types. Their excitation has been implicated in anxiety and mood. Deramciclane does not affect CYP3A4 activity in metabolizing other drugs, but it is a weak inhibitor of CYP2D6. Some studies also show the drug to have moderate affinity to dopamine D2 receptors and low affinity to dopamine receptor D1. Researchers are looking for alternatives to benzodiazepines for anxiolytic use because benzodiazepine drugs have sedative and muscle relaxant side effects.
Cmax is the maximum serum concentration that a drug achieves in a specified compartment or test area of the body after the drug has been administered and before the administration of a second dose. It is a standard measurement in pharmacokinetics.

Promegestone, sold under the brand name Surgestone, is a progestin medication which is used in menopausal hormone therapy and in the treatment of gynecological disorders. It is taken by mouth.
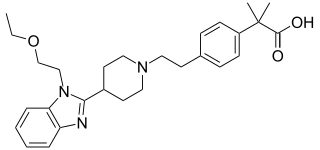
Bilastine, sold under the brand name Ilaxten among others, is a second-generation antihistamine medication which is used in the treatment of allergic rhinoconjunctivitis and urticaria (hives).

Oxogestone phenpropionate, also known as xinogestone, as well as 20β-hydroxy-19-norprogesterone 20β-(3-phenylpropionate), is a progestin related to the 19-norprogesterone derivatives which was developed as an injectable hormonal contraceptive, specifically a progestogen-only injectable contraceptive, in the 1960s and early 1970s but was never marketed. It was studied at a dose of 50 to 75 mg once a month by intramuscular injection but was associated with a high failure rate with this regimen and was not further developed. OPP is the 20β-(3-phenylpropionate) ester of oxogestone, which, similarly, was never marketed.
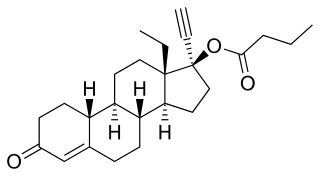
Levonorgestrel butanoate (LNG-B), or levonorgestrel 17β-butanoate, is a steroidal progestin of the 19-nortestosterone group which was developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) in collaboration with the Contraceptive Development Branch (CDB) of the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development as a long-acting injectable contraceptive. It is the C17β butanoate ester of levonorgestrel, and acts as a prodrug of levonorgestrel in the body. The drug is at or beyond the phase III stage of clinical development, but has not been marketed at this time. It was first described in the literature, by the WHO, in 1983, and has been under investigation for potential clinical use since then.

Nordoxepin, also known as N-desmethyldoxepin, is the major active metabolite of the tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) doxepin (Sinequan). It has been found to play a significant role in the antidepressant effects of doxepin.
In pharmacokinetics, the drug accumulation ratio (Rac) is the ratio of accumulation of a drug under steady state conditions as compared to a single dose. The higher the value, the more the drug accumulates in the body. An Rac of 1 means no accumulation.

Lynestrenol phenylpropionate (LPP), also known as ethynylestrenol phenylpropionate, is a progestin and a progestogen ester which was developed for potential use as a progestogen-only injectable contraceptive by Organon but was never marketed. It was assessed at doses of 25 to 75 mg in an oil solution once a month by intramuscular injection. LPP was associated with high contraceptive failure at the low dose and with poor cycle control. The medication was found to produce estrogenic effects in the endometrium in women due to transformation into estrogenic metabolites.














